
A bus X is travelling with a speed of $40{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ towards North. Another bus Y is travelling with a speed of $30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ towards East. The velocity of bus X with respect to bus Y is?
Answer
469.2k+ views
Hint: For the given question, a bus X is travelling with a speed of $40{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ and another bus Y is travelling with a speed of $30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ towards East, we have to find the velocity of X with respect to Y by vector addition. Then we will find the direction of the velocity from the trigonometric formula.
Complete answer:
It is given in the question that a bus X is travelling with a speed of $40{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ and another bus Y is travelling with a speed of $30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ towards East. We have to find the velocity of bus X with respect to bus Y.
This is a $2$-D problem which must be done by a careful vector addition.
Let us consider that the motion of X would be relative to Y if the bus X as stationary. With respect to Y, bus X would seem to be travelling toward the west at $30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$.
Now, we the actual speed of bus X is namely $40{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ to the north.
The velocity vectors are perpendicular to each other and hence by vector addition we will find the answer.
Let the velocity of bus X with respect to bus Y is ${v_r}$ and the velocity of bus X is given ${v_X} = 30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ and the velocity of Y is ${v_Y} = 40{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ as shown in the diagram, and using pythagoras theorem we get,
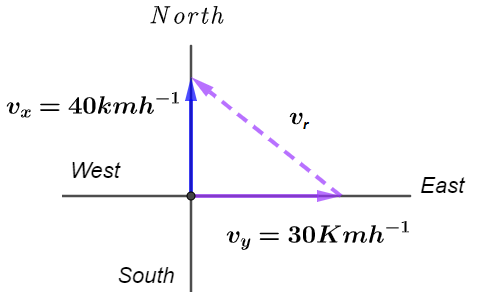
Now,
${v_r} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{v_{_X}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{v_Y}} \right)}^2}} $
Substituting the values we get,
${v_r} = \sqrt {{{\left( {30} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {40} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {2500} = 50$
Hence, we get the velocity ${v_r} = 50{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$.
The direction of the given velocity is, $\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{{v_Y}}}{{{v_X}}} = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{40}}{{30}} = {53.1^ \circ }$
Note:
It must be noted that it is a two-dimensional problem which must be solved carefully by using vector addition. We must be careful in the direction of the velocity since the angle ${53.1^ \circ }$ here must be measured clockwise from the direction of west.
Complete answer:
It is given in the question that a bus X is travelling with a speed of $40{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ and another bus Y is travelling with a speed of $30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ towards East. We have to find the velocity of bus X with respect to bus Y.
This is a $2$-D problem which must be done by a careful vector addition.
Let us consider that the motion of X would be relative to Y if the bus X as stationary. With respect to Y, bus X would seem to be travelling toward the west at $30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$.
Now, we the actual speed of bus X is namely $40{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ to the north.
The velocity vectors are perpendicular to each other and hence by vector addition we will find the answer.
Let the velocity of bus X with respect to bus Y is ${v_r}$ and the velocity of bus X is given ${v_X} = 30{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ and the velocity of Y is ${v_Y} = 40{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$ as shown in the diagram, and using pythagoras theorem we get,

Now,
${v_r} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{v_{_X}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{v_Y}} \right)}^2}} $
Substituting the values we get,
${v_r} = \sqrt {{{\left( {30} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {40} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {2500} = 50$
Hence, we get the velocity ${v_r} = 50{\text{ }}\dfrac{{km}}{{hr}}$.
The direction of the given velocity is, $\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{{v_Y}}}{{{v_X}}} = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{40}}{{30}} = {53.1^ \circ }$
Note:
It must be noted that it is a two-dimensional problem which must be solved carefully by using vector addition. We must be careful in the direction of the velocity since the angle ${53.1^ \circ }$ here must be measured clockwise from the direction of west.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




