
A circle touches all the four sides of a quadrilateral $ ABCD $ . Prove that $ AB + CD = BC + DA $
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: Use the property that the length of the tangents to the circle from the same point is equal in length. Then simplify the required result to get the lengths in terms of each other.
Complete step-by-step answer:
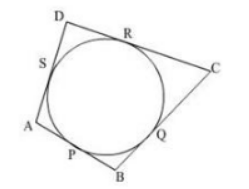
Assume that the sides of the quadrilateral $ ABCD $ touches the circles at the points $ P $ , $ Q $ , $ R $ and $ S $ .
As observed from the figure, the points $ P $ , $ Q $ , $ R $ and $ S $ are the points of tangency to the circle.
So, the lengths of the tangents originating from the same point to the circle are the same in length.
As the lines $ AP $ and $ AS $ both are tangents to the circle and both the tangents are originating from the same point $ A $ . So, they must be equal in length. Therefore, $ AP = AS $ .
Proceeding the same as above, the lines $ DS $ and $ DR $ both are tangents to the circle and both the tangents are originating from the same point $ D $ . So, they must be equal in length. Therefore, $ DS = DR $ .
Proceeding in the similar manner, we get $ BP = BQ $ and also $ CR = CQ $ .
Now simplify the left hand side of the equation $ AB + CD = BC + DA $ .
$
AB + CD = \left( {AP + PB} \right) + \left( {CR + RD} \right) \\
= \left( {AS + BQ} \right) + \left( {CQ + SD} \right) \\
= \left( {AS + SD} \right) + \left( {BQ + QC} \right) \\
= AD + BC \;
$
Hence, the result $ AB + CD = BC + DA $ is true for the given question.
So, the correct answer is “ $ AB + CD = BC + DA $ ”.
Note: Use the property of tangents that the tangents from the same point to the circle are always equal in length. Use the equalities wisely and combine it to get the required result not something else
Complete step-by-step answer:

Assume that the sides of the quadrilateral $ ABCD $ touches the circles at the points $ P $ , $ Q $ , $ R $ and $ S $ .
As observed from the figure, the points $ P $ , $ Q $ , $ R $ and $ S $ are the points of tangency to the circle.
So, the lengths of the tangents originating from the same point to the circle are the same in length.
As the lines $ AP $ and $ AS $ both are tangents to the circle and both the tangents are originating from the same point $ A $ . So, they must be equal in length. Therefore, $ AP = AS $ .
Proceeding the same as above, the lines $ DS $ and $ DR $ both are tangents to the circle and both the tangents are originating from the same point $ D $ . So, they must be equal in length. Therefore, $ DS = DR $ .
Proceeding in the similar manner, we get $ BP = BQ $ and also $ CR = CQ $ .
Now simplify the left hand side of the equation $ AB + CD = BC + DA $ .
$
AB + CD = \left( {AP + PB} \right) + \left( {CR + RD} \right) \\
= \left( {AS + BQ} \right) + \left( {CQ + SD} \right) \\
= \left( {AS + SD} \right) + \left( {BQ + QC} \right) \\
= AD + BC \;
$
Hence, the result $ AB + CD = BC + DA $ is true for the given question.
So, the correct answer is “ $ AB + CD = BC + DA $ ”.
Note: Use the property of tangents that the tangents from the same point to the circle are always equal in length. Use the equalities wisely and combine it to get the required result not something else
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




