
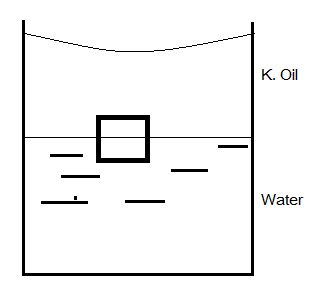
A cube of ice floats partly in water and partly in Kerosene oil (fig.). The ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in Kerosene oil is (specific gravity of the kerosene oil is 0.8 and that of the ice is 0.9)
A) 1:1
B) 1:2
C) 2:1
D) 4:5

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to determine the ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in Kerosene oil. For this, we will use the relation between the buoyancy force, the volume of the object in the liquid, and the density of the liquid, which is given as ${F_b} = V\rho g$.
Complete step by step answer:
As the ice is in stable condition (equilibrium position) in between the water and the kerosene oil so, the total force of buoyancy on the ice cube from both the sides, i.e., in kerosene oil and the water, equals to the sum of the force of buoyancy due to kerosene oil and the water. Mathematically, $F = {F_k} + {F_w}$
The product of the volume of the object in the liquid, density of the liquid, and the acceleration due to gravity results in the force of buoyancy on the object due to the liquid. Mathematically, ${F_b} = V\rho g$ where V is the volume of the object in the liquid of density $\rho $ and ‘g’ is the acceleration due to gravity.
Here, let us consider that the volume of the ice immersed in the water and in the kerosene oil be ${V_w}$ and ${V_k}$ respectively.
We know that the density of the water is ${\rho _w} = 1{\text{ g/cc}}$.
Also, the density of the ice and that of the kerosene oil is given in the question as:
$
{\rho _i} = 0.9 \\
{\rho _k} = 0.8 \\
$
Now, substituting the values in the formula $F = {F_k} + {F_w}$ we get,
$
F = {F_k} + {F_w} \\
{V_i} \times {\rho _i} \times g = {V_k} \times {\rho _k} \times g + {V_w} \times {\rho _w} \times g \\
{V_i} \times {\rho _i} = {V_k} \times {\rho _k} + {V_w} \times {\rho _w} - - - - (i) \\
$
Substitute ${\rho _w} = 1{\text{ g/cc}}$, ${\rho _i} = 0.9{\text{ g/cc}}$ and ${\rho _k} = 0.8{\text{ g/cc}}$ in the equation (i) we get,
$
{V_i} \times {\rho _i} = {V_k} \times {\rho _k} + {V_w} \times {\rho _w} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{V_k} + {V_w}} \right) \times 0.9 = {V_k} \times 0.8 + {V_w} \times 1 \\
\Rightarrow 0.9{V_k} + 0.9{V_w} = 0.8{V_k} + {V_w} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {0.9 - 0.8} \right){V_k} = \left( {1 - 0.9} \right){V_w} \\
\Rightarrow 0.1{V_k} = 0.1{V_w} \\
\Rightarrow {V_k} = {V_w} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_k}}}{{{V_w}}} = \dfrac{1}{1} \\
$
Hence, the ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in Kerosene oil is 1:1.
Option A is correct.
Note:It is worth noting down here that the density of the corresponding liquid is taken where we need to determine the force of buoyancy in the liquid, such as if we need to determine the force of buoyancy due to the kerosene oil in the liquid on the ice cube then, the specific density of the kerosene should be taken and not of the ice.
Complete step by step answer:
As the ice is in stable condition (equilibrium position) in between the water and the kerosene oil so, the total force of buoyancy on the ice cube from both the sides, i.e., in kerosene oil and the water, equals to the sum of the force of buoyancy due to kerosene oil and the water. Mathematically, $F = {F_k} + {F_w}$
The product of the volume of the object in the liquid, density of the liquid, and the acceleration due to gravity results in the force of buoyancy on the object due to the liquid. Mathematically, ${F_b} = V\rho g$ where V is the volume of the object in the liquid of density $\rho $ and ‘g’ is the acceleration due to gravity.
Here, let us consider that the volume of the ice immersed in the water and in the kerosene oil be ${V_w}$ and ${V_k}$ respectively.
We know that the density of the water is ${\rho _w} = 1{\text{ g/cc}}$.
Also, the density of the ice and that of the kerosene oil is given in the question as:
$
{\rho _i} = 0.9 \\
{\rho _k} = 0.8 \\
$
Now, substituting the values in the formula $F = {F_k} + {F_w}$ we get,
$
F = {F_k} + {F_w} \\
{V_i} \times {\rho _i} \times g = {V_k} \times {\rho _k} \times g + {V_w} \times {\rho _w} \times g \\
{V_i} \times {\rho _i} = {V_k} \times {\rho _k} + {V_w} \times {\rho _w} - - - - (i) \\
$
Substitute ${\rho _w} = 1{\text{ g/cc}}$, ${\rho _i} = 0.9{\text{ g/cc}}$ and ${\rho _k} = 0.8{\text{ g/cc}}$ in the equation (i) we get,
$
{V_i} \times {\rho _i} = {V_k} \times {\rho _k} + {V_w} \times {\rho _w} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{V_k} + {V_w}} \right) \times 0.9 = {V_k} \times 0.8 + {V_w} \times 1 \\
\Rightarrow 0.9{V_k} + 0.9{V_w} = 0.8{V_k} + {V_w} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {0.9 - 0.8} \right){V_k} = \left( {1 - 0.9} \right){V_w} \\
\Rightarrow 0.1{V_k} = 0.1{V_w} \\
\Rightarrow {V_k} = {V_w} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V_k}}}{{{V_w}}} = \dfrac{1}{1} \\
$
Hence, the ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in Kerosene oil is 1:1.
Option A is correct.
Note:It is worth noting down here that the density of the corresponding liquid is taken where we need to determine the force of buoyancy in the liquid, such as if we need to determine the force of buoyancy due to the kerosene oil in the liquid on the ice cube then, the specific density of the kerosene should be taken and not of the ice.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




