
A coin of diameter $\dfrac{1}{2}$ units is tossed randomly onto the rectangular cartesian plane, the probability that the coin does not intersect any line whose equation is of the form \[x = k\] , is
A.$\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
B.$1 - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
C.$\dfrac{1}{4}$
D.$\dfrac{1}{2}$
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: Here we use the concept of probability and x-y plane.
Required Formula: ${\text{Probability of an event = }}\dfrac{{{\text{favourable cases}}}}{{{\text{Total cases}}}}$
Complete step by Solution:
Given: Diameter of a coin tossed is $\dfrac{1}{2}$ $ \Rightarrow radius = \dfrac{{diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{4}$
Equation of the line is \[x = k\].
Consider two adjacent lines \[x = k{\text{ }}and\;x = k + 1\]
We need line equations of the form \[x = k{\text{ }}and\;x = k + 1\].
According to the question, For the favorable event, the centre of the coin should fall into a shaded region.
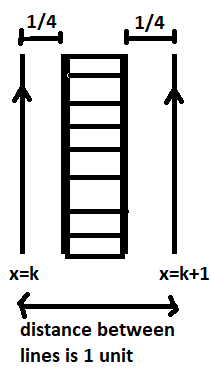
Distance between two adjacent lines \[x = k{\text{ }}and\;x = k + 1\] is $1$.
As radius is $\dfrac{1}{4}$ from both adjacent lines, If the coin falls exactly in the shaded region it will not intersect the two lines.
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Required probability = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Area of shaded portion}}}}{{{\text{Distance between two adjacent lines}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}}}{1}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}\]
Hence, Option choice D is the correct answer.
Note: In such types of questions which involves concept probability having an idea about the formula is needed. Sometimes probability questions may be accompanied with x-y planes. Graphing helps to solve the question. Follow the conditions in the question. Frame the equations accordingly to get the required value.
Required Formula: ${\text{Probability of an event = }}\dfrac{{{\text{favourable cases}}}}{{{\text{Total cases}}}}$
Complete step by Solution:
Given: Diameter of a coin tossed is $\dfrac{1}{2}$ $ \Rightarrow radius = \dfrac{{diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{4}$
Equation of the line is \[x = k\].
Consider two adjacent lines \[x = k{\text{ }}and\;x = k + 1\]
We need line equations of the form \[x = k{\text{ }}and\;x = k + 1\].
According to the question, For the favorable event, the centre of the coin should fall into a shaded region.

Distance between two adjacent lines \[x = k{\text{ }}and\;x = k + 1\] is $1$.
As radius is $\dfrac{1}{4}$ from both adjacent lines, If the coin falls exactly in the shaded region it will not intersect the two lines.
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Required probability = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Area of shaded portion}}}}{{{\text{Distance between two adjacent lines}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}}}{1}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}\]
Hence, Option choice D is the correct answer.
Note: In such types of questions which involves concept probability having an idea about the formula is needed. Sometimes probability questions may be accompanied with x-y planes. Graphing helps to solve the question. Follow the conditions in the question. Frame the equations accordingly to get the required value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




