
A cubical transparent slab is used as a paper weight. What should be the minimum refractive index of the material of the slab so that the letters below it are not visible from any of the vertical axis.
(A) $ \sqrt 2 $
(B) $ \sqrt 3 $
(C) $ \sqrt 5 $
(D) $ \sqrt 5 /\sqrt 3 $
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: To be seen from the vertical faces the light coming from inside the cube must exit it at the sides. Recall that for light coming from a denser medium to a less dense medium to exit the medium horizontally (i.e. through the vertical face), the incident radiation must be at the critical angle.
Formula used:
In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
$ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $ where $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of incident medium, and $ {\theta _1} $ is the angle of incidence. $ {n_2} $ is the refractive index of the refractive medium, and $ {\theta _2} $ is the angle of refraction.
Complete step by step answer:
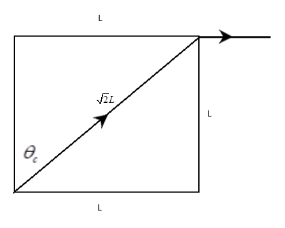
To see the letters below, the light coming from the material will exit the sides.
The light path for minimum refractive index would be as shown in the diagram above.
From the snell’s law, we have that
$ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $ where $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of incident medium, and $ {\theta _1} $ is the angle of incidence. $ {n_2} $ is the refractive index of the refractive medium, and $ {\theta _2} $ is the angle of refraction.
For the refracted light to be horizontal, the incident light must have an angle of incidence equal to the critical angle, hence, the snell's law for the case is
$ {n_1}\sin {\theta _c} = \sin 90 = 1 $ since the refractive index of air is 1.
As seen, the length travelled by the light would be $ \sqrt 2 L $
Hence,
$ \sin {\theta _c} = \dfrac{L}{{\sqrt 2 L}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} $ . Inserting this into the above equation, we have
$ {n_1}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} = 1 $
$ \Rightarrow {n_1} = \sqrt 2 $
Hence, the correct answer is A.
Note:
For clarity, the length of the diagonal can be gotten from the Pythagoras theorem, saying
$ {H^2} = {O^2} + {A^2} $ where $ H $ is the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle, $ O $ is the opposite and $ A $ is the adjacent. Hence,
$ {H^2} = {L^2} + {L^2} = 2{L^2} $
$ \Rightarrow H = \sqrt 2 L $ .
Formula used:
In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
$ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $ where $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of incident medium, and $ {\theta _1} $ is the angle of incidence. $ {n_2} $ is the refractive index of the refractive medium, and $ {\theta _2} $ is the angle of refraction.
Complete step by step answer:

To see the letters below, the light coming from the material will exit the sides.
The light path for minimum refractive index would be as shown in the diagram above.
From the snell’s law, we have that
$ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $ where $ {n_1} $ is the refractive index of incident medium, and $ {\theta _1} $ is the angle of incidence. $ {n_2} $ is the refractive index of the refractive medium, and $ {\theta _2} $ is the angle of refraction.
For the refracted light to be horizontal, the incident light must have an angle of incidence equal to the critical angle, hence, the snell's law for the case is
$ {n_1}\sin {\theta _c} = \sin 90 = 1 $ since the refractive index of air is 1.
As seen, the length travelled by the light would be $ \sqrt 2 L $
Hence,
$ \sin {\theta _c} = \dfrac{L}{{\sqrt 2 L}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} $ . Inserting this into the above equation, we have
$ {n_1}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} = 1 $
$ \Rightarrow {n_1} = \sqrt 2 $
Hence, the correct answer is A.
Note:
For clarity, the length of the diagonal can be gotten from the Pythagoras theorem, saying
$ {H^2} = {O^2} + {A^2} $ where $ H $ is the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle, $ O $ is the opposite and $ A $ is the adjacent. Hence,
$ {H^2} = {L^2} + {L^2} = 2{L^2} $
$ \Rightarrow H = \sqrt 2 L $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




