
A boy sitting on a swing which is moving at an angle of \[30^\circ \] from the vertical is blowing a whistle which is of frequency 1000 Hz. The whistle is 2 m from the point of the support of the swing, the maximum and minimum frequencies she will hear are
(velocity of sound =\[330\,m/s\], \[g = 9.8\,m/{s^2}\])
(A) 1000, 990 Hz
(B) 1007,1000 Hz
(C) 1007, 993 Hz
(D) 1100, 900 Hz
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint:The potential energy of the boy sitting on the swing at extreme position is converted into the kinetic energy at the lowest position of the swing. Use the law of conservation of energy to calculate the velocity of the source then use Doppler’s formula to calculate the maximum and minimum frequency heard by the girl.
Formula used:
\[\nu = {\nu _0}\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v \pm {v_s}}}} \right)\]
Here, v is the velocity of the sound, \[{v_s}\] is the velocity of the source, and \[{\nu _0}\] is the original frequency of the source.
Complete step by step answer:
Draw a schematic diagram of the swing to determine the distance between the ground and the extreme position of the swing as follows,
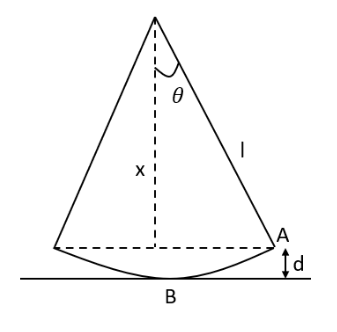
In the above figure, A and B are the extreme positions of the swing, l is the length of the rope of the swing and \[\theta \] is the vertical angle. Assume the point O is very close to the ground. Suppose the velocity of the swing at position A is \[{v_1}\] and the velocity of the swing at position O is \[{v_2}\].
Let’s calculate the distance between the ground and position A as follows,
\[\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{l}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = l\cos \theta \]
Therefore, the distance between the ground and position A is,
\[\Rightarrow d = l - l\cos \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow d = l\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)\]
The total energy of the swing at point A and O is the same. Therefore, we can write,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}mv_1^2 + mgl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_2^2 + mgh\]
At extreme positions A and B, the velocity of the swing is zero. Also, at position O, the height h is zero as it is very close to the ground.
Therefore, above equation becomes,
\[\Rightarrow mgl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_2^2\]
\[ \Rightarrow v_2^2 = 2gl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt {2gl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)} \]
Substitute \[g = 9.8\,m/{s^2}\], \[l = 2\,m\] and \[\theta = 30^\circ \] in the above equation.
\[\Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt {2\left( {9.8\,m/{s^2}} \right)\left( {2\,m} \right)\left( {1 - \cos 30^\circ } \right)} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt {5.252\,{m^2}/{s^2}} \]
\[\therefore {v_2} = 2.29\,m/s\]
This is the velocity of the source at extremum.
Use Doppler’s equation to determine the frequency heard by the girl as follows,
\[\Rightarrow \nu = {\nu _0}\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v \pm {v_s}}}} \right)\]
Here, v is the velocity of the sound, \[{v_s}\] is the velocity of the source, and \[{\nu _0}\] is the original frequency of the source.
For maximum frequency heard by the girl, the sign of \[{v_s}\] must be negative. Therefore, the maximum frequency heard by the girl is,
\[\Rightarrow \nu = {\nu _0}\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v - {v_s}}}} \right)\]
Substitute \[v = 330\,m/s\], \[{\nu _0} = 1000\,Hz\] and \[{v_s} = 2.29\,m/s\] in the above equation.
\[\Rightarrow \nu = \left( {1000\,Hz} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{330\,m/s}}{{330\,m/s - 2.29\,m/s}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \therefore \nu = 1007\,Hz\]
For the minimum frequency heard by the girl, the sign of \[{v_s}\] must be positive. Therefore, the minimum frequency heard by the girl is,
\[\Rightarrow \nu = {\nu _0}\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v + {v_s}}}} \right)\]
Substitute \[v = 330\,m/s\], \[{\nu _0} = 1000\,Hz\] and \[{v_s} = 2.29\,m/s\] in the above equation.
\[\Rightarrow \nu = \left( {1000\,Hz} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{330\,m/s}}{{330\,m/s + 2.29\,m/s}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \therefore \nu = 993\,Hz\]
Therefore, the maximum and minimum frequency heard by the girl is 1007 Hz and 993 Hz respectively.
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Here, we have neglected the distance between the ground and position O. In other questions, the distance between the ground and lowest position may have been given.
Formula used:
\[\nu = {\nu _0}\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v \pm {v_s}}}} \right)\]
Here, v is the velocity of the sound, \[{v_s}\] is the velocity of the source, and \[{\nu _0}\] is the original frequency of the source.
Complete step by step answer:
Draw a schematic diagram of the swing to determine the distance between the ground and the extreme position of the swing as follows,

In the above figure, A and B are the extreme positions of the swing, l is the length of the rope of the swing and \[\theta \] is the vertical angle. Assume the point O is very close to the ground. Suppose the velocity of the swing at position A is \[{v_1}\] and the velocity of the swing at position O is \[{v_2}\].
Let’s calculate the distance between the ground and position A as follows,
\[\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{l}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = l\cos \theta \]
Therefore, the distance between the ground and position A is,
\[\Rightarrow d = l - l\cos \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow d = l\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)\]
The total energy of the swing at point A and O is the same. Therefore, we can write,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}mv_1^2 + mgl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_2^2 + mgh\]
At extreme positions A and B, the velocity of the swing is zero. Also, at position O, the height h is zero as it is very close to the ground.
Therefore, above equation becomes,
\[\Rightarrow mgl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_2^2\]
\[ \Rightarrow v_2^2 = 2gl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt {2gl\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)} \]
Substitute \[g = 9.8\,m/{s^2}\], \[l = 2\,m\] and \[\theta = 30^\circ \] in the above equation.
\[\Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt {2\left( {9.8\,m/{s^2}} \right)\left( {2\,m} \right)\left( {1 - \cos 30^\circ } \right)} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_2} = \sqrt {5.252\,{m^2}/{s^2}} \]
\[\therefore {v_2} = 2.29\,m/s\]
This is the velocity of the source at extremum.
Use Doppler’s equation to determine the frequency heard by the girl as follows,
\[\Rightarrow \nu = {\nu _0}\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v \pm {v_s}}}} \right)\]
Here, v is the velocity of the sound, \[{v_s}\] is the velocity of the source, and \[{\nu _0}\] is the original frequency of the source.
For maximum frequency heard by the girl, the sign of \[{v_s}\] must be negative. Therefore, the maximum frequency heard by the girl is,
\[\Rightarrow \nu = {\nu _0}\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v - {v_s}}}} \right)\]
Substitute \[v = 330\,m/s\], \[{\nu _0} = 1000\,Hz\] and \[{v_s} = 2.29\,m/s\] in the above equation.
\[\Rightarrow \nu = \left( {1000\,Hz} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{330\,m/s}}{{330\,m/s - 2.29\,m/s}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \therefore \nu = 1007\,Hz\]
For the minimum frequency heard by the girl, the sign of \[{v_s}\] must be positive. Therefore, the minimum frequency heard by the girl is,
\[\Rightarrow \nu = {\nu _0}\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v + {v_s}}}} \right)\]
Substitute \[v = 330\,m/s\], \[{\nu _0} = 1000\,Hz\] and \[{v_s} = 2.29\,m/s\] in the above equation.
\[\Rightarrow \nu = \left( {1000\,Hz} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{330\,m/s}}{{330\,m/s + 2.29\,m/s}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \therefore \nu = 993\,Hz\]
Therefore, the maximum and minimum frequency heard by the girl is 1007 Hz and 993 Hz respectively.
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Here, we have neglected the distance between the ground and position O. In other questions, the distance between the ground and lowest position may have been given.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




