
(a) Construct a complete transcription unit with promoter and terminator on the basis of the hypothetical template strand given below:
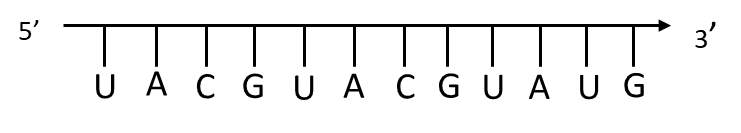
(b) Write the RNA strand transcribed from the above transcription unit along with its polarity.
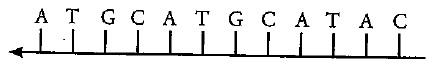
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: (a) A transcription unit consists of a promoter, a functional gene, and a terminator sequence. From the directional flow of the given strand, we can identify that this is a template strand.
(b) The RNA strand transcribed by the polymerase enzyme would have the same purine and pyrimidine sequence as shown in the question as it is the template strand and the major difference would be that the RNA sequence would have Uracil (U) instead of Thymine (T).
Complete answer: Transcription is the process where RNA strands are transcribed from a given DNA template. It is done by an RNA polymerase enzyme and other transcriptional factors. It is one of the several steps involved in the ‘Central dogma of molecular biology’.
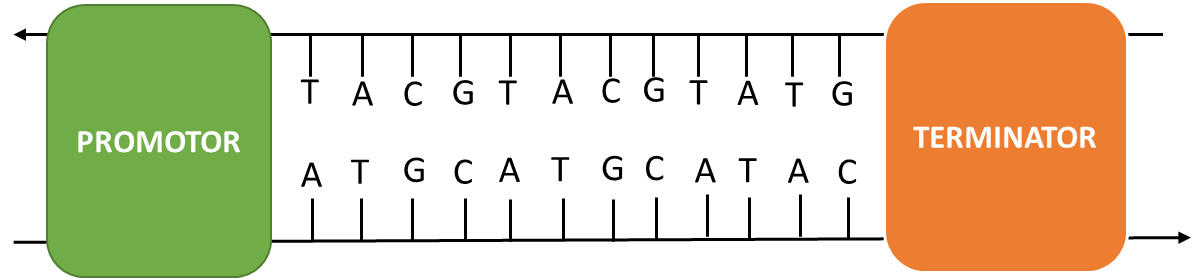
The transcriptional unit consists of a promoter sequence which is a small sequence of DNA found in the upstream region of the functional gene and a terminator sequence which is found in the downstream region of the functional gene. The promoter sequence serves as a binding site for the polymerase enzyme, which needs to first attach to the double-stranded DNA and uncoil them to read the template strand.
From the given example, we can see that the given strand is a template strand as the direction is from 3’ to 5’. So when constructing a transcription unit, we would construct a coding strand based on the complementarity of purines and pyrimidines and attach a promoter sequence upstream and a terminator sequence downstream.
The main aim of the transcription process is to produce an mRNA strand that possesses the sequence as that of the coding strand. This synthesized mRNA then moves on to translation where sequences are interpreted to form functional proteins.
The major difference between the DNA strand and the RNA strand is the presence of uracil (U). Uracil is a pyrimidine like adenosine and thymine but replaces thymine in RNA. Thus when constructing an mRNA strand it would be the same as the coding strand with the exception being that all the Thymine (T) would be replaced by Uracil (U).
Note:The main function of the promoter sequence is to serve as an initiation site where the polymerase enzyme binds along with other transcription factors. The transcription factors are what uncoil the double-strand and activate the polymerase enzyme. The direction of the coding strand is always 5’ to 3’ and the direction of the template strand is always 3’ to 5’.
(b) The RNA strand transcribed by the polymerase enzyme would have the same purine and pyrimidine sequence as shown in the question as it is the template strand and the major difference would be that the RNA sequence would have Uracil (U) instead of Thymine (T).
Complete answer: Transcription is the process where RNA strands are transcribed from a given DNA template. It is done by an RNA polymerase enzyme and other transcriptional factors. It is one of the several steps involved in the ‘Central dogma of molecular biology’.
The transcriptional unit consists of a promoter sequence which is a small sequence of DNA found in the upstream region of the functional gene and a terminator sequence which is found in the downstream region of the functional gene. The promoter sequence serves as a binding site for the polymerase enzyme, which needs to first attach to the double-stranded DNA and uncoil them to read the template strand.
From the given example, we can see that the given strand is a template strand as the direction is from 3’ to 5’. So when constructing a transcription unit, we would construct a coding strand based on the complementarity of purines and pyrimidines and attach a promoter sequence upstream and a terminator sequence downstream.

The main aim of the transcription process is to produce an mRNA strand that possesses the sequence as that of the coding strand. This synthesized mRNA then moves on to translation where sequences are interpreted to form functional proteins.
The major difference between the DNA strand and the RNA strand is the presence of uracil (U). Uracil is a pyrimidine like adenosine and thymine but replaces thymine in RNA. Thus when constructing an mRNA strand it would be the same as the coding strand with the exception being that all the Thymine (T) would be replaced by Uracil (U).

Note:The main function of the promoter sequence is to serve as an initiation site where the polymerase enzyme binds along with other transcription factors. The transcription factors are what uncoil the double-strand and activate the polymerase enzyme. The direction of the coding strand is always 5’ to 3’ and the direction of the template strand is always 3’ to 5’.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




