
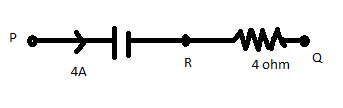
A cell has terminal voltage $2V$ in open circuit and internal resistance of the given cell is $2\Omega $. If $4A$ of current is flowing between points $P$ and $Q$ in the circuit and then the potential difference between $P$ and $Q$ is
A. $22V$
B. $24V$
C. $30V$
D. $26V$

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint:
Here we have to find the potential difference between the batteries in each terminal and compare them to find the potential difference between $P$ and $Q$.
First let us see what potential difference is-
The potential difference is the difference between two points in a circuit in the amount of energy that the charge carriers have.
Terminal potential difference- Terminal potential difference is usually found in cells or batteries.
The potential difference in a closed circuit between the two poles of a cell is called the cell’s terminal potential difference. When we measure the battery’s emf as we evaluate the potential difference between the terminals of a battery that is not a full circuit. This is the overall amount of work the battery can do to push charge from one terminal through the circuit to the other terminal per coulomb of charge.
Terminal voltage is mathematically represented by-
$V = emf - Ir$
where $emf$ is the electromotive force,
$I$ is the current flowing, and
$r$ is the resistance.
Complete step by step solution-
Given,
A cell has terminal voltage $2V$ in open circuit and internal resistance of the given cell is $2\Omega $
$4A$ of current is flowing between points $P$ and $Q$ in the circuit
$
E = 2V \\
I = 4A \\
r = 4\Omega \\
$
The potential difference between $P$ and $Q$ =?
Case 1
Terminal potential difference
$ = {V_P} - {V_R} = E + Ir = 2 + (4 \times 2) = 10V$
...... (1)
Case 2
Terminal potential difference
$ = {V_R} - {V_Q} = Ir = 4 \times 4 = 16V$
...... (2)
From equation (1) and (2), we get-
$
{V_P} - {V_R} + {V_R} - {V_Q} \\
= 10 + 16 \\
{V_P} - {V_Q} = 26V \\
$
Hence, the potential difference between $P$ and $Q$ is $26V$
Note:
Here as we can see from case (2) we have not added any emf with the second equation. It is because there is no induced emf in the terminal between $R$ and $Q$.
Here we have to find the potential difference between the batteries in each terminal and compare them to find the potential difference between $P$ and $Q$.
First let us see what potential difference is-
The potential difference is the difference between two points in a circuit in the amount of energy that the charge carriers have.
Terminal potential difference- Terminal potential difference is usually found in cells or batteries.
The potential difference in a closed circuit between the two poles of a cell is called the cell’s terminal potential difference. When we measure the battery’s emf as we evaluate the potential difference between the terminals of a battery that is not a full circuit. This is the overall amount of work the battery can do to push charge from one terminal through the circuit to the other terminal per coulomb of charge.
Terminal voltage is mathematically represented by-
$V = emf - Ir$
where $emf$ is the electromotive force,
$I$ is the current flowing, and
$r$ is the resistance.
Complete step by step solution-
Given,
A cell has terminal voltage $2V$ in open circuit and internal resistance of the given cell is $2\Omega $
$4A$ of current is flowing between points $P$ and $Q$ in the circuit
$
E = 2V \\
I = 4A \\
r = 4\Omega \\
$
The potential difference between $P$ and $Q$ =?
Case 1
Terminal potential difference
$ = {V_P} - {V_R} = E + Ir = 2 + (4 \times 2) = 10V$
...... (1)
Case 2
Terminal potential difference
$ = {V_R} - {V_Q} = Ir = 4 \times 4 = 16V$
...... (2)
From equation (1) and (2), we get-
$
{V_P} - {V_R} + {V_R} - {V_Q} \\
= 10 + 16 \\
{V_P} - {V_Q} = 26V \\
$
Hence, the potential difference between $P$ and $Q$ is $26V$
Note:
Here as we can see from case (2) we have not added any emf with the second equation. It is because there is no induced emf in the terminal between $R$ and $Q$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




