
A circle is inscribed in a triangle with sides 9, 12 and 15. The radius of the circle is
Answer
623.7k+ views
Hint: To find the radius of the incircle, first find the area of the triangle using the formula, $\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{height}$
Here we have to find the radius of a circle inscribed in a triangle of sides 9, 12, 15.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The sides of the triangle given in the question are 9, 12, 15.
Let AB = 9, BC = 12, CA = 15.
Now we will check whether the given triangle is a right angled triangle. For this we will use Pythagoras theorem.
$A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{9}^{2}}+{{12}^{2}}={{15}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 81+144=225 \\
& \Rightarrow 225=225 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we can see that the given triangle satisfies Pythagoras theorem, so the given triangle is a right angled triangle. So, the corresponding diagram will be,
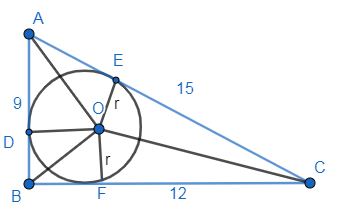
So, let the circle inscribed in the triangle ABC have the radius as ‘r’ and ‘O’ be the centre of the circle.
WE can see from the figure that the radius of the inscribed circle is perpendicular to the corresponding sides, so OD, OF, OE are perpendicular to AB, BC and AC respectively.
Now from figure, we can also say that
Area of triangle ABC = Area of triangle AOB + Area of triangle BOC + Area of triangle COA
Now we know the area of the triangle = ½ times base times height. So we can write it as,
$\begin{align}
& \Delta ABC=\Delta AOB+\Delta BOC+\Delta COA \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\times AB\times BC=\dfrac{1}{2}\times OD\times AB+\dfrac{1}{2}\times OF\times BC+\dfrac{1}{2}\times OE\times AC \\
\end{align}$
Substituting values from the above figure, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\times 9\times 12=\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 9+\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 12+\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 15$
Cancelling the like terms, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 108=9r+12r+15r \\
& \Rightarrow 108=36r \\
& \Rightarrow r=\dfrac{108}{36}=3 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the radius of the inscribed circle is 3.
Note: Another approach for this problem is using the formula,
$\text{radius}=\left( \dfrac{a+b-c}{2} \right)$
Here a and b are the sides and c is the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle.
This is used when the circle is inscribed in a right angled triangle.
Here we have to find the radius of a circle inscribed in a triangle of sides 9, 12, 15.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The sides of the triangle given in the question are 9, 12, 15.
Let AB = 9, BC = 12, CA = 15.
Now we will check whether the given triangle is a right angled triangle. For this we will use Pythagoras theorem.
$A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{9}^{2}}+{{12}^{2}}={{15}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 81+144=225 \\
& \Rightarrow 225=225 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we can see that the given triangle satisfies Pythagoras theorem, so the given triangle is a right angled triangle. So, the corresponding diagram will be,

So, let the circle inscribed in the triangle ABC have the radius as ‘r’ and ‘O’ be the centre of the circle.
WE can see from the figure that the radius of the inscribed circle is perpendicular to the corresponding sides, so OD, OF, OE are perpendicular to AB, BC and AC respectively.
Now from figure, we can also say that
Area of triangle ABC = Area of triangle AOB + Area of triangle BOC + Area of triangle COA
Now we know the area of the triangle = ½ times base times height. So we can write it as,
$\begin{align}
& \Delta ABC=\Delta AOB+\Delta BOC+\Delta COA \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\times AB\times BC=\dfrac{1}{2}\times OD\times AB+\dfrac{1}{2}\times OF\times BC+\dfrac{1}{2}\times OE\times AC \\
\end{align}$
Substituting values from the above figure, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\times 9\times 12=\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 9+\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 12+\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 15$
Cancelling the like terms, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 108=9r+12r+15r \\
& \Rightarrow 108=36r \\
& \Rightarrow r=\dfrac{108}{36}=3 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the radius of the inscribed circle is 3.
Note: Another approach for this problem is using the formula,
$\text{radius}=\left( \dfrac{a+b-c}{2} \right)$
Here a and b are the sides and c is the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle.
This is used when the circle is inscribed in a right angled triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




