
A body of mass $2{\text{ }}kg$ is dropped from the rest position $5{\text{ }}m$ above the ground. What is its velocity at height $3.0{\text{ }}m$ above the ground approximately?
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: We have to use the relation between final velocity of the particle, initial velocity of the particle, acceleration of the particle, distance covered by the particle to find the final velocity. We have to consider the initial velocity as zero since it starts from the rest.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the question that a body of mass $2{\text{ }}kg$ is dropped from a rest position at a height of $5{\text{ }}m$ above the ground.
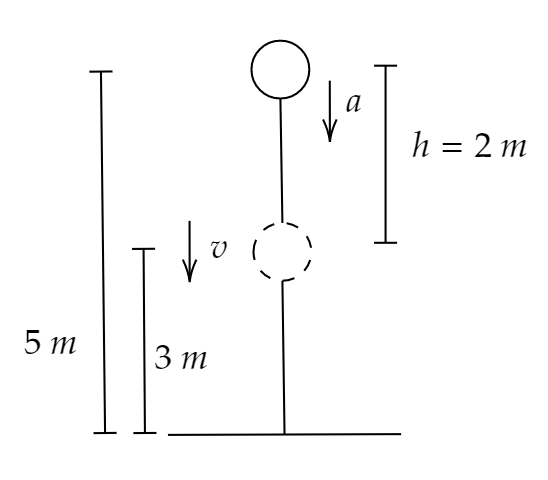
Let the initial velocity be $u$.
So, the initial velocity here is $u = 0$ as the particle is dropped from its rest position.
Let the final velocity of the body be $v$.
The height to which the velocity is to be measured is $h = 2.0{\text{ }}m$ from the initial point.
From the motions equation we get,
${v^2} - {u^2} = 2as$
The variables are defined as,
$v = $ final velocity of the particle
$u = $ initial velocity of the particle
$a = $ acceleration of the particle
$s = $ distance covered by the particle
In the given question,
$u = 0$, $a = g = $ acceleration due to gravity$ = 9.8{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$ and $s = h = $ height covered by the particle $ = \left( {5 - 3} \right) = 2{\text{ }}m$
Substituting the values in the equation we get,
${v^2} - 0 = 2 \times 9.8 \times 2 = 39.2$
Square root of we get,
$v = \sqrt {39.2} = 6.26$
The velocity of the particle at the height of $3.0{\text{ }}m$from the ground is ${\text{6}}{\text{.26 }}\dfrac{m}{s}$.
Note: It must be noted that the acceleration of the particle is considered as acceleration due to gravity as the particle is acting on the Y-axis where there is the acceleration due to gravity which acts on the particle. The initial velocity of the particle is $0{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}$ as it is at rest position initially. The distance covered by the particle should be considered from the starting point.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the question that a body of mass $2{\text{ }}kg$ is dropped from a rest position at a height of $5{\text{ }}m$ above the ground.

Let the initial velocity be $u$.
So, the initial velocity here is $u = 0$ as the particle is dropped from its rest position.
Let the final velocity of the body be $v$.
The height to which the velocity is to be measured is $h = 2.0{\text{ }}m$ from the initial point.
From the motions equation we get,
${v^2} - {u^2} = 2as$
The variables are defined as,
$v = $ final velocity of the particle
$u = $ initial velocity of the particle
$a = $ acceleration of the particle
$s = $ distance covered by the particle
In the given question,
$u = 0$, $a = g = $ acceleration due to gravity$ = 9.8{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$ and $s = h = $ height covered by the particle $ = \left( {5 - 3} \right) = 2{\text{ }}m$
Substituting the values in the equation we get,
${v^2} - 0 = 2 \times 9.8 \times 2 = 39.2$
Square root of we get,
$v = \sqrt {39.2} = 6.26$
The velocity of the particle at the height of $3.0{\text{ }}m$from the ground is ${\text{6}}{\text{.26 }}\dfrac{m}{s}$.
Note: It must be noted that the acceleration of the particle is considered as acceleration due to gravity as the particle is acting on the Y-axis where there is the acceleration due to gravity which acts on the particle. The initial velocity of the particle is $0{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}$ as it is at rest position initially. The distance covered by the particle should be considered from the starting point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




