
A container of width \[2a\] is filled with a liquid. A thin wire of the weight per unit length \[\lambda \] is gently placed over the liquid surface in the middle of the surface as shown in the figure. As a result, the liquid surface is depressed by a distance \[y\left( {y < < a} \right)\] and determines the surface tension of the liquid.


Answer
471.6k+ views
Hint: The surface tension of a liquid is occurred by the attraction of the particles in the surface layer by the bulk of the liquid, which tends to minimize surface area is also defined as the surface tension.The liquid particles together along the surface when the particles are pulled toward the rest of the liquid. The surface tension is the ratio of the surface force to the length along which the force acts. We can determine the surface tension of the liquid by using the given diagram.
Complete step by step answer:
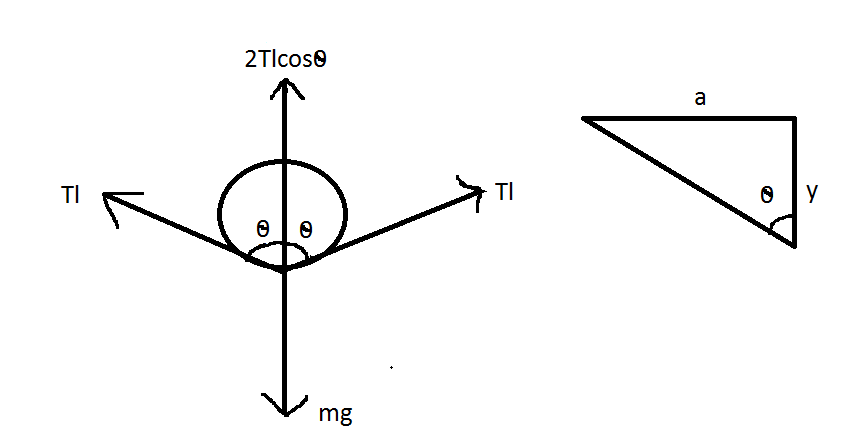
The figure shows that the free body diagram of a wire.
Let \[l\] be the length of the wire. If \[\lambda \] is mass per unit length of wire, the weight of wire \[ = \left( {lx} \right)g\] (acting vertically downward).
Vertical force due to surface tension \[ = 2Tl\cos \theta \] (upward)
Therefore for vertical equilibrium \[2Tl\cos \theta = \left( {l\lambda } \right)g\]
\[T = \dfrac{{\lambda g}}{{2\cos \theta }}\]
From the figure,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = y\sqrt {{y^2}} + {a^2} = \dfrac{y}{a}\] (For\[y < < a\])
\[ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{\lambda g}}{{2\left( {\dfrac{y}{a}} \right)}} = \dfrac{{\lambda g}}{{2y}}\]
Thus, the correct answer of the surface tension of the liquid is \[T = \dfrac{{\lambda g}}{{2y}}\].
Note:
The attractive forces between the particles in the given liquid but also on the forces of attraction of solid, liquid, or gas in contact with it do not only depend upon the surface tension.
The energy responsible for the phenomenon of surface tension may be almost equal to the equivalent of the work or energy required to remove the surface layer of molecules in a unit area.
Complete step by step answer:

The figure shows that the free body diagram of a wire.
Let \[l\] be the length of the wire. If \[\lambda \] is mass per unit length of wire, the weight of wire \[ = \left( {lx} \right)g\] (acting vertically downward).
Vertical force due to surface tension \[ = 2Tl\cos \theta \] (upward)
Therefore for vertical equilibrium \[2Tl\cos \theta = \left( {l\lambda } \right)g\]
\[T = \dfrac{{\lambda g}}{{2\cos \theta }}\]
From the figure,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = y\sqrt {{y^2}} + {a^2} = \dfrac{y}{a}\] (For\[y < < a\])
\[ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{\lambda g}}{{2\left( {\dfrac{y}{a}} \right)}} = \dfrac{{\lambda g}}{{2y}}\]
Thus, the correct answer of the surface tension of the liquid is \[T = \dfrac{{\lambda g}}{{2y}}\].
Note:
The attractive forces between the particles in the given liquid but also on the forces of attraction of solid, liquid, or gas in contact with it do not only depend upon the surface tension.
The energy responsible for the phenomenon of surface tension may be almost equal to the equivalent of the work or energy required to remove the surface layer of molecules in a unit area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




