
A car starting from rest accelerates at the rate f through a distance s, then continues at constant speed for time t and then decelerates at the rate \[\dfrac{f}{2}\] to come to rest. If the total distance traversed is 15 s, then \[s=\]?
A. \[s=\dfrac{f{{t}^{2}}}{72}\]
B. \[s=\dfrac{f{{t}^{2}}}{4}\]
C. \[s=\dfrac{f{{t}^{2}}}{6}\]
D. \[s=\dfrac{f{{t}^{2}}}{2}\]
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: It is better to split the whole travel into three sections since the acceleration is changing in each section. With the help of kinematic equations, we can find out the distance and time taken for each period. By splitting the whole travel of the car into three sections, we can calculate distance and time for each section. Then we can combine these distances to compare it with the total distance. So, we can find the s.
Formula used:
\[s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}\], where s is the displacement, u is the initial velocity, t is the time and a is the acceleration.
\[v=u+at\], where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity and t is the time.
\[{{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as\], v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity and a is the acceleration and s is the displacement.
Complete step by step answer:
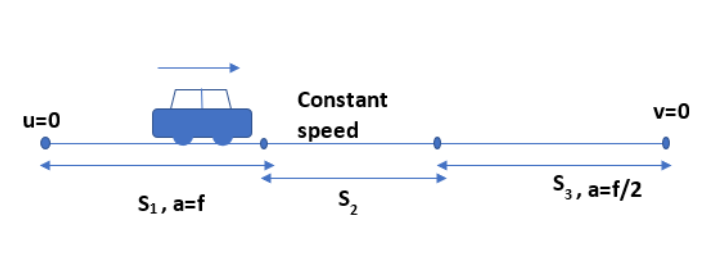
We can assume that a car starts from a point and travels with an acceleration of f. At the beginning, the initial velocity will be zero. We can assume that a car takes \[{{t}_{1}}\] time to achieve the constant speed. According to the kinematic equation,
\[s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}\], where s is the displacement, u is the initial velocity, t is the time and a is the acceleration.
\[{{s}_{1}}=0\times {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{2}f{{t}_{1}}^{2}\]
\[{{s}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}f{{t}_{1}}^{2}\]……………………………..(1)
\[v=u+at\], where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity and t is the time.
The velocity at the time \[{{t}_{1}}\] will be,
\[{{v}_{1}}=0+f{{t}_{1}}\]
\[{{v}_{1}}=f{{t}_{1}}\]………………………..(2)
After \[{{t}_{1}}\] time the car achieves constant velocity and travels for some time \[({{t}_{2}})\]. Since the velocity is the same, we can multiply the velocity \[({{v}_{1}})\] with the time \[({{t}_{2}})\] to find the distance covered within \[{{t}_{2}}\] seconds.
\[{{s}_{2}}={{v}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=f{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\]………………….(3)
If the car takes \[{{t}_{3}}\] seconds for the deceleration and finally come to rest, then the distance covered within \[{{t}_{3}}\] seconds can be found from the following formula.
\[{{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as\], v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity and a is the acceleration and s is the displacement.
In this case, the final velocity will become zero and the distance will be \[{{s}_{3}}\]. The car decelerates at a deceleration of \[-\dfrac{f}{2}\].
\[{{0}^{2}}-{{v}_{1}}^{2}=-2\dfrac{f}{2}{{s}_{3}}\]
\[{{s}_{3}}=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}^{2}}{f}\]
We can assign equation (2) into this.
\[{{s}_{3}}=\dfrac{{{(f{{t}_{1}})}^{2}}}{f}\]
\[{{s}_{3}}=f{{t}_{1}}^{2}\]…………………………(4)
According to equation (1), we can say that,
\[{{s}_{3}}=2{{s}_{1}}\]………………………(5)
In the question, \[{{s}_{1}}=s\]
Therefore, the total displacement can be written as,
\[15\text{ s = }{{\text{s}}_{1}}+{{\text{s}}_{2}}+{{\text{s}}_{3}}\]
\[15\text{ s = s}+f{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}+2\text{ s}\]
\[12\text{ s = }f{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\]…………………………(6)
We can find the time \[{{t}_{1}}\] by dividing the equation (6) with equation (1).
\[\dfrac{12\text{ s}}{\text{s}}\text{ =}\dfrac{\text{ }f{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{\dfrac{1}{2}f{{t}_{1}}^{2}}\]
\[\dfrac{{{t}_{2}}}{6}={{t}_{1}}\]…………………………….(7)
We can assign this value in the equation (1)
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}f{{\left[ \dfrac{{{t}_{2}}}{6} \right]}^{2}}\]
Since the time taken during the constant speed is t. So, we can write \[{{t}_{2}}\] as t.
\[s=\dfrac{f{{t}^{2}}}{72}\]
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note: When we are calculating distance \[{{s}_{3}}\], we should consider the deceleration as negative. Since the acceleration is negative here. If we are doing with the positive sign, then the calculation will be wrong. We can do the problem directly by choosing \[{{t}_{2}}\] as t and \[{{s}_{1}}\] as s. So you can avoid some steps and earn some time.
Formula used:
\[s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}\], where s is the displacement, u is the initial velocity, t is the time and a is the acceleration.
\[v=u+at\], where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity and t is the time.
\[{{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as\], v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity and a is the acceleration and s is the displacement.
Complete step by step answer:

We can assume that a car starts from a point and travels with an acceleration of f. At the beginning, the initial velocity will be zero. We can assume that a car takes \[{{t}_{1}}\] time to achieve the constant speed. According to the kinematic equation,
\[s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}\], where s is the displacement, u is the initial velocity, t is the time and a is the acceleration.
\[{{s}_{1}}=0\times {{t}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{2}f{{t}_{1}}^{2}\]
\[{{s}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}f{{t}_{1}}^{2}\]……………………………..(1)
\[v=u+at\], where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity and t is the time.
The velocity at the time \[{{t}_{1}}\] will be,
\[{{v}_{1}}=0+f{{t}_{1}}\]
\[{{v}_{1}}=f{{t}_{1}}\]………………………..(2)
After \[{{t}_{1}}\] time the car achieves constant velocity and travels for some time \[({{t}_{2}})\]. Since the velocity is the same, we can multiply the velocity \[({{v}_{1}})\] with the time \[({{t}_{2}})\] to find the distance covered within \[{{t}_{2}}\] seconds.
\[{{s}_{2}}={{v}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=f{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\]………………….(3)
If the car takes \[{{t}_{3}}\] seconds for the deceleration and finally come to rest, then the distance covered within \[{{t}_{3}}\] seconds can be found from the following formula.
\[{{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as\], v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity and a is the acceleration and s is the displacement.
In this case, the final velocity will become zero and the distance will be \[{{s}_{3}}\]. The car decelerates at a deceleration of \[-\dfrac{f}{2}\].
\[{{0}^{2}}-{{v}_{1}}^{2}=-2\dfrac{f}{2}{{s}_{3}}\]
\[{{s}_{3}}=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}^{2}}{f}\]
We can assign equation (2) into this.
\[{{s}_{3}}=\dfrac{{{(f{{t}_{1}})}^{2}}}{f}\]
\[{{s}_{3}}=f{{t}_{1}}^{2}\]…………………………(4)
According to equation (1), we can say that,
\[{{s}_{3}}=2{{s}_{1}}\]………………………(5)
In the question, \[{{s}_{1}}=s\]
Therefore, the total displacement can be written as,
\[15\text{ s = }{{\text{s}}_{1}}+{{\text{s}}_{2}}+{{\text{s}}_{3}}\]
\[15\text{ s = s}+f{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}+2\text{ s}\]
\[12\text{ s = }f{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\]…………………………(6)
We can find the time \[{{t}_{1}}\] by dividing the equation (6) with equation (1).
\[\dfrac{12\text{ s}}{\text{s}}\text{ =}\dfrac{\text{ }f{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{\dfrac{1}{2}f{{t}_{1}}^{2}}\]
\[\dfrac{{{t}_{2}}}{6}={{t}_{1}}\]…………………………….(7)
We can assign this value in the equation (1)
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}f{{\left[ \dfrac{{{t}_{2}}}{6} \right]}^{2}}\]
Since the time taken during the constant speed is t. So, we can write \[{{t}_{2}}\] as t.
\[s=\dfrac{f{{t}^{2}}}{72}\]
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note: When we are calculating distance \[{{s}_{3}}\], we should consider the deceleration as negative. Since the acceleration is negative here. If we are doing with the positive sign, then the calculation will be wrong. We can do the problem directly by choosing \[{{t}_{2}}\] as t and \[{{s}_{1}}\] as s. So you can avoid some steps and earn some time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




