
A coil possessing both inductance L and resistance R is connected to a $24V$ dc supply having negligible internal resistance. The dc current in this circuit is found to be $3A$. When the coil is connected to a $24V$, $50Hz$ ac supply, the circuit current is found to be $0.8A$ . Find:
(a) the resistance of the coil.
(b) the inductance of the coil.
Answer
478.2k+ views
Hint: This question utilizes the concept of Circuits. We know that the inductor does not work on a dc circuit, thus we can find resistance from there. Then we can use this value in the case of ac circuit and find out the inductance
Formulae used:
\[{I_{DC}} = \dfrac{{{V_{DC}}}}{R}\]
where ${I_{DC}}$ is the current in the circuit, ${V_{DC}}$ is the voltage and $R$ is the resistance of the coil.
${Z^2} = {R^2} + {X_L}^2$
where $Z$ is the impedance, $R$ is the resistance and ${X_L}$ is the inductive reactance.
${X_L} = \omega L = 2\pi fL$
where $\omega $ is the angular frequency, $f$ is the frequency of the ac circuit and $L$ is the inductance.
Complete step by step answer:
As we are considering inductance $L$ and resistance $R$ of the same coil, it becomes a series $LR$ circuit. Now we have two cases-
(a) $24V$ dc supply connected. Inductance does not play any role in dc source. Thus, the circuit has resistance $R$
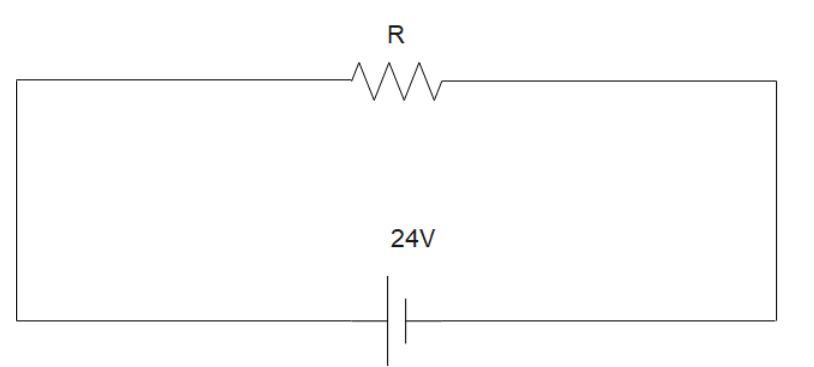
Now, the current in the coil is given by
\[{I_{DC}} = \dfrac{{{V_{DC}}}}{R}\]
where ${I_{DC}}$ is the current in the circuit, ${V_{DC}}$ is the voltage and $R$ is the resistance of the coil.
Inserting given values we get
\[\Rightarrow 3 = \dfrac{{24}}{R} \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{24}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow R = 8\Omega \\ \]
(b) $24V$ , $50Hz$ ac supply connected to the circuit with Resistance $R$ and inductance $L$
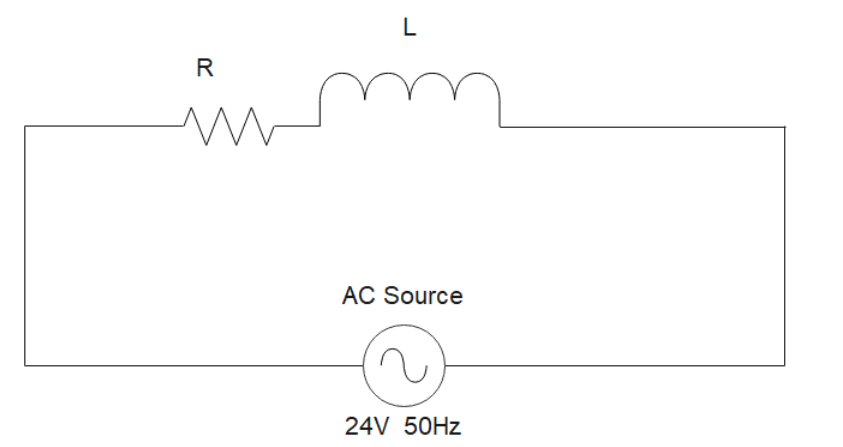
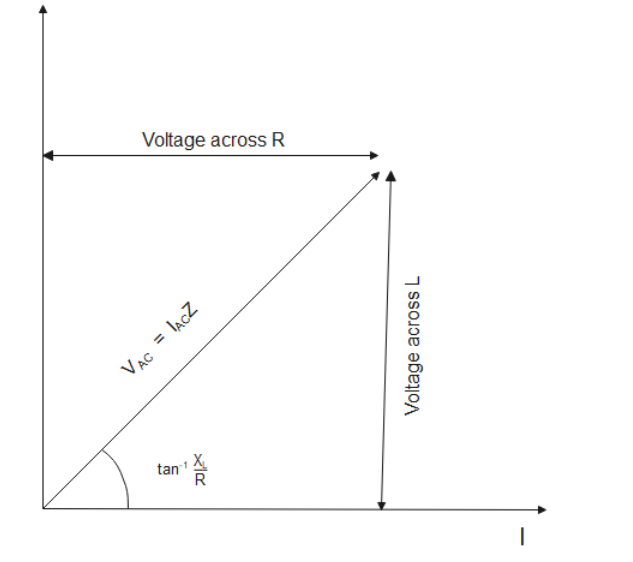
Now, we find circuit impedance using the formula ${Z^2} = {R^2} + {X_L}^2$ where $Z$ is the impedance, $R$ is the resistance and ${X_L}$ is the inductive reactance.
$ \Rightarrow {Z^2} = {R^2} + {X_L}^2$ ---------------(i)
We know that ${X_L} = \omega L = 2\pi fL$ where $\omega $ is the angular frequency, $f$ is the frequency of the ac circuit and $L$ is the inductance
Thus, we have eq (i) as
$ \Rightarrow {Z^2} = {R^2} + {\left( {2\pi fL} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow Z = \sqrt {{R^2} + {{\left( {2\pi fL} \right)}^2}} $ ---------------(ii)
Now, for ac circuits
$ \Rightarrow {I_{AC}} = \dfrac{{{V_{AC}}}}{Z}$
Substituting from eq (ii), we get
$ \Rightarrow {I_{AC}} = \dfrac{{{V_{AC}}}}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {{\left( {2\pi fL} \right)}^2}} }}$
Inserting values from the question, we get
$ \Rightarrow 0.8 = \dfrac{{24}}{{\sqrt {{8^2} + {{\left( {2\pi \times 50 \times L} \right)}^2}} }}$
Squaring both the sides and rearranging, we get
$\Rightarrow {8^2} + {\left( {2\pi \times 50 \times L} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {24} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {0.8} \right)}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {2\pi \times 50 \times L} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {24} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {0.8} \right)}^2}}} - {8^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {2\pi \times 50 \times L} \right)^2} = 836 \\
\Rightarrow 2\pi \times 50 \times L = \sqrt {836} \\
\Rightarrow L = \dfrac{{\sqrt {836} }}{{100\pi }} \\ $
$\therefore L = 0.9\,H$
Therefore, the resistance of the coil is $8\Omega $ and inductance is $0.9H$.
Note:Here, $H$ is the unit of inductance called Henry. Students should be careful not to mix up ${X_L}$ and$L$ . The first one of them is inductive reactance, whereas the second one is inductance. Mixing up the two will result in the wrong answer.
Formulae used:
\[{I_{DC}} = \dfrac{{{V_{DC}}}}{R}\]
where ${I_{DC}}$ is the current in the circuit, ${V_{DC}}$ is the voltage and $R$ is the resistance of the coil.
${Z^2} = {R^2} + {X_L}^2$
where $Z$ is the impedance, $R$ is the resistance and ${X_L}$ is the inductive reactance.
${X_L} = \omega L = 2\pi fL$
where $\omega $ is the angular frequency, $f$ is the frequency of the ac circuit and $L$ is the inductance.
Complete step by step answer:
As we are considering inductance $L$ and resistance $R$ of the same coil, it becomes a series $LR$ circuit. Now we have two cases-
(a) $24V$ dc supply connected. Inductance does not play any role in dc source. Thus, the circuit has resistance $R$

Now, the current in the coil is given by
\[{I_{DC}} = \dfrac{{{V_{DC}}}}{R}\]
where ${I_{DC}}$ is the current in the circuit, ${V_{DC}}$ is the voltage and $R$ is the resistance of the coil.
Inserting given values we get
\[\Rightarrow 3 = \dfrac{{24}}{R} \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{24}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow R = 8\Omega \\ \]
(b) $24V$ , $50Hz$ ac supply connected to the circuit with Resistance $R$ and inductance $L$


Now, we find circuit impedance using the formula ${Z^2} = {R^2} + {X_L}^2$ where $Z$ is the impedance, $R$ is the resistance and ${X_L}$ is the inductive reactance.
$ \Rightarrow {Z^2} = {R^2} + {X_L}^2$ ---------------(i)
We know that ${X_L} = \omega L = 2\pi fL$ where $\omega $ is the angular frequency, $f$ is the frequency of the ac circuit and $L$ is the inductance
Thus, we have eq (i) as
$ \Rightarrow {Z^2} = {R^2} + {\left( {2\pi fL} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow Z = \sqrt {{R^2} + {{\left( {2\pi fL} \right)}^2}} $ ---------------(ii)
Now, for ac circuits
$ \Rightarrow {I_{AC}} = \dfrac{{{V_{AC}}}}{Z}$
Substituting from eq (ii), we get
$ \Rightarrow {I_{AC}} = \dfrac{{{V_{AC}}}}{{\sqrt {{R^2} + {{\left( {2\pi fL} \right)}^2}} }}$
Inserting values from the question, we get
$ \Rightarrow 0.8 = \dfrac{{24}}{{\sqrt {{8^2} + {{\left( {2\pi \times 50 \times L} \right)}^2}} }}$
Squaring both the sides and rearranging, we get
$\Rightarrow {8^2} + {\left( {2\pi \times 50 \times L} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {24} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {0.8} \right)}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {2\pi \times 50 \times L} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {24} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {0.8} \right)}^2}}} - {8^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {2\pi \times 50 \times L} \right)^2} = 836 \\
\Rightarrow 2\pi \times 50 \times L = \sqrt {836} \\
\Rightarrow L = \dfrac{{\sqrt {836} }}{{100\pi }} \\ $
$\therefore L = 0.9\,H$
Therefore, the resistance of the coil is $8\Omega $ and inductance is $0.9H$.
Note:Here, $H$ is the unit of inductance called Henry. Students should be careful not to mix up ${X_L}$ and$L$ . The first one of them is inductive reactance, whereas the second one is inductance. Mixing up the two will result in the wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




