
A boy standing on the ground, spots a balloon moving with the wind in a horizontal line at a constant height. The angle of elevation of the balloon from the boy at an instant is \[60^\circ .\] After \[2\] minutes, from the same point of observation, the angle of elevation reduces to \[30^\circ .\] If the speed of the wind is \[29\sqrt 3 \] m/min. then, find the height of the balloon from the ground level.
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, first we will construct a figure to get the better idea of it. Then we will obtain the distance covered by the balloon in \[2\] mins by equating with the speed of wind. After that using the basic rule of trigonometry, we will get our required answer, the height of the balloon from the ground level.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given that a boy is standing on the ground, he spots a balloon moving with the wind in a horizontal line at a constant height. It is given that the angle of elevation of the balloon from the boy at an instant is \[60^\circ .\] Then, after two minutes, from the same point of observation, the angle of elevation reduces to \[30^\circ .\] It is also given that the speed of the wind is \[29\sqrt 3 \] m/min. We need to find the height of the balloon from the ground level.
Let us construct a figure, using given information, we get
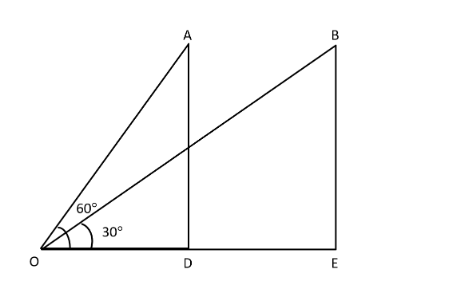
Let the point of observation be O, and let the boy spot the balloon at point A, then the angle of elevation from his eyes, i.e., point O to the balloon is \[60^\circ .\]
Then, let after two minutes the balloon reaches to the point B and now the angle of elevation from the eyes is $30^\circ .$
Here, the speed of the wind is equal to the distance covered by the balloon in \[2\] mins be AB.
On applying the values, we get
\[\Rightarrow 29\sqrt 3 \]\[m/min = \dfrac{{AB}}{2}\]
$\Rightarrow AB = 58\sqrt 3 m$\[ \ldots ..eq.\left( 1 \right)\]
Now, in the $\Delta AOD.$
$
\Rightarrow \tan 60^\circ = \dfrac{{AD}}{{OD}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{AD}}{{OD}}........(\because \tan 60^\circ = \sqrt 3 ) \\
\Rightarrow AD = \sqrt 3 OD....eq.(2) \\
$
Now, in the $\Delta BOE.$
$
\Rightarrow \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{BE}}{{OE}} = \dfrac{{BE}}{{OD + DE}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{AD}}{{OD + DE}}.........(\because \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}) \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 AD = OD + DE \\
$
Now, on using $AD = \sqrt 3 OD$, we get
$
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 (\sqrt 3 OD) = OD + DE \\
\Rightarrow 3OD = OD + DE \\
\Rightarrow 2OD = DE \\
\Rightarrow 2OD = AB \\
\Rightarrow 2OD = 58\sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow OD = 29\sqrt 3 \\
$
Now, the height of the balloon from the ground level is AD.
$ \Rightarrow AD = \sqrt 3 (29\sqrt 3 )........(\because AD = \sqrt 3 OD)$
$\Rightarrow AD = 87m$
So, the height of the balloon from the ground level is \[87{\text{ }}m.\]
Note: In the solutions, we have taken the speed of the wind equal to the distance covered by the balloon in \[2\] mins be AB. Since, the wind is caused by a difference in air pressure. Air travels from areas of higher pressure to low pressure places.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given that a boy is standing on the ground, he spots a balloon moving with the wind in a horizontal line at a constant height. It is given that the angle of elevation of the balloon from the boy at an instant is \[60^\circ .\] Then, after two minutes, from the same point of observation, the angle of elevation reduces to \[30^\circ .\] It is also given that the speed of the wind is \[29\sqrt 3 \] m/min. We need to find the height of the balloon from the ground level.
Let us construct a figure, using given information, we get

Let the point of observation be O, and let the boy spot the balloon at point A, then the angle of elevation from his eyes, i.e., point O to the balloon is \[60^\circ .\]
Then, let after two minutes the balloon reaches to the point B and now the angle of elevation from the eyes is $30^\circ .$
Here, the speed of the wind is equal to the distance covered by the balloon in \[2\] mins be AB.
On applying the values, we get
\[\Rightarrow 29\sqrt 3 \]\[m/min = \dfrac{{AB}}{2}\]
$\Rightarrow AB = 58\sqrt 3 m$\[ \ldots ..eq.\left( 1 \right)\]
Now, in the $\Delta AOD.$
$
\Rightarrow \tan 60^\circ = \dfrac{{AD}}{{OD}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{AD}}{{OD}}........(\because \tan 60^\circ = \sqrt 3 ) \\
\Rightarrow AD = \sqrt 3 OD....eq.(2) \\
$
Now, in the $\Delta BOE.$
$
\Rightarrow \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{{BE}}{{OE}} = \dfrac{{BE}}{{OD + DE}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{AD}}{{OD + DE}}.........(\because \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}) \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 AD = OD + DE \\
$
Now, on using $AD = \sqrt 3 OD$, we get
$
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 (\sqrt 3 OD) = OD + DE \\
\Rightarrow 3OD = OD + DE \\
\Rightarrow 2OD = DE \\
\Rightarrow 2OD = AB \\
\Rightarrow 2OD = 58\sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow OD = 29\sqrt 3 \\
$
Now, the height of the balloon from the ground level is AD.
$ \Rightarrow AD = \sqrt 3 (29\sqrt 3 )........(\because AD = \sqrt 3 OD)$
$\Rightarrow AD = 87m$
So, the height of the balloon from the ground level is \[87{\text{ }}m.\]
Note: In the solutions, we have taken the speed of the wind equal to the distance covered by the balloon in \[2\] mins be AB. Since, the wind is caused by a difference in air pressure. Air travels from areas of higher pressure to low pressure places.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




