
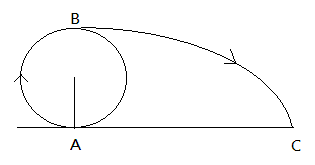
A body is rotated in the vertical plane by means of thread of length $l = 4m$ with minimum possible speed. At the highest point B the thread breaks and the body moves under gravity and strikes at C. What is horizontal range AC (in m)?

Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Just before breaking there will be three forces acting on the body at point B. From there we will get velocity. After that we can solve this problem considering that a body at height $l = 4m$ is projected horizontally. Calculate range for this case.
Complete step by step answer:
Let's first understand the question, a body is tied to a thread of length $l = 4m$ , the thread is vertically rotated just like a ferris wheel. Now when the body reaches at point B, that is at the top, the thread breaks.
Let’s understand what happens at this point. At point B, the body was in rotation due to the centripetal force and when the thread breaks, this centripetal force no longer acts on the body.
At this point only gravitational force acts on the body, so at point B just before breaking, centripetal force must be equal to the gravitational force.
$$ \Rightarrow R = 2 \times 4 = 2l = 8m$$
Where $m$ is the mass of the body.
$v$ is the velocity of the body
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity
And $r$ is the radius of the circle in rotational motion.
Here $r = l$ , solving above equation we have:
$v = \sqrt {gl} $
The range from point B, is given by the formula
$$R = v\sqrt {\dfrac{{2(2l)}}{g}} $$
$$ \Rightarrow R = \sqrt {gl} \sqrt {\dfrac{{2(2l)}}{g}} $$
$$ \Rightarrow R = 2l$$
$$ \therefore R = 2 \times 4 = 8m$$
Therefore, the horizontal range AC is $$8m$$
Note:
Remember that at point B tension is also acting on the body but as soon as the thread breaks, tension becomes zero. The formula of range for such cases must be remembered.
Alternate solution; after thread breaks, calculate time taken for the body to cover a vertical distance of $$2l = 8m$$ . Now we have time and velocity at point B, so horizontal range can be easily calculated.
Complete step by step answer:
Let's first understand the question, a body is tied to a thread of length $l = 4m$ , the thread is vertically rotated just like a ferris wheel. Now when the body reaches at point B, that is at the top, the thread breaks.
Let’s understand what happens at this point. At point B, the body was in rotation due to the centripetal force and when the thread breaks, this centripetal force no longer acts on the body.
At this point only gravitational force acts on the body, so at point B just before breaking, centripetal force must be equal to the gravitational force.
$$ \Rightarrow R = 2 \times 4 = 2l = 8m$$
Where $m$ is the mass of the body.
$v$ is the velocity of the body
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity
And $r$ is the radius of the circle in rotational motion.
Here $r = l$ , solving above equation we have:
$v = \sqrt {gl} $
The range from point B, is given by the formula
$$R = v\sqrt {\dfrac{{2(2l)}}{g}} $$
$$ \Rightarrow R = \sqrt {gl} \sqrt {\dfrac{{2(2l)}}{g}} $$
$$ \Rightarrow R = 2l$$
$$ \therefore R = 2 \times 4 = 8m$$
Therefore, the horizontal range AC is $$8m$$
Note:
Remember that at point B tension is also acting on the body but as soon as the thread breaks, tension becomes zero. The formula of range for such cases must be remembered.
Alternate solution; after thread breaks, calculate time taken for the body to cover a vertical distance of $$2l = 8m$$ . Now we have time and velocity at point B, so horizontal range can be easily calculated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




