
A boy jumping on a trampoline feels three times his normal weight when he lands on the trampoline surface.
Which free body diagram best represents this situation in terms of the forces acting on the boy while he feels this sensation of three times his normal weight?
The upward forces represented are exerted by the trampoline on the boy. The downward forces are the forces exerted by the earth on the boy. Here m stands for the boy's mass and g for what is usually called the acceleration of gravity. The amounts of force are all expressed in terms of $m$ and $g$.
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Clearly Newton’s third law is applicable in it. When a body exerts some force the same amount of force is exerted by the opposite object by it. But here mg is normally exerted by the earth on boys plus the force by trampoline also.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1:
Before we start lets us know about Newton’s third law of motion:
Newton’s first two laws of motion explain how the motion of a single object changes
According to Newton’s third law of motion, forces always act in equal but opposite pairs. Another way of saying this is for every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction. This means that when you push on a wall, the wall pushes back on you with a force equal in strength to the force you exerted. When one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts the same size force on the first object.
Step 2:
Here is the diagram according to the question and the explanation also.
This will give a clear view of what is happening with respect to the force and solution of the question.
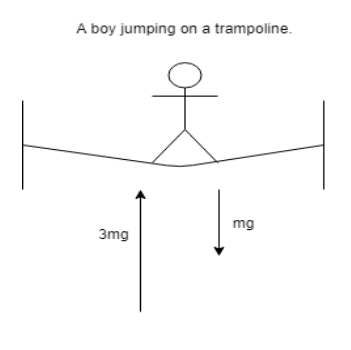
We are given that a boy jumping on a trampoline feels three times his normal weight when he lands on the trampoline surface. The upward forces represented are exerted by the trampoline on the boy.
In the above diagram, $m$ stands for the boy's mass and $g$ for what is usually called the acceleration of gravity
The force acting downward is the force exerted by the earth on the boy, which is always equal to mg independent of any motion.
The weight 'felt' by the boy is the normal reaction exerted by the trampoline on the boy.
Hence the normal reaction acting upward must be 3mg.
Note:
We can also say it as when a boy exerts a force of mg on the trampoline then the same amount of force is exerted by the earth too. But some potential energy gets stored into the trampoline and then it also exerts some force to the boy which then becomes equal to 3mg.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1:
Before we start lets us know about Newton’s third law of motion:
Newton’s first two laws of motion explain how the motion of a single object changes
According to Newton’s third law of motion, forces always act in equal but opposite pairs. Another way of saying this is for every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction. This means that when you push on a wall, the wall pushes back on you with a force equal in strength to the force you exerted. When one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts the same size force on the first object.
Step 2:
Here is the diagram according to the question and the explanation also.
This will give a clear view of what is happening with respect to the force and solution of the question.

We are given that a boy jumping on a trampoline feels three times his normal weight when he lands on the trampoline surface. The upward forces represented are exerted by the trampoline on the boy.
In the above diagram, $m$ stands for the boy's mass and $g$ for what is usually called the acceleration of gravity
The force acting downward is the force exerted by the earth on the boy, which is always equal to mg independent of any motion.
The weight 'felt' by the boy is the normal reaction exerted by the trampoline on the boy.
Hence the normal reaction acting upward must be 3mg.
Note:
We can also say it as when a boy exerts a force of mg on the trampoline then the same amount of force is exerted by the earth too. But some potential energy gets stored into the trampoline and then it also exerts some force to the boy which then becomes equal to 3mg.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




