
A concave mirror is made by cutting a portion of a hollow glass sphere of radius 24 cm. Find the focal length of the mirror.
A) 24 cm
B) 12 cm
C) 6 cm
D) 18 cm
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Focal length of a mirror is the distance between pole and focal point of mirror.
Focal point is the point where all parallel rays converge or appear to converge.
As we know that for a small size spherical mirror the focal length is equal to half the radius of curvature.
So, we can write $f = R/2$
Where
$f$ = focal length
$R$ = Radius of sphere or sometimes known as radius of curvature
Complete step by step answer:
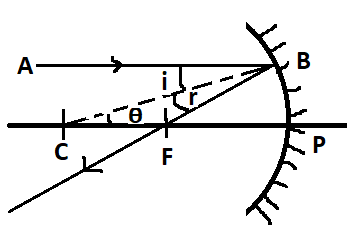
Consider a concave mirror as shown in figure
According to the second law of reflection i.e. angle of reflection is always equal to angle of incidence.
So, we can write
$\angle r = \angle i$
Where,
$\angle i = $ angle of incidence
$\angle r = $angle of reflection
We know that AB is parallel to the principal axis, $\angle i$ and $\angle \theta $ are alternate angles. So, they must be equal
$\because \angle i = \angle \theta - - - (1)$
We know in a triangle sides opposite to equal angles are equal.
So, In $\vartriangle CFB$
$FC = FB - - - (2)$
Since we know that the mirror is small and focused, it is very near to the principal axis.
So, we can write
$FB = FP - - - (3)$
Form (2) & (3) we get
$FC = FB = FP - - - (4)$
From figure we can see
$CP = FC + FP - - - (5)$
Further substituting the $FC = FP$ from (4)
$
CP = FP + FP \\
CP = 2FP \\
$
We know $CP = R$ and $FP = f$
$
R = 2f \\
f = R/2 \\
$
So,
$f = R/2 = 24/2 = 12$ cm
Note: $f = R/2$ is true even when the mirror is immersed in liquid as focal length doesn’t depend on the medium in which it is kept but, when $R$ is large enough then this formula is not valid.
Using this relation and triangle properties, we can also derive formula
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
Where,
$f = $ focal length of mirror
$u = $ position of object from pole
$v = $position of image from pole
Above formula is known as mirror formula
Focal point is the point where all parallel rays converge or appear to converge.
As we know that for a small size spherical mirror the focal length is equal to half the radius of curvature.
So, we can write $f = R/2$
Where
$f$ = focal length
$R$ = Radius of sphere or sometimes known as radius of curvature
Complete step by step answer:

Consider a concave mirror as shown in figure
According to the second law of reflection i.e. angle of reflection is always equal to angle of incidence.
So, we can write
$\angle r = \angle i$
Where,
$\angle i = $ angle of incidence
$\angle r = $angle of reflection
We know that AB is parallel to the principal axis, $\angle i$ and $\angle \theta $ are alternate angles. So, they must be equal
$\because \angle i = \angle \theta - - - (1)$
We know in a triangle sides opposite to equal angles are equal.
So, In $\vartriangle CFB$
$FC = FB - - - (2)$
Since we know that the mirror is small and focused, it is very near to the principal axis.
So, we can write
$FB = FP - - - (3)$
Form (2) & (3) we get
$FC = FB = FP - - - (4)$
From figure we can see
$CP = FC + FP - - - (5)$
Further substituting the $FC = FP$ from (4)
$
CP = FP + FP \\
CP = 2FP \\
$
We know $CP = R$ and $FP = f$
$
R = 2f \\
f = R/2 \\
$
So,
$f = R/2 = 24/2 = 12$ cm
Note: $f = R/2$ is true even when the mirror is immersed in liquid as focal length doesn’t depend on the medium in which it is kept but, when $R$ is large enough then this formula is not valid.
Using this relation and triangle properties, we can also derive formula
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v}$
Where,
$f = $ focal length of mirror
$u = $ position of object from pole
$v = $position of image from pole
Above formula is known as mirror formula
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




