
When a colloidal solution is viewed from the direction at right angles of the light beam, the path of the beam is illuminated due to scattering of light. In the given figure \[{\text{(A)}}\] and \[{\text{(B)}}\] are:
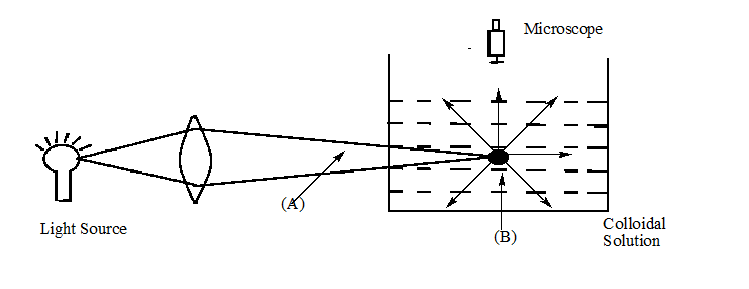
A.A – Tyndall cone, B – Scattered light
B.A – scattered light, B – Tyndall cone
C.A – Tyndall cone, B – Blind spot
D.A – Tyndall effect, B – Tyndall cone

Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Tyndall effect is well connected with colloidal solution. In colloidal solutions light gets scattered when passed through light. As we can see in image a cone shape image is being formed.
Complete step by step solution:
Tyndall effect is shown by all the colloidal solutions. This is the phenomenon in which the particles in the colloidal solution scatter the beam of light when light on them. It is used to check whether the solution is colloidal or not. The intensity of the scattered light depends upon two factors, the frequency of the incident light and the density of colloidal particles.
Basically in the Tyndall effect when we pass light from the colloidal solution, it does not let the light to completely pass through the solution. It actually scatters the light when the light is passed through. This does not happen when we pass light in non- colloidal solutions. The scattering of blue light is more and red light scattered the least. As we know blue light has minimum wavelength and red light has maximum wavelength.
The bright cone known as Tyndall cone is formed when we view the solution at right angle and bluish light appears due to Tyndall effect. In part A formation of Tyndall cones is occurring and in part B light is being scattered.
Due to the above facts, the correct option is A.
Note: This effect was first observed by the scientist John Tyndall and the effect was named after his name. Daily life examples of Tyndall effect are milk. Milk is a colloidal solution of fats and protein.
Complete step by step solution:
Tyndall effect is shown by all the colloidal solutions. This is the phenomenon in which the particles in the colloidal solution scatter the beam of light when light on them. It is used to check whether the solution is colloidal or not. The intensity of the scattered light depends upon two factors, the frequency of the incident light and the density of colloidal particles.
Basically in the Tyndall effect when we pass light from the colloidal solution, it does not let the light to completely pass through the solution. It actually scatters the light when the light is passed through. This does not happen when we pass light in non- colloidal solutions. The scattering of blue light is more and red light scattered the least. As we know blue light has minimum wavelength and red light has maximum wavelength.
The bright cone known as Tyndall cone is formed when we view the solution at right angle and bluish light appears due to Tyndall effect. In part A formation of Tyndall cones is occurring and in part B light is being scattered.
Due to the above facts, the correct option is A.
Note: This effect was first observed by the scientist John Tyndall and the effect was named after his name. Daily life examples of Tyndall effect are milk. Milk is a colloidal solution of fats and protein.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




