
A consistent force $F = {m_1}g/2$ is applied on the block of mass ${m_2}$ as shown in figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of ${m_2}$.
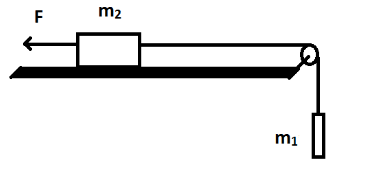

Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint:To solve this problem, we need to use two main concepts. First is the tensile force and second is Newton's second law of motion. We will consider the horizontal forces acting on mass ${m_2}$ and vertical forces on the mass ${m_1}$. By this we can obtain two equations which will help us find the value of the acceleration of ${m_2}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider the forces on the system as shown in figure. Let T be the tension in the rope.
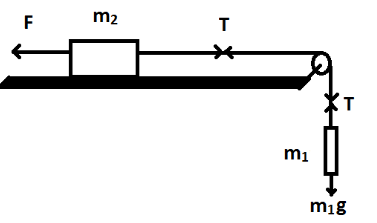
Now, we will consider the horizontal forces action on mass ${m_2}$.
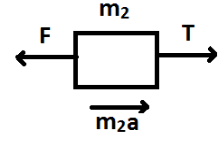
As shown in the figure, two forces are clearly visible action in the opposite direction on mass ${m_2}$. First is force F and second is the tensile force T. Moreover. If we take acceleration as a, then according to Newton’s second law of motion, there is another force ${m_2}a$acting in the right direction.
Equating these horizontal forces, we get
$F = {m_2}a + T$
It is given that $F = {m_1}g/2$
$
\dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} = {m_2}a + T \\
\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} - {m_2}a \\ $
Now, we will consider vertical forces acting on mass ${m_1}$.
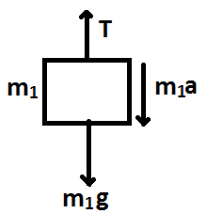
Here, tensile force is acting upwards and weight and force due to motion acts downwards.
Equating the vertical forces, we get
$T = {m_1}a + {m_1}g$
Putting $T = \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} - {m_2}a$ in this equation, we get
$
\dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} - {m_2}a = {m_1}a + {m_1}g \\
\Rightarrow {m_1}a + {m_2}a = \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} - {m_1}g \\
\Rightarrow a\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right) = - \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} \\
\therefore a = - \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{{2\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}} $
Thus the acceleration of ${m_2}$is $ - \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{{2\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}$.
Note:Here, we have used Newton’s second law of motion to determine the answer of this question. This law states that the acceleration of an object is directly related to the net force and inversely related to its mass. Thus, when a force is applied on the body and if its mass is known, then the acceleration can be determined by applying this law.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider the forces on the system as shown in figure. Let T be the tension in the rope.

Now, we will consider the horizontal forces action on mass ${m_2}$.

As shown in the figure, two forces are clearly visible action in the opposite direction on mass ${m_2}$. First is force F and second is the tensile force T. Moreover. If we take acceleration as a, then according to Newton’s second law of motion, there is another force ${m_2}a$acting in the right direction.
Equating these horizontal forces, we get
$F = {m_2}a + T$
It is given that $F = {m_1}g/2$
$
\dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} = {m_2}a + T \\
\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} - {m_2}a \\ $
Now, we will consider vertical forces acting on mass ${m_1}$.

Here, tensile force is acting upwards and weight and force due to motion acts downwards.
Equating the vertical forces, we get
$T = {m_1}a + {m_1}g$
Putting $T = \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} - {m_2}a$ in this equation, we get
$
\dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} - {m_2}a = {m_1}a + {m_1}g \\
\Rightarrow {m_1}a + {m_2}a = \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} - {m_1}g \\
\Rightarrow a\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right) = - \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{2} \\
\therefore a = - \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{{2\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}} $
Thus the acceleration of ${m_2}$is $ - \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{{2\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}$.
Note:Here, we have used Newton’s second law of motion to determine the answer of this question. This law states that the acceleration of an object is directly related to the net force and inversely related to its mass. Thus, when a force is applied on the body and if its mass is known, then the acceleration can be determined by applying this law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




