
A concave mirror forms the real image of an object which is magnified $ 4 $ times. The object is moved $ 3cm $ away, the magnification of the image is $ 3 $ times. What is the focal length of the mirror?
A. $ 3cm $
B. $ 4cm $
C. $ 12cm $
D. $ 36cm $
Answer
488.7k+ views
Hint: There are three types of mirrors that are commonly used. There are mainly three types of mirrors: plain, convex, and concave. All of them will be used for different purposes. Various mirrors have different properties. In the case of convex mirrors, virtual images are always formed. Plain mirrors create virtual pictures, while concave mirrors create both virtual and real images. In the sense that it is real, it is an inverted image. Whatever the direction, we may use a magnification formula to calculate the image size.
$ m = - \dfrac{v}{u} = \dfrac{f}{{f - u}} $
Where,
$ m $ is the magnification.
$ v $ is the object distance.
$ u $ is the image distance and
$ f $ is the focal length.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Various placements of an object in front of a concave mirror provide different image positions. When an object is put between the concave mirror's pole and focus, an image is generated on the opposite side of the mirror. That image can be enlarged or shrunk, and it can be virtual. When an object is placed between the focus and the centre, the picture is produced away from the centre and is actual and inverted. As illustrated in the diagram, the image will be larger than the object.
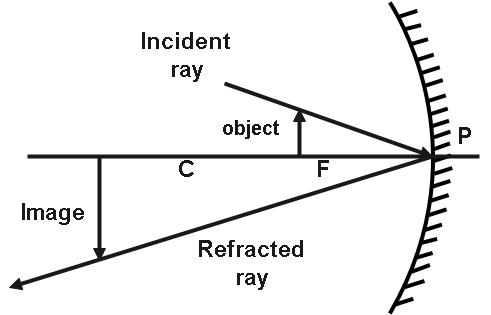
The magnification given by the concave mirror is $ 3 $ . Because it is a real image that has been magnified, it will come within the above diagram. As a result, the image will be magnified and inverted. As a result, magnification with the correct sign will be $ - 3 $ . The distance between the object and the sign is $ - vcm $ .
And we know magnification is given as,
$ m = \dfrac{f}{{f - u}} $
$
- 3 = \dfrac{f}{{u - 3}} \\
\Rightarrow f = 3u + 9 \\
$
Also, in this case we can write,
$ \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{3u + 9}} - \dfrac{1}{{u + 3}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{f} $ -----(1)
And in first case,
$ \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} $
And as per question it will become,
$ \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{4u}} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{f} $ -----(2)
Now, solving equation 1 and 2
$ f = \dfrac{{4u}}{5} $
And taking common $ u + 3 $ from equation 1
$
\dfrac{{1 + 3}}{{3\left( {u + 3} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{f} \\
\Rightarrow 4f = \dfrac{{3\left( {u + 3} \right)}}{1} \\
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{{3\left( {u + 3} \right)}}{4} \\
$
Now we have got two values of $ f $ now comparing both the values and finding the values of $ u $
$
\dfrac{{4u}}{5} = \dfrac{{3\left( {u + 3} \right)}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow 16u = 15u + 45 \\
\Rightarrow u = 45 \\
$
And putting the values of $ u $ in $ f = \dfrac{{4u}}{5} $
$
f = \dfrac{{4 \times 45}}{5} \\
\Rightarrow f = 36 \\
$
Therefore, the focal length of the mirror is $ 36cm $ .
Hence option D is the correct option.
Note:
The image we get at the end of the process is an inverted real-sized image. We should place the object between the pole and the focus of the mirror if we need a virtual expanded image of the same magnification. When we place something between the mirror's centre and focus, we get an inverted enlarged image.
$ m = - \dfrac{v}{u} = \dfrac{f}{{f - u}} $
Where,
$ m $ is the magnification.
$ v $ is the object distance.
$ u $ is the image distance and
$ f $ is the focal length.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Various placements of an object in front of a concave mirror provide different image positions. When an object is put between the concave mirror's pole and focus, an image is generated on the opposite side of the mirror. That image can be enlarged or shrunk, and it can be virtual. When an object is placed between the focus and the centre, the picture is produced away from the centre and is actual and inverted. As illustrated in the diagram, the image will be larger than the object.

The magnification given by the concave mirror is $ 3 $ . Because it is a real image that has been magnified, it will come within the above diagram. As a result, the image will be magnified and inverted. As a result, magnification with the correct sign will be $ - 3 $ . The distance between the object and the sign is $ - vcm $ .
And we know magnification is given as,
$ m = \dfrac{f}{{f - u}} $
$
- 3 = \dfrac{f}{{u - 3}} \\
\Rightarrow f = 3u + 9 \\
$
Also, in this case we can write,
$ \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{3u + 9}} - \dfrac{1}{{u + 3}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{f} $ -----(1)
And in first case,
$ \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} $
And as per question it will become,
$ \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{4u}} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{f} $ -----(2)
Now, solving equation 1 and 2
$ f = \dfrac{{4u}}{5} $
And taking common $ u + 3 $ from equation 1
$
\dfrac{{1 + 3}}{{3\left( {u + 3} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{f} \\
\Rightarrow 4f = \dfrac{{3\left( {u + 3} \right)}}{1} \\
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{{3\left( {u + 3} \right)}}{4} \\
$
Now we have got two values of $ f $ now comparing both the values and finding the values of $ u $
$
\dfrac{{4u}}{5} = \dfrac{{3\left( {u + 3} \right)}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow 16u = 15u + 45 \\
\Rightarrow u = 45 \\
$
And putting the values of $ u $ in $ f = \dfrac{{4u}}{5} $
$
f = \dfrac{{4 \times 45}}{5} \\
\Rightarrow f = 36 \\
$
Therefore, the focal length of the mirror is $ 36cm $ .
Hence option D is the correct option.
Note:
The image we get at the end of the process is an inverted real-sized image. We should place the object between the pole and the focus of the mirror if we need a virtual expanded image of the same magnification. When we place something between the mirror's centre and focus, we get an inverted enlarged image.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




