
A boy on a train of height ${h_1}$ projects a coin to his friend of height ${h_2}$ standing on the same train, with a velocity $v$ relative to the train, at an angle $\theta $ with horizontal. If the train moves with a constant velocity $v$ in the direction of $x$ motion of the coin, find the
$\left( a \right)$ Distance between the boys so the second boy can catch the coin.
$\left( b \right)$ Maximum height attained by the coin, and
$\left( c \right)$ Speed with which the second boy catches the coin relative to himself (train) and ground.
Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: This problem is based on projectile motion. It is the motion of an object projected or thrown into the air with a certain angle with respect to the ground which is subjected to acceleration due to gravity. The equation for trajectory that is path traced will be utilized to find the distance between two boys.
Complete step by step answer:
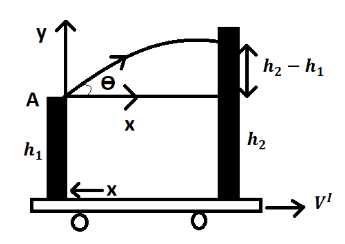
$\left( a \right)$ Distance between the boys so the second boy can catch the coin.
Taking point $A$ as origin, the equation for trajectory is given as
$y = x\tan \theta - \dfrac{{g{x^2}}}{{2{u^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta }}$ …… $\left( 1 \right)$
From the figure it is clear that,
$y = {h_2} - {h_1}$ ……… $\left( 2 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 2 \right)$ in equation $\left( 1 \right)$
${h_2} - {h_1} = x\tan \theta - \dfrac{{g{x^2}}}{{2{u^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta }}$ ……… $\left( 3 \right)$
Since, the degree of equation $\left( 3 \right)$ is two we can get two values for $x$ and both the values of $x$ will be valid.
$\left( b \right)$ When the body is in projectile motion the general equation for maximum height is given as
${h_2} - {h_1} = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}}$……… $\left( 4 \right)$
And maximum height attained by the coin is ${h_2}$
Therefore, from equation $\left( 4 \right)$
Maximum height that is from ground (Refer the figure) is ${h_2} = {h_1} + \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}}$ ……… $\left( 5 \right)$
$\left( c \right)$ Speed with which the second boy catches the coin relative to himself (train) and ground.
With respect to himself (train)
Splitting the velocity into horizontal and vertical components we can write ${v_x}$ and ${v_y}$ as follows
That is, ${v_x} = v\cos \theta $ ……… $\left( 6 \right)$
and \[v_y^2 = {\left( {v\sin \theta } \right)^2} - 2g\left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)\]……… $\left( 7 \right)$
The final speed can be written as
${v_f} = \sqrt {v_x^2 + v_y^2} $ ……. $\left( 8 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 6 \right)$ and equation $\left( 7 \right)$ in equation $\left( 8 \right)$ , we get
${v_f} = \sqrt {{{\left( {v\cos \theta } \right)}^2} + {{\left( {v\sin \theta } \right)}^2} - 2g({h_2} - {h_1})} $
On simplifying the above equation, we get
${v_f} = \sqrt {\left( {{v^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta } \right) + \left( {{v^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta } \right) - 2g({h_2} - {h_1})} $
Therefore final speed with respect to himself (train),
${v_f} = \sqrt {{v^2} - 2g({h_2} - {h_1})} $
With respect to ground:
${v_x} = {v^I} + v\cos \theta $ ……. $\left( 9 \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {v_y}^2 = {\left( {v\sin \theta } \right)^2} - 2g\left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)$ ……. $\left( {10} \right)$
Therefore final speed with respect to ground is,
${v_f} = \sqrt {v_x^2 + v_y^2} $ ……. $\left( {11} \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 9 \right)$ and equation $\left( {10} \right)$ in equation $\left( {11} \right)$ , we get
$\therefore {v_f} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{v^I} + v\cos \theta } \right)}^2} + {{\left( {v\sin \theta } \right)}^2} - 2g\left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)} $
Note: It should be noted that, in projectile motion, there are two simultaneous independent rectilinear motions of the object that is along the x-axis uniform velocity, responsible for forward motion of the particle and along y-axis uniform acceleration, responsible for downwards motion of the particle.
Complete step by step answer:

$\left( a \right)$ Distance between the boys so the second boy can catch the coin.
Taking point $A$ as origin, the equation for trajectory is given as
$y = x\tan \theta - \dfrac{{g{x^2}}}{{2{u^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta }}$ …… $\left( 1 \right)$
From the figure it is clear that,
$y = {h_2} - {h_1}$ ……… $\left( 2 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 2 \right)$ in equation $\left( 1 \right)$
${h_2} - {h_1} = x\tan \theta - \dfrac{{g{x^2}}}{{2{u^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta }}$ ……… $\left( 3 \right)$
Since, the degree of equation $\left( 3 \right)$ is two we can get two values for $x$ and both the values of $x$ will be valid.
$\left( b \right)$ When the body is in projectile motion the general equation for maximum height is given as
${h_2} - {h_1} = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}}$……… $\left( 4 \right)$
And maximum height attained by the coin is ${h_2}$
Therefore, from equation $\left( 4 \right)$
Maximum height that is from ground (Refer the figure) is ${h_2} = {h_1} + \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta }}{{2g}}$ ……… $\left( 5 \right)$
$\left( c \right)$ Speed with which the second boy catches the coin relative to himself (train) and ground.
With respect to himself (train)
Splitting the velocity into horizontal and vertical components we can write ${v_x}$ and ${v_y}$ as follows
That is, ${v_x} = v\cos \theta $ ……… $\left( 6 \right)$
and \[v_y^2 = {\left( {v\sin \theta } \right)^2} - 2g\left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)\]……… $\left( 7 \right)$
The final speed can be written as
${v_f} = \sqrt {v_x^2 + v_y^2} $ ……. $\left( 8 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 6 \right)$ and equation $\left( 7 \right)$ in equation $\left( 8 \right)$ , we get
${v_f} = \sqrt {{{\left( {v\cos \theta } \right)}^2} + {{\left( {v\sin \theta } \right)}^2} - 2g({h_2} - {h_1})} $
On simplifying the above equation, we get
${v_f} = \sqrt {\left( {{v^2}{{\cos }^2}\theta } \right) + \left( {{v^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta } \right) - 2g({h_2} - {h_1})} $
Therefore final speed with respect to himself (train),
${v_f} = \sqrt {{v^2} - 2g({h_2} - {h_1})} $
With respect to ground:
${v_x} = {v^I} + v\cos \theta $ ……. $\left( 9 \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {v_y}^2 = {\left( {v\sin \theta } \right)^2} - 2g\left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)$ ……. $\left( {10} \right)$
Therefore final speed with respect to ground is,
${v_f} = \sqrt {v_x^2 + v_y^2} $ ……. $\left( {11} \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 9 \right)$ and equation $\left( {10} \right)$ in equation $\left( {11} \right)$ , we get
$\therefore {v_f} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{v^I} + v\cos \theta } \right)}^2} + {{\left( {v\sin \theta } \right)}^2} - 2g\left( {{h_2} - {h_1}} \right)} $
Note: It should be noted that, in projectile motion, there are two simultaneous independent rectilinear motions of the object that is along the x-axis uniform velocity, responsible for forward motion of the particle and along y-axis uniform acceleration, responsible for downwards motion of the particle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




