
A boy playing on the roof of a $10m$ high building throws a ball with a speed of $10\;m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$ at an angle of ${30^ \circ }$ with the horizontal. How far from the throwing point will the ball he at the height of $10m$ from the ground$\left( {g = 10m{s^{ - 2}},sin{{30}^ \circ } = 21,cos{{30}^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)$.
$\eqalign{
& \left( A \right)8.6m \cr
& \left( B \right)9.6m \cr
& \left( C \right)10.6m \cr
& \left( D \right)11.6m \cr} $
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: It is the case of projectile motion and in this calculate the range of projectile by using the given dimensions. An object embarked on the projectile motion will have an initial launch angle anywhere from 0 to 90 degrees. The range of an object, having the initial launch angle and initial velocity.
Formula used: $R = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
Complete answer:
The scenario given in the given can be completely understood by the following illustration:
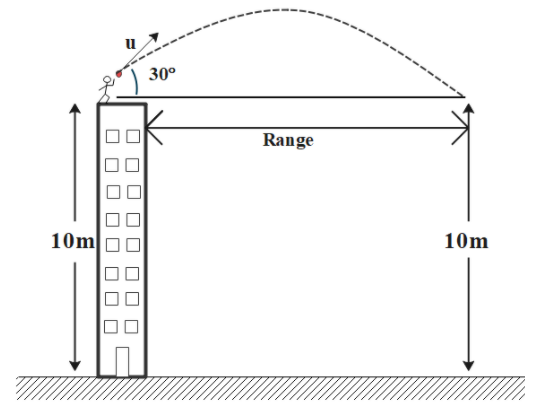
As given in question:
Initial velocity $u$= $10\;m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$
Angle of launch $\theta = {30^ \circ }$
Acceleration due to gravity $g = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
So, range of projectile is calculated as:
$R = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{{\left( {10} \right)}^2}\sin \left( {2 \times {{30}^ \circ }} \right)}}{{10}} \cr
& \Rightarrow R = 5\sqrt 3 \cr
& \therefore R = 8.66m \cr} $
Hence, the correct option for this is option (A).
Additional Information:
A projectile is an object upon which the sole force acting is gravity. There is a spread of samples of projectiles. An object dropped from rest may be a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). An object that's thrown vertically upward is additionally a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). And an object which is thrown upward at an angle to the horizontal is additionally a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). A projectile when projected or dropped continues in motion by its own inertia and is influenced only by the downward force of gravity.
Note:
In handling the motion of a projectile in air, we ignore the effect of air resistance on the motion. Due to air resistance, the entire energy of the particle also as its horizontal component velocity will continue decreasing with time, making the autumn of the projectile steeper than its rise.
Formula used: $R = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
Complete answer:
The scenario given in the given can be completely understood by the following illustration:

As given in question:
Initial velocity $u$= $10\;m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$
Angle of launch $\theta = {30^ \circ }$
Acceleration due to gravity $g = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
So, range of projectile is calculated as:
$R = \dfrac{{{u^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g}$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{{\left( {10} \right)}^2}\sin \left( {2 \times {{30}^ \circ }} \right)}}{{10}} \cr
& \Rightarrow R = 5\sqrt 3 \cr
& \therefore R = 8.66m \cr} $
Hence, the correct option for this is option (A).
Additional Information:
A projectile is an object upon which the sole force acting is gravity. There is a spread of samples of projectiles. An object dropped from rest may be a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). An object that's thrown vertically upward is additionally a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). And an object which is thrown upward at an angle to the horizontal is additionally a projectile (provided that the influence of air resistance is negligible). A projectile when projected or dropped continues in motion by its own inertia and is influenced only by the downward force of gravity.
Note:
In handling the motion of a projectile in air, we ignore the effect of air resistance on the motion. Due to air resistance, the entire energy of the particle also as its horizontal component velocity will continue decreasing with time, making the autumn of the projectile steeper than its rise.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




