
A chord of a circle subtends an angle of $\theta $ at the center of the circle. The area of the minor segment cut off by the chord is one eighth of the area of the circle. Prove that
$8\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} + \pi = \dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{45}}$
Answer
614.1k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the problem first find the relation by the help of a problem statement. Here the area of the minor segment cut off by the chord will be given by subtracting the area of the triangle from the area of the sector. Use the basic formula for area of sector and triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In order to solve the problem let us use the following figure.
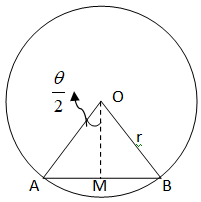
Let the radius of the given circle = r
Area of the circle $ = \pi {r^2}$
AB is a chord, OA, OB are joined with $OM \bot AB$ . This OM bisects AB as well as $\angle AOB$
So we have:
$
\angle AOM = \angle MOB = \dfrac{{\angle AOB}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\theta \\
AB = 2AM \\
$
Now let us find the value of $\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}\& \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}$ from the triangles in order to substitute in the given problem statement.
In $\Delta AOM,\angle AMO = {90^0}$
$
\because \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{{AM}}{{AD}} \\
\Rightarrow AM = AD\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} = r\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
\because \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{{OM}}{{AD}} \\
\Rightarrow OM = AD\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = r\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
\because AB = 2AM \\
\Rightarrow AB = 2r\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
$
Now let us find out the area of the segment cut off by the chord AB.
Area of the segment cut off by the chord AB = Area of the sector – Area of the triangle
$
= \dfrac{\theta }{{{{360}^0}}} \times \pi {r^2} - \dfrac{1}{2} \times AB \times OM \\
= \dfrac{\theta }{{{{360}^0}}} \times \pi {r^2} - \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2r\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times r\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
= {r^2}\left[ {\dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{360}^0}}} - \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right] \\
$
Also we have the relation between the area of the segment and the area of the circle given in the problem.
According to the problem
Area of the segment cut off by the chord AB = $\dfrac{1}{8} \times$ Area of the circle
Substituting the area of the segment found above and the area of the circle we get:
$ \Rightarrow {r^2}\left[ {\dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{360}^0}}} - \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right] = \dfrac{1}{8} \times \pi {r^2}$
Now let us simplify the equation to prove the result
$
\Rightarrow \left[ {\dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{360}^0}}} - \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right] = \dfrac{1}{8} \times \pi \\
\Rightarrow 8 \times \dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{360}^0}}} - 8 \times \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \pi \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{45}^0}}} - 8 \times \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \pi \\
\Rightarrow 8 \times \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} + \pi = \dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{45}^0}}} \\
$
Hence, the given result is proved.
Note: A circular segment is a region of a circle which is "cut off" from the rest of the circle by a secant or a chord. More formally, a circular segment is a region of two-dimensional space that is bounded by an arc of a circle and by the chord connecting the endpoints of the arc. A circular sector of circle sector, is the portion of a disk enclosed by two radii and an arc, where the smaller area is known as the minor sector and the larger being the major sector.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In order to solve the problem let us use the following figure.

Let the radius of the given circle = r
Area of the circle $ = \pi {r^2}$
AB is a chord, OA, OB are joined with $OM \bot AB$ . This OM bisects AB as well as $\angle AOB$
So we have:
$
\angle AOM = \angle MOB = \dfrac{{\angle AOB}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\theta \\
AB = 2AM \\
$
Now let us find the value of $\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}\& \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}$ from the triangles in order to substitute in the given problem statement.
In $\Delta AOM,\angle AMO = {90^0}$
$
\because \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{{AM}}{{AD}} \\
\Rightarrow AM = AD\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} = r\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
\because \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{{OM}}{{AD}} \\
\Rightarrow OM = AD\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = r\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
\because AB = 2AM \\
\Rightarrow AB = 2r\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
$
Now let us find out the area of the segment cut off by the chord AB.
Area of the segment cut off by the chord AB = Area of the sector – Area of the triangle
$
= \dfrac{\theta }{{{{360}^0}}} \times \pi {r^2} - \dfrac{1}{2} \times AB \times OM \\
= \dfrac{\theta }{{{{360}^0}}} \times \pi {r^2} - \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2r\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times r\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
= {r^2}\left[ {\dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{360}^0}}} - \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right] \\
$
Also we have the relation between the area of the segment and the area of the circle given in the problem.
According to the problem
Area of the segment cut off by the chord AB = $\dfrac{1}{8} \times$ Area of the circle
Substituting the area of the segment found above and the area of the circle we get:
$ \Rightarrow {r^2}\left[ {\dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{360}^0}}} - \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right] = \dfrac{1}{8} \times \pi {r^2}$
Now let us simplify the equation to prove the result
$
\Rightarrow \left[ {\dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{360}^0}}} - \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right] = \dfrac{1}{8} \times \pi \\
\Rightarrow 8 \times \dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{360}^0}}} - 8 \times \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \pi \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{45}^0}}} - 8 \times \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \pi \\
\Rightarrow 8 \times \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} + \pi = \dfrac{{\pi \theta }}{{{{45}^0}}} \\
$
Hence, the given result is proved.
Note: A circular segment is a region of a circle which is "cut off" from the rest of the circle by a secant or a chord. More formally, a circular segment is a region of two-dimensional space that is bounded by an arc of a circle and by the chord connecting the endpoints of the arc. A circular sector of circle sector, is the portion of a disk enclosed by two radii and an arc, where the smaller area is known as the minor sector and the larger being the major sector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




