
A cricket ball is hit at an angle of $30^\circ $ to the horizontal with kinetic energy E. What is its kinetic energy, when it reaches the highest point?
A. $\dfrac{{\text{E}}}{2}$
B. $0$
C. $\dfrac{{2{\text{E}}}}{3}$
D. $\dfrac{{3{\text{E}}}}{4}$
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: When the ball reaches the highest point, its vertical component of velocity becomes zero, but the horizontal component remains the same as it was initially. So, K.E can be solved by formula $\dfrac{1}{2}{\text{m}}{{\text{v}}^2}$
Step by step answer:
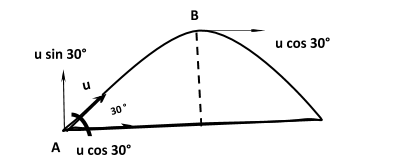
Let's say the ball is hit at point A at an angle of $30^\circ $ with horizontal. Suppose its initial velocity is u. So the horizontal is ${\text{u}}\cos 30^\circ $ and the vertical component is ${\text{u}}\sin 30^\circ $.
${\text{E}} = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{m}}{{\text{u}}^2}$…………. equation (1)
When the ball reaches the height point (i.e. at B), its vertical component will become zero because it is already at its highest point and cannot go further up. But under the influence of gravity (which acts downward), there will be no change in its horizontal velocity.
So, at the highest velocity is ${\text{u}}\cos 30^\circ $. Therefore, kinetic energy at B is:
${\text{K}}{\text{.}}{{\text{E}}_{\text{B}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{mv}}_{\text{B}}^2$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{m}}{\left( {{\text{u cos 30}}^\circ } \right)^2}$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{m}}{\left( {{\text{u}} \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)^2}$
${\text{K}}{\text{.}}{{\text{E}}_{\text{B}}} = \dfrac{3}{8}{\text{m}}{{\text{u}}^2}$………….. equation (2)
So, now divide equation (2) by equation (1)
$\dfrac{{{\text{K}}{\text{.}}{{\text{E}}_{\text{B}}}}}{{\text{E}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{8}{\text{m}}{{\text{u}}^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}{\text{m}}{{\text{u}}^2}}}$
${\text{K}}{\text{.}}{{\text{E}}_{\text{B}}} = \dfrac{3}{4}{\text{E}}$
So, the answer is (D).
Note: The vertical component of velocity is zero at highest point but that does not mean acceleration is also zero. At highest point acceleration is g (i.e. acceleration due to gravity having value $9.81\dfrac{{\text{m}}}{{{{\text{s}}^2}}}$).
Step by step answer:
Let's say the ball is hit at point A at an angle of $30^\circ $ with horizontal. Suppose its initial velocity is u. So the horizontal is ${\text{u}}\cos 30^\circ $ and the vertical component is ${\text{u}}\sin 30^\circ $.

${\text{E}} = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{m}}{{\text{u}}^2}$…………. equation (1)
When the ball reaches the height point (i.e. at B), its vertical component will become zero because it is already at its highest point and cannot go further up. But under the influence of gravity (which acts downward), there will be no change in its horizontal velocity.
So, at the highest velocity is ${\text{u}}\cos 30^\circ $. Therefore, kinetic energy at B is:
${\text{K}}{\text{.}}{{\text{E}}_{\text{B}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{mv}}_{\text{B}}^2$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{m}}{\left( {{\text{u cos 30}}^\circ } \right)^2}$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{m}}{\left( {{\text{u}} \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)^2}$
${\text{K}}{\text{.}}{{\text{E}}_{\text{B}}} = \dfrac{3}{8}{\text{m}}{{\text{u}}^2}$………….. equation (2)
So, now divide equation (2) by equation (1)
$\dfrac{{{\text{K}}{\text{.}}{{\text{E}}_{\text{B}}}}}{{\text{E}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{8}{\text{m}}{{\text{u}}^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}{\text{m}}{{\text{u}}^2}}}$
${\text{K}}{\text{.}}{{\text{E}}_{\text{B}}} = \dfrac{3}{4}{\text{E}}$
So, the answer is (D).
Note: The vertical component of velocity is zero at highest point but that does not mean acceleration is also zero. At highest point acceleration is g (i.e. acceleration due to gravity having value $9.81\dfrac{{\text{m}}}{{{{\text{s}}^2}}}$).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




