
A cork ball is floating on the surface of water in a beaker. The beaker is covered with a bell jar and the air is evacuated. What will happen to the ball?
(A) Sink a little
(B) Rise a little
(C)Remain unchanged
(D)Sink completely
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we are going to first consider the two cases for the cork ball before the evacuation of the chamber and after the evacuation, after that it is analyzed what impact does change in pressure has over the change in the heights of the cork and the correct option is chosen.
The pressure force is given by
$ {p_1} = w = \rho g{h_1} \times A $
Complete step by step solution:
As it is given in the question that the cork ball is floating on the surface of water in a beaker and the beaker being covered with a bell jar and the air is evacuated.
Now, before evacuation, let the pressure and height under the water of the cork ball be $ {p_1} $ and $ {h_1} $ respectively.
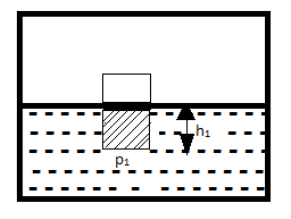
Thus, the pressure force is balanced by the weight of the cork, i.e.,
$ {p_1} = w = \rho g{h_1} \times A $
Thus, calculating the height $ {h_1} $ from it
$ {h_1} = \dfrac{w}{{\rho gA}} - - - \left( 1 \right) $
Considering the second situation after the evacuation of the air from the beaker, let the pressure and the height of the beaker be $ {p_2} $ and $ {h_2} $ respectively.
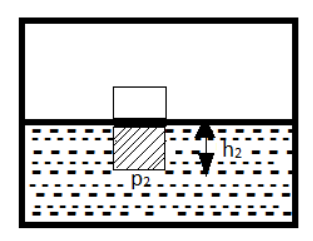
This pressure force is also balanced by the weight of the cork, i.e.,
$ {p_2} = w = \rho g{h_2} \times A $
Now, calculating the height $ {h_2} $ from it,
$ {h_2} = \dfrac{w}{{\rho gA}} - - - \left( 2 \right) $
Now, from equations $ \left( 1 \right) $ and $ \left( 2 \right) $ ,
The both heights are equal to the term $ \dfrac{w}{{\rho gA}} $ , thus, there is no change in the heights with the change in the pressures or with the evacuation of the chamber.
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
The height of the cork dipped in the water depends upon the density of the water, the area of the cork and the gravity. It has nothing to do with the pressure of the beaker. That is why, on increasing or decreasing the pressure or the temperature, there will be no change in the level of the cork in the beaker.
The pressure force is given by
$ {p_1} = w = \rho g{h_1} \times A $
Complete step by step solution:
As it is given in the question that the cork ball is floating on the surface of water in a beaker and the beaker being covered with a bell jar and the air is evacuated.
Now, before evacuation, let the pressure and height under the water of the cork ball be $ {p_1} $ and $ {h_1} $ respectively.

Thus, the pressure force is balanced by the weight of the cork, i.e.,
$ {p_1} = w = \rho g{h_1} \times A $
Thus, calculating the height $ {h_1} $ from it
$ {h_1} = \dfrac{w}{{\rho gA}} - - - \left( 1 \right) $
Considering the second situation after the evacuation of the air from the beaker, let the pressure and the height of the beaker be $ {p_2} $ and $ {h_2} $ respectively.

This pressure force is also balanced by the weight of the cork, i.e.,
$ {p_2} = w = \rho g{h_2} \times A $
Now, calculating the height $ {h_2} $ from it,
$ {h_2} = \dfrac{w}{{\rho gA}} - - - \left( 2 \right) $
Now, from equations $ \left( 1 \right) $ and $ \left( 2 \right) $ ,
The both heights are equal to the term $ \dfrac{w}{{\rho gA}} $ , thus, there is no change in the heights with the change in the pressures or with the evacuation of the chamber.
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
The height of the cork dipped in the water depends upon the density of the water, the area of the cork and the gravity. It has nothing to do with the pressure of the beaker. That is why, on increasing or decreasing the pressure or the temperature, there will be no change in the level of the cork in the beaker.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




