
What is a critical photoperiod? On the basis of this, plants are categorized in how many types?
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: The photoperiod is defined as the duration of light which each day is received by the plants and the development of the plant depends on the light hours received by it.
Complete answer:
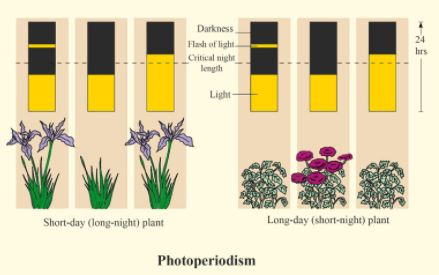
The fixed day length light period below or above of which the plant never blooms is known as critical photoperiod. Different species of plants have different critical photoperiods. On the basis of this, plants are categorized into three types. The three types are as follows:-
-Short Day Plants (SDP):
Short-day plants generally require a light period of but 12 hours i.e. 8-10 hour and a continuous dark period of about 14-16 hour for subsequent flowering. Most of the winter flowering plants belong to the present category e.g. Xanthium, Dahlia, sugarcane, rice, potato.
-Long Day Plants (LDP):
Long day plants require a light period of 14-16 hour for subsequent flowering. The quality of those plants is that a long night period entirely prevents flowering. But sometimes long nights are interrupted by light, even briefly, cause the inhibitive effect of the night to be lost, and therefore the plant's flower. These plants are sometimes also called as short night plants. E.g. Spinach etc.
- Day Neutral Plants:
These plants flower altogether during photoperiods and may blossom throughout the year. Examples are tomato, cucumber, etc. These plants produced more fruits as they require normal conditions.
Note: It is very interesting to note that the photoperiod also affects the milk yielding of the animals. If cows received sunlight for a long time it was recorded that milk yield increased by 8%–10%. In 1920, photoperiod was discovered by Garner and Allard.
Complete answer:
The fixed day length light period below or above of which the plant never blooms is known as critical photoperiod. Different species of plants have different critical photoperiods. On the basis of this, plants are categorized into three types. The three types are as follows:-
-Short Day Plants (SDP):
Short-day plants generally require a light period of but 12 hours i.e. 8-10 hour and a continuous dark period of about 14-16 hour for subsequent flowering. Most of the winter flowering plants belong to the present category e.g. Xanthium, Dahlia, sugarcane, rice, potato.
-Long Day Plants (LDP):
Long day plants require a light period of 14-16 hour for subsequent flowering. The quality of those plants is that a long night period entirely prevents flowering. But sometimes long nights are interrupted by light, even briefly, cause the inhibitive effect of the night to be lost, and therefore the plant's flower. These plants are sometimes also called as short night plants. E.g. Spinach etc.
- Day Neutral Plants:
These plants flower altogether during photoperiods and may blossom throughout the year. Examples are tomato, cucumber, etc. These plants produced more fruits as they require normal conditions.

Note: It is very interesting to note that the photoperiod also affects the milk yielding of the animals. If cows received sunlight for a long time it was recorded that milk yield increased by 8%–10%. In 1920, photoperiod was discovered by Garner and Allard.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




