
A car is moving on a road and rain is falling vertically. Select the correct option.
A. The rain will strike the back screen only
B. The rain will strike the front screen only
C. The rain will strike both the screens
D. The rain will not strike any of the screens
Answer
540k+ views
Hint :To solve the given question, use the concept of relative motion. To make things easy and understandable assume a specific direction for the velocity of the car and draw a vector diagram of the velocities of the car and the rain. Then find the direction of the rain with respect to the car.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
It is given that a car is moving on a road and rain is falling down vertically.
Now, since the car is in motion, the man inside the car will see the rain coming in a different direction. The direction of the rain will be with the motion of the man, i.e. with respect to the motion of the car.
To find the direction of the rainfall with respect to the car, we have to apply the concept of relative motion. According to the concept of relative motion (like velocity and acceleration), the motion of body B with respect to a body A is equal to difference in the vectors of motion of B and A.
i.e. $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{BA}}}=\overrightarrow{{{v}_{B}}}-\overrightarrow{{{v}_{A}}} $ , where $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{BA}}} $ is relative motion of B with respect to A.
Suppose the car is moving along the positive x-axis and the rain is falling down along the negative y-axis.
Let the velocity of the car be $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{A}}} $ and the velocity of the rain be $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{B}}} $
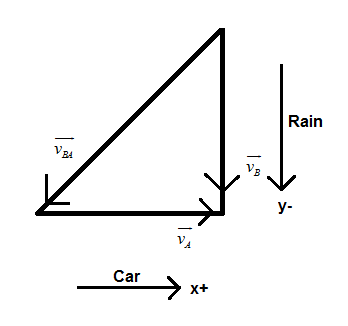
Then, the velocity of rain with respect to car is $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{BA}}}=\overrightarrow{{{v}_{B}}}-\overrightarrow{{{v}_{A}}} $
From the figure we understand that $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{BA}}} $ is somewhere towards the south-west and the car is moving towards the east. Therefore, the rain will hit the front part of the car.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note :
Note that the concept of relative motion is only applicable for physical quantities that are vectors. For example, velocities, acceleration and momentum.
Also note that we can calculate the relative motion between two bodies for the same physical quantities. For example, we cannot calculate relative acceleration of a body with respect to the velocity of another.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
It is given that a car is moving on a road and rain is falling down vertically.
Now, since the car is in motion, the man inside the car will see the rain coming in a different direction. The direction of the rain will be with the motion of the man, i.e. with respect to the motion of the car.
To find the direction of the rainfall with respect to the car, we have to apply the concept of relative motion. According to the concept of relative motion (like velocity and acceleration), the motion of body B with respect to a body A is equal to difference in the vectors of motion of B and A.
i.e. $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{BA}}}=\overrightarrow{{{v}_{B}}}-\overrightarrow{{{v}_{A}}} $ , where $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{BA}}} $ is relative motion of B with respect to A.
Suppose the car is moving along the positive x-axis and the rain is falling down along the negative y-axis.
Let the velocity of the car be $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{A}}} $ and the velocity of the rain be $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{B}}} $

Then, the velocity of rain with respect to car is $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{BA}}}=\overrightarrow{{{v}_{B}}}-\overrightarrow{{{v}_{A}}} $
From the figure we understand that $ \overrightarrow{{{v}_{BA}}} $ is somewhere towards the south-west and the car is moving towards the east. Therefore, the rain will hit the front part of the car.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note :
Note that the concept of relative motion is only applicable for physical quantities that are vectors. For example, velocities, acceleration and momentum.
Also note that we can calculate the relative motion between two bodies for the same physical quantities. For example, we cannot calculate relative acceleration of a body with respect to the velocity of another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




