
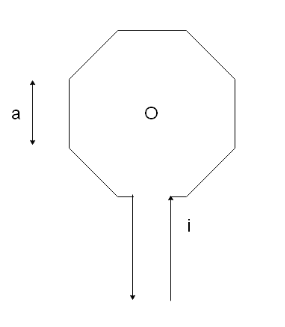
A current $ I $ is flowing in an octagonal coil of side $ a $ as shown in the figure. The magnetic field induction at the centre O of the coil will be
A) $ \dfrac{{5{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}} $
B) $ \dfrac{{5\sqrt 2 {\mu _0}I}}{{\pi a}} $
C) $ \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{\sqrt 5 \pi a}} $
D) $ \dfrac{{\sqrt 5 {\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi a}} $

Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint : We will break the octagon down into 8 finite current-carrying cables instead of measuring the field due to an octagon. Then we will calculate the net magnetic field at the centre of the octagon due to these 8 currents carrying cables.
Formula used: In this question, we will use the following formula:
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi l}}(\sin {\phi _1} + \sin {\phi _2}) $ where $ B $ is the magnetic field generated by a current-carrying cable at a point that is a distance $ l $ away from the wire and subtends angles $ {\phi _1} $ and $ {\phi _2} $ with respect to the line perpendicular to the current-carrying cable.
Complete step by step answer
We’ve been given a current-carrying octagon and have been asked to find the magnetic field at the center of the octagon. Let us break the octagon down into 8 finite straight current-carrying cables that will exert an equal amount of magnetic field at the center of the coil. Then we can find the magnetic field due to one of these cables using the formula
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi l}}(\sin {\phi _1} + \sin {\phi _2}) $
The angle subtended by one of the sides of the octagon at the centre of the octagon will be equal to,
$\Rightarrow \phi = \dfrac{{360}}{{{\text{number of sides of octagon}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \phi = \dfrac{{360}}{8} = 45^\circ $
Since we have a regular octagon the angle subtended by the two ends of the line with respect to the line perpendicular to the side will have the values,
$\Rightarrow {\phi _1} = {\phi _2} = \dfrac{\phi }{2} $
$ \Rightarrow {\phi _1} = {\phi _2} = 22.5^\circ $
To determine the perpendicular distance between the side and the point, we use the tangent of the angle $ {\phi _1} $ as,
$\Rightarrow \tan {\phi _1} = \dfrac{{a/2}}{l} $
$ \Rightarrow l = \dfrac{a}{{2 \times \tan 22.5^\circ }} $
Substituting the values of $ {\phi _1} = {\phi _2} = 22.5^\circ $ and $ l = \dfrac{a}{{2 \times \tan 22.5^\circ }} $ , we can calculate the magnetic field as
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi \dfrac{a}{{2 \times \tan 22.5^\circ }}}}(\sin 22.5^\circ + \sin 22.5^\circ ) $
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}(4 \times \tan 22.5^\circ \times \sin 22.5^\circ ) $
For 8 current-carrying cables, the total magnetic field will be8 times the magnetic field due to one current-carrying cable
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}(32 \times \tan 22.5^\circ \times \sin 22.5^\circ ) $
Which can then be simplified to,
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{5{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}} $ which corresponds to option (A).
Note
We can alternatively find the magnetic field using the formula for a polygon of $ n $ sides that has perimeter $ P $ as:
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi P}}4{n^2}\tan \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{n}} \right)\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{n}} \right) $
Since $ P = 8a $ and $ n = 8 $ , we can determine
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}(32 \times \tan 22.5^\circ \times \sin 22.5^\circ ) $ which again gives us option (A).
Formula used: In this question, we will use the following formula:
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi l}}(\sin {\phi _1} + \sin {\phi _2}) $ where $ B $ is the magnetic field generated by a current-carrying cable at a point that is a distance $ l $ away from the wire and subtends angles $ {\phi _1} $ and $ {\phi _2} $ with respect to the line perpendicular to the current-carrying cable.
Complete step by step answer
We’ve been given a current-carrying octagon and have been asked to find the magnetic field at the center of the octagon. Let us break the octagon down into 8 finite straight current-carrying cables that will exert an equal amount of magnetic field at the center of the coil. Then we can find the magnetic field due to one of these cables using the formula
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi l}}(\sin {\phi _1} + \sin {\phi _2}) $
The angle subtended by one of the sides of the octagon at the centre of the octagon will be equal to,
$\Rightarrow \phi = \dfrac{{360}}{{{\text{number of sides of octagon}}}} $
$ \Rightarrow \phi = \dfrac{{360}}{8} = 45^\circ $
Since we have a regular octagon the angle subtended by the two ends of the line with respect to the line perpendicular to the side will have the values,
$\Rightarrow {\phi _1} = {\phi _2} = \dfrac{\phi }{2} $
$ \Rightarrow {\phi _1} = {\phi _2} = 22.5^\circ $
To determine the perpendicular distance between the side and the point, we use the tangent of the angle $ {\phi _1} $ as,
$\Rightarrow \tan {\phi _1} = \dfrac{{a/2}}{l} $
$ \Rightarrow l = \dfrac{a}{{2 \times \tan 22.5^\circ }} $
Substituting the values of $ {\phi _1} = {\phi _2} = 22.5^\circ $ and $ l = \dfrac{a}{{2 \times \tan 22.5^\circ }} $ , we can calculate the magnetic field as
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi \dfrac{a}{{2 \times \tan 22.5^\circ }}}}(\sin 22.5^\circ + \sin 22.5^\circ ) $
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}(4 \times \tan 22.5^\circ \times \sin 22.5^\circ ) $
For 8 current-carrying cables, the total magnetic field will be8 times the magnetic field due to one current-carrying cable
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}(32 \times \tan 22.5^\circ \times \sin 22.5^\circ ) $
Which can then be simplified to,
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{5{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}} $ which corresponds to option (A).
Note
We can alternatively find the magnetic field using the formula for a polygon of $ n $ sides that has perimeter $ P $ as:
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi P}}4{n^2}\tan \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{n}} \right)\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{n}} \right) $
Since $ P = 8a $ and $ n = 8 $ , we can determine
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi a}}(32 \times \tan 22.5^\circ \times \sin 22.5^\circ ) $ which again gives us option (A).
Recently Updated Pages
Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

The coating formed on the metals such as iron silver class 12 chemistry CBSE

Metals are refined by using different methods Which class 12 chemistry CBSE

What do you understand by denaturation of proteins class 12 chemistry CBSE

Assertion Nitrobenzene is used as a solvent in FriedelCrafts class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




