
A change of 200mV in base-emitter voltage causes a change of 100μA in the base current. The input resistance of the transistor is
A. $2K\Omega $
B. $2\Omega $
C. $2m\Omega $
D. $10K\Omega $
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Firstly try to recall the working of a transistor. In order to find the input resistance, you should know which voltage and current is considered under input characteristics. Then, simply by taking their ratio gives you one of the important ac parameters of the transistor that is the input resistance.
Formula used: Expression for input resistance of a transistor,
${{r}_{i}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{BE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}} \right)}_{{{V}_{CE}}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Before going directly into the question let us first discuss a bit about transistors and its characteristics for better understanding of the concept dealt here.
A transistor consists of 3 terminals- emitter (E), base (B) and collector (C). The input and output connections are made by any one of these terminals made as common. Three configurations are: common emitter, common base and common collector. Since CE configuration n-p-n transistors are widely used let us use the same here for explanation.
CE transistor characteristics:
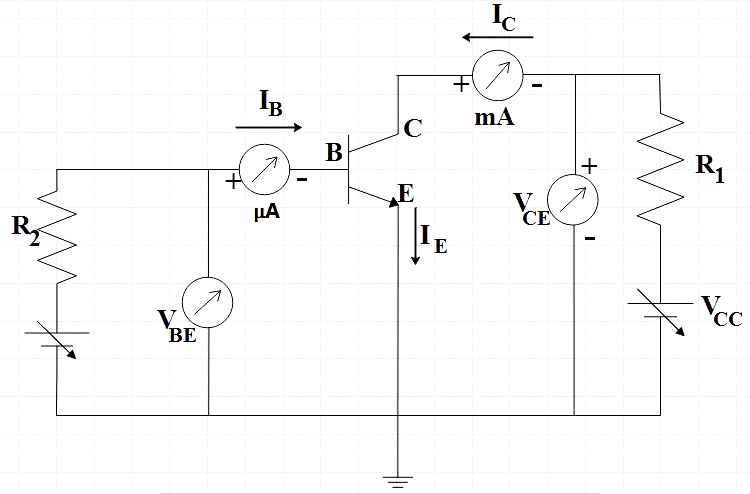
The input here is between the base and the emitter and the output is placed in between collector and the emitter. Input characteristics is the variation of base current ${{I}_{B}}$ with base-emitter voltage ${{V}_{BE}}$, similarly, the output characteristics is the variation of collector current ${{I}_{C}}$ with collector-emitter voltage ${{V}_{CE}}$. We should note here that output characteristics are influenced by the input characteristics, that is, collector current changes with the base current. When we are studying the input characteristics, voltage ${{V}_{CE}}$ is kept constant. Somewhere in the range of 3V to 20V we obtain the input characteristics.
We use the linear segments of both input and output characteristics to calculate some of the important ac parameters of transistors like – input resistance $\left( {{r}_{i}} \right)$, output resistance $\left( {{r}_{o}} \right)$ and current amplification factor $\left( \beta \right)$.
Since, we are asked to find the input resistance in the given question, let us focus on that.
Input resistance is the ratio of change in base-emitter voltage $\left( \Delta {{V}_{BE}} \right)$ to the resulting change in base current $\left( {{I}_{B}} \right)$ at constant ${{V}_{CE}}$. It may have values ranging from a few hundreds to a few thousand ohms.
Input resistance ${{r}_{i}}$ is given by,
${{r}_{i}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{BE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}} \right)}_{{{V}_{CE}}}}$ …………………………….. (1)
From the given question,
$\Delta {{V}_{BE}}=200mV$
$\Delta {{I}_{B}}=100\mu A$
Therefore (1) becomes,
${{r}_{i}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{BE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}} \right)}_{{{V}_{CE}}}}=\dfrac{200\times {{10}^{-3}}}{100\times {{10}^{-6}}}=2\times {{10}^{3}}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {{r}_{i}}=2k\Omega $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We are supposed to obtain the input characteristic with the transistor in the active state. So we keep the collector emitter voltage really high so that the base collector junction is reverse-biased. Also, determining only one input characteristic is actually enough since input characteristics for various values of ${{V}_{CE}}$ will give almost identical curves.
Formula used: Expression for input resistance of a transistor,
${{r}_{i}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{BE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}} \right)}_{{{V}_{CE}}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Before going directly into the question let us first discuss a bit about transistors and its characteristics for better understanding of the concept dealt here.
A transistor consists of 3 terminals- emitter (E), base (B) and collector (C). The input and output connections are made by any one of these terminals made as common. Three configurations are: common emitter, common base and common collector. Since CE configuration n-p-n transistors are widely used let us use the same here for explanation.
CE transistor characteristics:

The input here is between the base and the emitter and the output is placed in between collector and the emitter. Input characteristics is the variation of base current ${{I}_{B}}$ with base-emitter voltage ${{V}_{BE}}$, similarly, the output characteristics is the variation of collector current ${{I}_{C}}$ with collector-emitter voltage ${{V}_{CE}}$. We should note here that output characteristics are influenced by the input characteristics, that is, collector current changes with the base current. When we are studying the input characteristics, voltage ${{V}_{CE}}$ is kept constant. Somewhere in the range of 3V to 20V we obtain the input characteristics.
We use the linear segments of both input and output characteristics to calculate some of the important ac parameters of transistors like – input resistance $\left( {{r}_{i}} \right)$, output resistance $\left( {{r}_{o}} \right)$ and current amplification factor $\left( \beta \right)$.
Since, we are asked to find the input resistance in the given question, let us focus on that.
Input resistance is the ratio of change in base-emitter voltage $\left( \Delta {{V}_{BE}} \right)$ to the resulting change in base current $\left( {{I}_{B}} \right)$ at constant ${{V}_{CE}}$. It may have values ranging from a few hundreds to a few thousand ohms.
Input resistance ${{r}_{i}}$ is given by,
${{r}_{i}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{BE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}} \right)}_{{{V}_{CE}}}}$ …………………………….. (1)
From the given question,
$\Delta {{V}_{BE}}=200mV$
$\Delta {{I}_{B}}=100\mu A$
Therefore (1) becomes,
${{r}_{i}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{BE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}} \right)}_{{{V}_{CE}}}}=\dfrac{200\times {{10}^{-3}}}{100\times {{10}^{-6}}}=2\times {{10}^{3}}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {{r}_{i}}=2k\Omega $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We are supposed to obtain the input characteristic with the transistor in the active state. So we keep the collector emitter voltage really high so that the base collector junction is reverse-biased. Also, determining only one input characteristic is actually enough since input characteristics for various values of ${{V}_{CE}}$ will give almost identical curves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




