
A bus accelerates from rest at \[1\,{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\] for 10 sec and then retards at the same rate till it comes to rest. Draw a-t graph.
Answer
541.8k+ views
Hint: Using the given values of the acceleration and the time, we will draw the acceleration versus time graph. The magnitudes of the acceleration and the retardation are equal, with only the direction being opposite.
Formulae used:
\[a=\dfrac{dv}{dt}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
The acceleration and the retardation of the bus, \[1\,{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\]
The time taken, \[10\,s\].
The acceleration time graph gives the value of the change in the velocity of the moving object. By finding the value of the area under the curve, the value of the change in the velocity can be obtained.
The mathematical representation of the same is, \[a=\dfrac{dv}{dt}\].
As the bus accelerates and retards at the same rate from the rest till it comes to rest, thus, we will get constant values for these situations.
For the time from 0 seconds to the 10 seconds, we get a straight line parallel to the time axis with the acceleration being \[a=+1{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\]. Similarly, for the time from 10 seconds to the 20 seconds, we get a straight line parallel to the time axis with the acceleration being \[a=-1{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\]. This negative sign indicates the decrease in the acceleration.
The acceleration versus the time graph is,
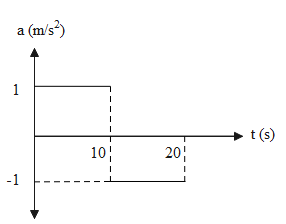
Hence the graph of acceleration versus time for a bus accelerating from the rest at \[1{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\] for 10 sec and then retarding at the same rate till it comes to rest.
Note: The distance time graph, the velocity time graph and the acceleration time graph are different for the same moving object. The magnitudes of the acceleration and the retardation are equal, with only the direction being opposite.
Formulae used:
\[a=\dfrac{dv}{dt}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
The acceleration and the retardation of the bus, \[1\,{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\]
The time taken, \[10\,s\].
The acceleration time graph gives the value of the change in the velocity of the moving object. By finding the value of the area under the curve, the value of the change in the velocity can be obtained.
The mathematical representation of the same is, \[a=\dfrac{dv}{dt}\].
As the bus accelerates and retards at the same rate from the rest till it comes to rest, thus, we will get constant values for these situations.
For the time from 0 seconds to the 10 seconds, we get a straight line parallel to the time axis with the acceleration being \[a=+1{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\]. Similarly, for the time from 10 seconds to the 20 seconds, we get a straight line parallel to the time axis with the acceleration being \[a=-1{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\]. This negative sign indicates the decrease in the acceleration.
The acceleration versus the time graph is,

Hence the graph of acceleration versus time for a bus accelerating from the rest at \[1{m}/{{{s}^{2}}}\;\] for 10 sec and then retarding at the same rate till it comes to rest.
Note: The distance time graph, the velocity time graph and the acceleration time graph are different for the same moving object. The magnitudes of the acceleration and the retardation are equal, with only the direction being opposite.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




