
A container having a hole at the bottom is free to move on a horizontal surface. As the liquid comes out, the container moves in a backward direction with an acceleration $\alpha $ and finally acquires a velocity $v$ (when all liquid has drained out). Neglect the mass of the container. The correct option out of the following is:
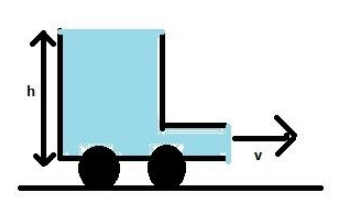
(A) Only $v$ depends on $h$
(B) Only $\alpha $ depends on $h$
(C) Both $v$ and $\alpha $ depend on $h$
(D) Neither $v$ nor $\alpha $ depends on $h$

Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint:Here, we have to find the dependency of height $h$ on velocity $v$ and acceleration $\alpha $. Therefore, here we will use the laws of fluid mechanics and relation between velocity and acceleration for solving this problem. It means that first we have to know how the height of the container affects its velocity and how the change of velocity affects its acceleration.
Formula used:
$v = \sqrt {2gh}$,
Where, $v$ is velocity, $g$ is acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is height.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, according to the laws of fluid mechanics, the velocity of the liquid through the hole of the container is given by:
$v = \sqrt {2gh} $
In the given case, initially the container is at rest and therefore it has no initial velocity.
So we can say that initial velocity ${v_0} = 0 m/s$.
However, the container gains its final velocity $v$ as the liquid comes out.
From this it is clear that there is a change in velocity from ${v_0} = 0 m/s$ to $v m/s$ of the container due to which it accelerates with acceleration $\alpha$.It is clear that acceleration $\alpha$ is dependent on the change of velocity. But this change velocity is dependent on the height of the container $h$. So, we can say that acceleration $\alpha$ is also dependent on the height of the container $h$.Thus, both velocity $v$ and acceleration $\alpha$ depend on the height of the container $h$.
Hence, option C is the right choice.
Note:In this problem, we have concluded that the height of the container affects both its velocity and acceleration.We have used the formula $v = \sqrt {2gh}$ in this problem which is called Torricelli’s theorem or velocity of efflux.
Formula used:
$v = \sqrt {2gh}$,
Where, $v$ is velocity, $g$ is acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is height.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, according to the laws of fluid mechanics, the velocity of the liquid through the hole of the container is given by:
$v = \sqrt {2gh} $
In the given case, initially the container is at rest and therefore it has no initial velocity.
So we can say that initial velocity ${v_0} = 0 m/s$.
However, the container gains its final velocity $v$ as the liquid comes out.
From this it is clear that there is a change in velocity from ${v_0} = 0 m/s$ to $v m/s$ of the container due to which it accelerates with acceleration $\alpha$.It is clear that acceleration $\alpha$ is dependent on the change of velocity. But this change velocity is dependent on the height of the container $h$. So, we can say that acceleration $\alpha$ is also dependent on the height of the container $h$.Thus, both velocity $v$ and acceleration $\alpha$ depend on the height of the container $h$.
Hence, option C is the right choice.
Note:In this problem, we have concluded that the height of the container affects both its velocity and acceleration.We have used the formula $v = \sqrt {2gh}$ in this problem which is called Torricelli’s theorem or velocity of efflux.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




