
A capacitor of capacity ${C_1}$ is charged up to voltage $V$ volt and then connected in parallel to an uncharged capacitor of capacity ${C_2}$ . The final potential difference across each potential difference across each capacitor will be:
A. $\dfrac{{{C_1}V}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}$
B. $\dfrac{{{C_2}V}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}$
C. $(1 + \dfrac{{{C_1}}}{{{C_2}}})V$
D. \[(1 + \dfrac{{{C_2}}}{{{C_1}}})V\]
Answer
494.7k+ views
Hint: When the two or more capacitors are connected in parallel then the total charge will be the sum of the charge across all capacitors. For example
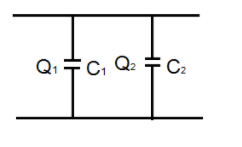
Then total charge $Q$ in the given circuit will be
$Q = {Q_1} + {Q_2}$
Formula used:
$C = \dfrac{Q}{V}$ ……………. (1)
Where $C$ is capacitance, $Q$ is charge, $V$ is voltage
When two capacitor ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ are connected in parallel combination then equivalent capacitance ${C_{eq}}$ will be ${C_{eq}} = {C_1} + {C_2}$ ……………. (2)
Complete step by step solution:
Given in question that ${C_1}$ is charged up to $V$
So the charge stored from equation (1) will be ${q_1} = {C_1}V$ …………. (3)
${q_2} = {C_2}V$ …………. (4)
Now capacitors ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ are connected in parallel so the potential difference across them will be the same. ${V_A} - {V_B} = \dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{{C_1}}} = \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{C_2}}}$ …………… (5)
From equation (5) we can write
${q_1}{C_2} = {q_2}{C_1}$ ……………… (6)
Also from question we know that $q = {q_1} + {q_2}$
And \[{q_2} = q - {q_1}\]
By putting the value of ${q_2}$ in equation (6)
We get \[{q_1}{C_2} = (q - {q_1}){C_1}\]
\[{q_1}{C_2} = q{C_1} - {q_{1}}{C_1}\]
\[{q_1}({C_1} + {C_2}) = {C_1}V.{C_1}\]
\[{q_{1}} = \dfrac{{{C_1}^2V}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}\]
Hence, \[\]\[{V_A} - {V_{B}} = \dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{{C_1}}}\]
\[{V_A} - {V_{B}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{C_1}^2V}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}}}{{{C_1}}}\]
\[{V_A} - {V_B} = \dfrac{{{C_1}V}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}\]
So the correct option is (a)
Note:
-In nature we can say an object is in balance if it is not moving, So when an object is moving it is in the state of equilibrium.
The center of gravity is the average position of the force of gravity on a body. Sometimes it is at the object’s geometric center for example ruler, where other times it isn’t (e.g. ruler with an eraser on one end). An object can be balanced or in equilibrium if it is supported directly under its center of gravity.
Common balance can be defined as the balance which is having each arm suspended. The unidentified mass is kept in one arm and the known mass in another until they both become equivalent. Therefore this balance is working on the principle of the moment of weights.

Then total charge $Q$ in the given circuit will be
$Q = {Q_1} + {Q_2}$
Formula used:
$C = \dfrac{Q}{V}$ ……………. (1)
Where $C$ is capacitance, $Q$ is charge, $V$ is voltage
When two capacitor ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ are connected in parallel combination then equivalent capacitance ${C_{eq}}$ will be ${C_{eq}} = {C_1} + {C_2}$ ……………. (2)
Complete step by step solution:
Given in question that ${C_1}$ is charged up to $V$
So the charge stored from equation (1) will be ${q_1} = {C_1}V$ …………. (3)
${q_2} = {C_2}V$ …………. (4)
Now capacitors ${C_1}$ and ${C_2}$ are connected in parallel so the potential difference across them will be the same. ${V_A} - {V_B} = \dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{{C_1}}} = \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{C_2}}}$ …………… (5)
From equation (5) we can write
${q_1}{C_2} = {q_2}{C_1}$ ……………… (6)
Also from question we know that $q = {q_1} + {q_2}$
And \[{q_2} = q - {q_1}\]
By putting the value of ${q_2}$ in equation (6)
We get \[{q_1}{C_2} = (q - {q_1}){C_1}\]
\[{q_1}{C_2} = q{C_1} - {q_{1}}{C_1}\]
\[{q_1}({C_1} + {C_2}) = {C_1}V.{C_1}\]
\[{q_{1}} = \dfrac{{{C_1}^2V}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}\]
Hence, \[\]\[{V_A} - {V_{B}} = \dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{{C_1}}}\]
\[{V_A} - {V_{B}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{C_1}^2V}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}}}{{{C_1}}}\]
\[{V_A} - {V_B} = \dfrac{{{C_1}V}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}\]
So the correct option is (a)
Note:
-In nature we can say an object is in balance if it is not moving, So when an object is moving it is in the state of equilibrium.
The center of gravity is the average position of the force of gravity on a body. Sometimes it is at the object’s geometric center for example ruler, where other times it isn’t (e.g. ruler with an eraser on one end). An object can be balanced or in equilibrium if it is supported directly under its center of gravity.
Common balance can be defined as the balance which is having each arm suspended. The unidentified mass is kept in one arm and the known mass in another until they both become equivalent. Therefore this balance is working on the principle of the moment of weights.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




