
A cube of side 'a' has a charge q placed at each of its eight corners. The potential at the centre of the cube due to all the charges is:
A) \[\dfrac{16q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}a\sqrt{3}}\]
B) \[\dfrac{16q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}a}\]
C) \[\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}a}\]
D) \[\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}a\sqrt{3}}\]
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Here, we calculate potential at centre due to each charge. The distance between each charge and centre is equal to half of the diagonal. The total potential due to 8 charges at the corner will give potential at the centre.
Complete answer:
A diagram can be illustrated as follows:
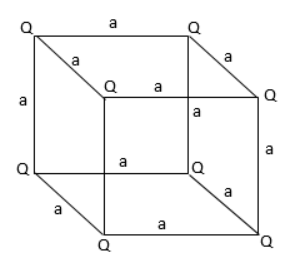
Let the cube of side be 'a’
So the length of each diagonal is given by \[D=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}\]
\[=\sqrt{3{{a}^{2}}}=\sqrt{3}a\]
Distance of each corner from the Centre O is half of its diagonal\[r=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}a}{2}\]
Potential at O due to charge q at each centre is given by
\[V=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}.\dfrac{a}{r}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}.\dfrac{q}{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}a}{2}} \]
\[ =\dfrac{2q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\sqrt{3}a} \]
Therefore, net potential at O due to all the 8 changes at the corners of the cubes \[V=8\times \dfrac{2q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\sqrt{3}a}\]
\[V=\dfrac{16q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\sqrt{3}a}\]
The electric field at O due to charge at all the corners of the cube is zero, since the electric field due to charges at opposite 8 corners are equal and opposite.
Note:
As we know that the cube of side a and diagonal is \[D=\sqrt{3}a\]. So, Be careful during the calculation of distance of each corner from the Centre is half of its diagonal i.e. \[r=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}a}{2}\] and the potential \[V=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{2q}{\sqrt{3}a}\] For eight corners we multiplied it by 8 we get the results.
Complete answer:
A diagram can be illustrated as follows:

Let the cube of side be 'a’
So the length of each diagonal is given by \[D=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}\]
\[=\sqrt{3{{a}^{2}}}=\sqrt{3}a\]
Distance of each corner from the Centre O is half of its diagonal\[r=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}a}{2}\]
Potential at O due to charge q at each centre is given by
\[V=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}.\dfrac{a}{r}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}.\dfrac{q}{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}a}{2}} \]
\[ =\dfrac{2q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\sqrt{3}a} \]
Therefore, net potential at O due to all the 8 changes at the corners of the cubes \[V=8\times \dfrac{2q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\sqrt{3}a}\]
\[V=\dfrac{16q}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}\sqrt{3}a}\]
The electric field at O due to charge at all the corners of the cube is zero, since the electric field due to charges at opposite 8 corners are equal and opposite.
Note:
As we know that the cube of side a and diagonal is \[D=\sqrt{3}a\]. So, Be careful during the calculation of distance of each corner from the Centre is half of its diagonal i.e. \[r=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}a}{2}\] and the potential \[V=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{2q}{\sqrt{3}a}\] For eight corners we multiplied it by 8 we get the results.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




