
A bomber is flying horizontally with a constant speed of $150\;m/s$ at a height of $78.4\;m$. The pilot has to drop a bomb at an energy target. At what horizontal distance from the target should be releasing the bomb.
A. Zero
B. 300 m
C. 600 m
D. 750 m
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: Here, we use the concept of projectile motion which is fired horizontally from a certain height having a parabolic path. If an object is thrown with an initial velocity and which is then allowed to move under the action of gravity alone is called a projectile. Also, the path followed by a projectile during its flight is called a trajectory.
Complete step by step answer:
According to this question, when a bomb is dropped by the pilot to hit the target, the velocity of the bomb is unaffected by the vertical acceleration and its initial velocity becomes zero.
A bomb can be drop at certain height (h) $ = 78.4\;m$
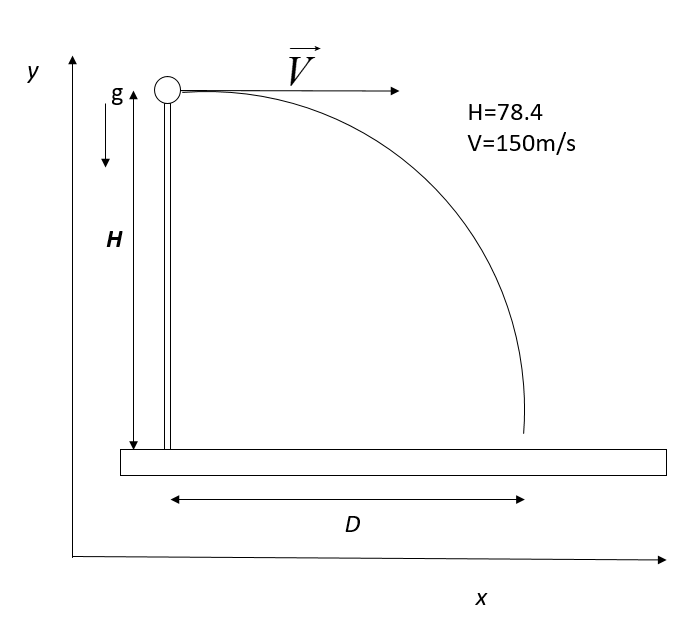
So, the time ($T$) of flight for bomb ${\rm{T = }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2{\rm{h}}}}{{\rm{g}}}} $
$\therefore {\rm{T = }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 78.4}}{{9.8}}} = \sqrt {16} = 4{\rm{s}}$
Where g is gravity $ = 9.8\;m/s$
Now we find the horizontal distance from the target when the bomb is released.
So, the horizontal range in projectile motion ${\rm{R = u}} \times {\rm{T}}$
Where T is the time of flight, and u is the initial velocity given $ = 150\;m/s$
$\therefore {\rm{R = 150}}\;{\rm{m/s}} \times {\rm{4s = 600 m}}$
Therefore the bomb is released $600\;m$ away from the target. Hence the correct option is (C).
Note:
Since in this problem, the motion is regarding the projectile and if we were asked to calculate the maximum range of a projectile then we can determine it by using the formula,
Formula used: ${\rm{R}} = \dfrac{{{{\rm{u}}^2}\sin 2\theta }}{{\rm{g}}}$
Here R is the range, g is the acceleration due to gravity, u is the initial velocity, $\theta $ is the angle of projection.
When $\theta = 45^\circ $ ,
$ \Rightarrow {{\rm{R}}_{\max }}{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{{{\rm{u}}^2}}}{{\rm{g}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
According to this question, when a bomb is dropped by the pilot to hit the target, the velocity of the bomb is unaffected by the vertical acceleration and its initial velocity becomes zero.
A bomb can be drop at certain height (h) $ = 78.4\;m$

So, the time ($T$) of flight for bomb ${\rm{T = }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2{\rm{h}}}}{{\rm{g}}}} $
$\therefore {\rm{T = }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 78.4}}{{9.8}}} = \sqrt {16} = 4{\rm{s}}$
Where g is gravity $ = 9.8\;m/s$
Now we find the horizontal distance from the target when the bomb is released.
So, the horizontal range in projectile motion ${\rm{R = u}} \times {\rm{T}}$
Where T is the time of flight, and u is the initial velocity given $ = 150\;m/s$
$\therefore {\rm{R = 150}}\;{\rm{m/s}} \times {\rm{4s = 600 m}}$
Therefore the bomb is released $600\;m$ away from the target. Hence the correct option is (C).
Note:
Since in this problem, the motion is regarding the projectile and if we were asked to calculate the maximum range of a projectile then we can determine it by using the formula,
Formula used: ${\rm{R}} = \dfrac{{{{\rm{u}}^2}\sin 2\theta }}{{\rm{g}}}$
Here R is the range, g is the acceleration due to gravity, u is the initial velocity, $\theta $ is the angle of projection.
When $\theta = 45^\circ $ ,
$ \Rightarrow {{\rm{R}}_{\max }}{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{{{\rm{u}}^2}}}{{\rm{g}}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




