
Where should a convex lens of focal length 9 cm be placed \[\left( {in{\text{ }}cm} \right)\] between two point sources \[S_1\] and \[S_2\] which are \[24\;cm\] apart, so that images of both the sources are formed at the same place. You have to find the distance of the lens from \[S_1\] or \[S_2\] whichever is lesser.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint:
- You should know the difference between the images formed in convex to the concave.
- You should know the convex lens equation.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the convex lens equation,
\[\dfrac{1}{f}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{v}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{u}\] Where, u is the distance from the object, v is the distance from the image and f is the focal length.
It relates the focal length of a lens with the distance of an object placed in front of it and the image formed of that object. All image or object left to the optical point is negative and all image or object on the right side of the optic centre is positive.
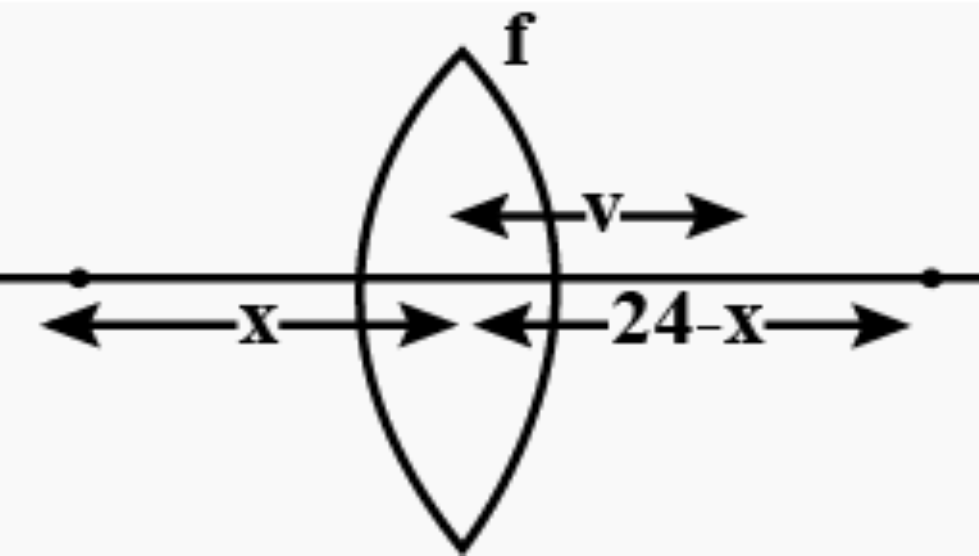
For refraction from left hand source \[{S_1}\],
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - v}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - x}} = \dfrac{1}{9}\]
For refraction from right hand source \[{S_2}\],
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - v}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - \left( {24 - x} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{9}\]
Adding the equations gives,
\[{x^2} - 24x + 108 = 0\]
Therefore
\[x = 6cm\]
\[x = 18cm\]
Smaller distance is 6cm.
Note:
- Memorize basic equations.
- Should have a good conceptual clarity in the image formed in the lens.
- You should be aware of numerical errors.
- You should be aware of negative signs which are used in the solution.
- You should know the difference between the images formed in convex to the concave.
- You should know the convex lens equation.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the convex lens equation,
\[\dfrac{1}{f}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{v}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{u}\] Where, u is the distance from the object, v is the distance from the image and f is the focal length.
It relates the focal length of a lens with the distance of an object placed in front of it and the image formed of that object. All image or object left to the optical point is negative and all image or object on the right side of the optic centre is positive.

For refraction from left hand source \[{S_1}\],
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - v}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - x}} = \dfrac{1}{9}\]
For refraction from right hand source \[{S_2}\],
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - v}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - \left( {24 - x} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{9}\]
Adding the equations gives,
\[{x^2} - 24x + 108 = 0\]
Therefore
\[x = 6cm\]
\[x = 18cm\]
Smaller distance is 6cm.
Note:
- Memorize basic equations.
- Should have a good conceptual clarity in the image formed in the lens.
- You should be aware of numerical errors.
- You should be aware of negative signs which are used in the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




