
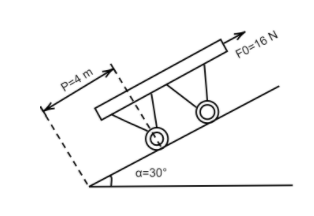
A cart having $4$ wheels is drawn with a constant force ${{F}_{0}}=16\text{ N}$ up an inclined plane, making an angle $\alpha =30{}^\circ $ with the horizontal. The platform of the cart weighs ${{W}_{0}}=18\text{ N}$ and each of its uniform wheels (cylindrical) weighs $W=2\text{ N}$. If the initial velocity is zero, the linear velocity ${{v}_{1}}$ (in $m{{s}^{-1}}$) of the cart when it has travelled a distance of $P=4\text{ m}$ is:
(Given: The wheels roll without slipping and neglect rolling friction)
A. $1.4$
B. $2.8$
C. $9.8$
D. $4.2$

Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will use the work energy equation. The work done on the system by the force as given in the question makes the cart move up the inclined plane. Work and energy of the system remain conserved if any non-conservative forces do not act on the system. In this case there is no conservative force work done will get converted into some other form to do the required work.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The work done by given force ${{F}_{0}}$ will go away in giving a kinetic energy to the cart and pulling it up by a distance of $P=4\text{ m}$. The kinetic energy of the system i.e., the kinetic energy of the cart and the four wheels that constitute the system will be as follows:
$\begin{align}
& E={{E}_{platform}}+4{{E}_{wheel}} \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{platform}}{{v}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{platform}}{{v}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{{{m}_{wheel}}{{R}^{2}}}{2}\times \dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{{{R}^{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{platform}}{{v}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{4}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{platform}}{{v}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{3}{4}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{{{W}_{0}}}{g}\times {{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{3W}{g}\times {{v}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2g}\left( {{W}_{0}}+6W \right){{v}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Work done in pulling the cart up by a distance of $P=4\text{ m}$ will be:
$W'=\left( {{W}_{0}}+W \right)\left( P\sin \alpha \right)$
Now, we will add the two values that we received, i.e., the value of work done in pulling the cart up by a distance of $P=4\text{ m}$ and the kinetic energy imparted to the system by the force applied on the body. On writing the work energy equation, we get the following equation:
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{0}}\times P=\dfrac{1}{2g}\left( {{W}_{0}}+6W \right){{v}^{2}}+\left( {{W}_{0}}+4W \right)\left( P\sin \alpha \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2g}\left( {{W}_{0}}+6W \right){{v}^{2}}=\left[ {{F}_{0}}-\left( {{W}_{0}}+4W \right)\sin \alpha \right]P \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{2gP\left[ {{F}_{0}}-\left( {{W}_{0}}+4W \right)\sin \alpha \right]}{\left( {{W}_{0}}+6W \right)}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{2\times 9.8\times 4\left[ 16-\left( 18+4\times 2 \right)\sin 30{}^\circ \right]}{\left( 18+6\times 2 \right)}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{78.4\left[ 16-13 \right]}{30}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{78.4\times 3}{30}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{235.2}{30}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{7.84} \\
& \therefore v=2.8\text{ m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We have taken the value of moment of inertia in the solution as $I=\dfrac{m{{R}^{2}}}{2}$ because the wheels are given to be in cylindrical shape. Also, the kinetic energy of one wheel will be multiplied by $4$ to calculate the kinetic energies of all the four wheels that are attached to the cart.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The work done by given force ${{F}_{0}}$ will go away in giving a kinetic energy to the cart and pulling it up by a distance of $P=4\text{ m}$. The kinetic energy of the system i.e., the kinetic energy of the cart and the four wheels that constitute the system will be as follows:
$\begin{align}
& E={{E}_{platform}}+4{{E}_{wheel}} \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{platform}}{{v}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{platform}}{{v}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{{{m}_{wheel}}{{R}^{2}}}{2}\times \dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{{{R}^{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{platform}}{{v}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{4}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{platform}}{{v}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{3}{4}{{m}_{wheel}}{{v}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{{{W}_{0}}}{g}\times {{v}^{2}}+\dfrac{3W}{g}\times {{v}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{2g}\left( {{W}_{0}}+6W \right){{v}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Work done in pulling the cart up by a distance of $P=4\text{ m}$ will be:
$W'=\left( {{W}_{0}}+W \right)\left( P\sin \alpha \right)$
Now, we will add the two values that we received, i.e., the value of work done in pulling the cart up by a distance of $P=4\text{ m}$ and the kinetic energy imparted to the system by the force applied on the body. On writing the work energy equation, we get the following equation:
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{0}}\times P=\dfrac{1}{2g}\left( {{W}_{0}}+6W \right){{v}^{2}}+\left( {{W}_{0}}+4W \right)\left( P\sin \alpha \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2g}\left( {{W}_{0}}+6W \right){{v}^{2}}=\left[ {{F}_{0}}-\left( {{W}_{0}}+4W \right)\sin \alpha \right]P \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{2gP\left[ {{F}_{0}}-\left( {{W}_{0}}+4W \right)\sin \alpha \right]}{\left( {{W}_{0}}+6W \right)}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{2\times 9.8\times 4\left[ 16-\left( 18+4\times 2 \right)\sin 30{}^\circ \right]}{\left( 18+6\times 2 \right)}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{78.4\left[ 16-13 \right]}{30}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{78.4\times 3}{30}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{235.2}{30}} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\sqrt{7.84} \\
& \therefore v=2.8\text{ m}{{\text{s}}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We have taken the value of moment of inertia in the solution as $I=\dfrac{m{{R}^{2}}}{2}$ because the wheels are given to be in cylindrical shape. Also, the kinetic energy of one wheel will be multiplied by $4$ to calculate the kinetic energies of all the four wheels that are attached to the cart.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




