
A catalyst increases the rate by:
A) Decreasing \[{{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}\]
B) Increasing \[{{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}\]
C) Decreasing pressure
D) Increasing entropy
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: Catalyst alters the rate of a reaction without changing the reaction products. It increases the rate of reaction by providing an alternate pathway so that the reactant molecules collide with enough energy to cross the energy barrier.
Complete step by step answer:
All molecules which undergo the reaction possess a minimum amount of energy. This energy is either kinetic energy or potential energy. When the reacting molecules collide the kinetic energy of the reactant can be used to stretch, bend, or ultimately break the bond. This leads to a chemical reaction. If reactant molecules collide with the improper orientation they do not react. However, when the reactant collides with proper orientation the reaction occurs.
Thus the minimum amount of energy required for the chemical reaction to occur is called activation energy. It is represented by${{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}$.
Let's plot a graph of Gibbs's free energy against the reaction coordinate. The plot is as shown below,
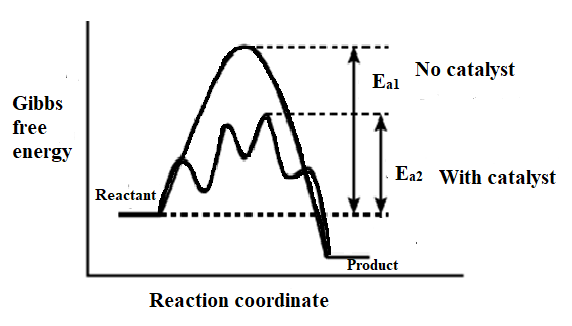
Now, let's comment on the path followed by the reaction when no catalyst was added. Here, the energy difference between the reactant and that of the transition state is known as the activation energy. Let’s consider the activation energy${{\text{E}}_{\text{a1}}}$.
- Catalyst is a substance which alters the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change in chemical composition or mass during the reaction.
- When the catalyst is introduced into the reaction, it accelerates the rate of reaction. Catalyst provides the alternate path for the progress of a reaction. The path taken by the reactants requires less amount of activation energy than that of the original path. They alter the mechanism of the reaction. This changes the nature and energy of the transition state.
- Let's have a look at the plot of Gibbs's energy against the reaction progress. The reaction requires less energy with a catalyst. A catalyst participates in various chemical transformations. It provides the surface for the reactants to react. The catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state since lower the transition energy lower is the activation energy.
- The figure indicates that the catalyst helps to lower down the energy barrier and hence the minimum amount of energy is sufficient for the maximum collisions of reactant. This increases the rate of reaction.
The rate of reaction and activation energy are related as,
$\text{k=A}{{\text{e}}^{\text{-}\frac{{{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}}{\text{RT}}}}$
This is called an Arrhenius equation.
K is the rate constant
${{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}$is the activation energy
R is the gas constant
T is the temperature in Kelvin
A is an Arrhenius factor
Thus we know that catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy. In other words, catalyst lowers the energy barrier for easy progress of a reaction.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Additional information:
1) Precatalyst: Precatalyst converts into the catalyst in the reaction. For example, Wilkinson's catalyst \[\text{RhCl(PP}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}~\]loses triphenylphosphine ligand and converts into a catalyst.
2) Some catalysts reduce the rate of reaction. This is called a negative catalyst or inhibitors. Inhibitors decrease the rate of reaction by increasing the activation energy for the reaction. The reaction does not proceed through the non-catalysed path. Instead of that, the inhibitors remove the reaction intermediate produced.
3) Co-catalyst or promoters: They work opposite to the inhibitor. Promoters increase the catalytic activity of the catalyst. They do not act as a catalyst.
Note: We notice that the energies of reactants and products are the same for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reaction. Therefore the overall energy$\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{H}}_{\text{rxn}}}$ released during the progress of the reaction does not change. This says that the rate of reaction is not directly related to the thermodynamics of reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
All molecules which undergo the reaction possess a minimum amount of energy. This energy is either kinetic energy or potential energy. When the reacting molecules collide the kinetic energy of the reactant can be used to stretch, bend, or ultimately break the bond. This leads to a chemical reaction. If reactant molecules collide with the improper orientation they do not react. However, when the reactant collides with proper orientation the reaction occurs.
Thus the minimum amount of energy required for the chemical reaction to occur is called activation energy. It is represented by${{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}$.
Let's plot a graph of Gibbs's free energy against the reaction coordinate. The plot is as shown below,

Now, let's comment on the path followed by the reaction when no catalyst was added. Here, the energy difference between the reactant and that of the transition state is known as the activation energy. Let’s consider the activation energy${{\text{E}}_{\text{a1}}}$.
- Catalyst is a substance which alters the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change in chemical composition or mass during the reaction.
- When the catalyst is introduced into the reaction, it accelerates the rate of reaction. Catalyst provides the alternate path for the progress of a reaction. The path taken by the reactants requires less amount of activation energy than that of the original path. They alter the mechanism of the reaction. This changes the nature and energy of the transition state.
- Let's have a look at the plot of Gibbs's energy against the reaction progress. The reaction requires less energy with a catalyst. A catalyst participates in various chemical transformations. It provides the surface for the reactants to react. The catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state since lower the transition energy lower is the activation energy.
- The figure indicates that the catalyst helps to lower down the energy barrier and hence the minimum amount of energy is sufficient for the maximum collisions of reactant. This increases the rate of reaction.
The rate of reaction and activation energy are related as,
$\text{k=A}{{\text{e}}^{\text{-}\frac{{{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}}{\text{RT}}}}$
This is called an Arrhenius equation.
K is the rate constant
${{\text{E}}_{\text{a}}}$is the activation energy
R is the gas constant
T is the temperature in Kelvin
A is an Arrhenius factor
Thus we know that catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy. In other words, catalyst lowers the energy barrier for easy progress of a reaction.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Additional information:
1) Precatalyst: Precatalyst converts into the catalyst in the reaction. For example, Wilkinson's catalyst \[\text{RhCl(PP}{{\text{h}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}~\]loses triphenylphosphine ligand and converts into a catalyst.
2) Some catalysts reduce the rate of reaction. This is called a negative catalyst or inhibitors. Inhibitors decrease the rate of reaction by increasing the activation energy for the reaction. The reaction does not proceed through the non-catalysed path. Instead of that, the inhibitors remove the reaction intermediate produced.
3) Co-catalyst or promoters: They work opposite to the inhibitor. Promoters increase the catalytic activity of the catalyst. They do not act as a catalyst.
Note: We notice that the energies of reactants and products are the same for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reaction. Therefore the overall energy$\text{ }\!\!\Delta\!\!\text{ }{{\text{H}}_{\text{rxn}}}$ released during the progress of the reaction does not change. This says that the rate of reaction is not directly related to the thermodynamics of reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




