
A car which has front and rear glass screens almost vertical is moving on a road when raindrops are falling vertically downwards. The rain will strike;
A. The front screen only
B. The rear screen only
C. Both the screens
D. The particular screen depending upon the velocity
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: Solution of problems involving relative motion in two dimensions involves evaluation of vector equations. The evaluation or analysis of vector equations is not limited to the use of Pythagoras theorem, but significantly makes use of geometric consideration like evaluating trigonometric ratios.
Complete step-by-step solution:
When solving questions like these keep in mind the concepts regarding relative motion, and more importantly relative motion cases based on falling of rain. Keep in mind that when you are in a car and look out of the front mirror, rain always seems to fall towards you no matter what direction you drive in.
In questions like the ones we have in front of us, it is important to identify what we are trying to find, and identify all the variables we already have infront of us. We need the velocities of the object in question, velocity of rain and the velocity of rain which is relative to the object.
Let \[v\] be the speed of the car. For easy calculation and understanding we will assume that the car is travelling with a constant velocity.
Now the rain seems to be falling on the car vertically, key word, seems to be. We need to find out the actual direction of rain falling in this question.
Now assume \[v'\]to be the velocity of rain falling on car as it appears from the front screen
Now assume \[{V_{RC}}\]to be the velocity of rain with respect to the car.
Assuming the car to be moving in the right direction or moving towards east.
When we draw the diagram to depict the directions of all three velocities we get;
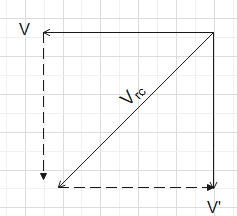
From the diagram we understand that the rain will not be hitting the back screen at all, instead all the rain will be facing the front screen only.
Hence we can conclude this question by saying that option (a) is the correct option.
Note:On occasion objects move within a medium which is moving with respect to an observer. For example if we take an airplane, it usually encounters wind which is air that is moving with respect to an observer on the ground below. Another example can be of a motorboat in a river amidst a river current.
Complete step-by-step solution:
When solving questions like these keep in mind the concepts regarding relative motion, and more importantly relative motion cases based on falling of rain. Keep in mind that when you are in a car and look out of the front mirror, rain always seems to fall towards you no matter what direction you drive in.
In questions like the ones we have in front of us, it is important to identify what we are trying to find, and identify all the variables we already have infront of us. We need the velocities of the object in question, velocity of rain and the velocity of rain which is relative to the object.
Let \[v\] be the speed of the car. For easy calculation and understanding we will assume that the car is travelling with a constant velocity.
Now the rain seems to be falling on the car vertically, key word, seems to be. We need to find out the actual direction of rain falling in this question.
Now assume \[v'\]to be the velocity of rain falling on car as it appears from the front screen
Now assume \[{V_{RC}}\]to be the velocity of rain with respect to the car.
Assuming the car to be moving in the right direction or moving towards east.
When we draw the diagram to depict the directions of all three velocities we get;

From the diagram we understand that the rain will not be hitting the back screen at all, instead all the rain will be facing the front screen only.
Hence we can conclude this question by saying that option (a) is the correct option.
Note:On occasion objects move within a medium which is moving with respect to an observer. For example if we take an airplane, it usually encounters wind which is air that is moving with respect to an observer on the ground below. Another example can be of a motorboat in a river amidst a river current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




