
A conducting loop in the shape of a right angled isosceles triangle of height $10\,cm$ is kept such that the ${90^o}$ vertex is very close to an infinitely long conducting wire (see the figure). The wire is electricity insulted from the loop. The hypotenuse of the triangle is parallel to the wire. The current in the triangle loop is in counter clockwise direction and increases at a constant rate of $10\,A\,{s^{ - 1}}$.
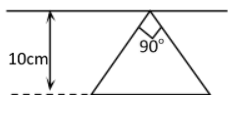
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true?
(A) The magnitude of induced emf in the wire is $\left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi }} \right)volt$
(B) If the loop is rotated at a constant angular speed about the wire, an additional emf of $\left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi }} \right)$
(C) The induced current in the wire is in opposite direction to the current along the hypotenuse
(D) There is a repulsive force between the wire and the loop

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: When an emf is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faraday's Law, the polarity of the induced emf is such that it produces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change which produces it.
Complete step by step answer:
The rate of change of current in the loop is anticlockwise.
$\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} = 10\,A/s$
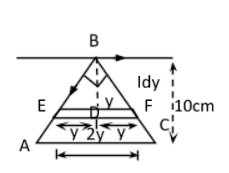
Let take a strip of thickness by at perpendicular distance$Y$. Hence$\Delta \,EDC$ is isosceles triangle hence sides $ED = \,BD\, = Y$
Magnetic flux due to straight wire is
$d\phi = B.dA$ ……………………..(i)
$B$is magnetic field due to straight wire and $dA$is area of strip.
$d\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi y}}(2y.dy)$ ……………………(ii)
$d\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{\pi }dy$ …………………..(iii)
Integrate equation (iii) w.r.t. limits of ${y_1} = 0$to ${y_2} = 0.1\,m$
$\int {d\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{\pi }\int_{{y_1} = 0}^{{y_2} = \,0.1m} {dy} } $
$\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{\pi }\left[ {0.1 - 0} \right]$
$\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{10\pi }}$ …………………..(iv)
Differentiate equation (iv) w.r.t. time
$\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{10\pi }}\,\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}$
\[\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi }\] $\left[ {\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} = 10A/s} \right]$
$E = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi }$
$\left[ {E = \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}} \right]$
Note:
If current in two parallel wires is in the same direction then they attract each other but if direction is in the opposite direction then they repel each other.
Complete step by step answer:
The rate of change of current in the loop is anticlockwise.
$\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} = 10\,A/s$

Let take a strip of thickness by at perpendicular distance$Y$. Hence$\Delta \,EDC$ is isosceles triangle hence sides $ED = \,BD\, = Y$
Magnetic flux due to straight wire is
$d\phi = B.dA$ ……………………..(i)
$B$is magnetic field due to straight wire and $dA$is area of strip.
$d\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi y}}(2y.dy)$ ……………………(ii)
$d\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{\pi }dy$ …………………..(iii)
Integrate equation (iii) w.r.t. limits of ${y_1} = 0$to ${y_2} = 0.1\,m$
$\int {d\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{\pi }\int_{{y_1} = 0}^{{y_2} = \,0.1m} {dy} } $
$\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{\pi }\left[ {0.1 - 0} \right]$
$\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{10\pi }}$ …………………..(iv)
Differentiate equation (iv) w.r.t. time
$\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{10\pi }}\,\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}$
\[\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi }\] $\left[ {\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} = 10A/s} \right]$
$E = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{\pi }$
$\left[ {E = \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}} \right]$
Note:
If current in two parallel wires is in the same direction then they attract each other but if direction is in the opposite direction then they repel each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




