
A body is falling freely from a point A at a certain height from the ground and passes through points \[B,C\;and\;D\;\] (vertically as shown) so that \[BC = CD\] . The time taken by the particle to move from \[B\;to\;C\;\] is \[2\;seconds\] and from \[C\;to\;D\;\] is \[1{\text{ }}second\] . Time taken to move from \[A\;to\;B\;\] in seconds is
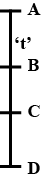
(a) 0.6
(b) 0.5
(c) 0.4
(d) 0.2
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: Using the formula of the law of motion equations, this problem is often solved. This problem solution is mainly based on the formation of the equations of distances and then finding the difference between the identical.
Formula used: \[v = u + gt\]
\[S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}\]
Where, \[u\]-initial velocity, \[v\]-final velocity, \[t\]-time taken and \[S\]-distance traveled
Complete step-by-step solution:
The velocity of the body at point A, \[{u_A} = 0\]
Let the velocity of the body at point B and C will be \[{u_B},{u_C}\]
Let \[BC = CD = S\]
For journey A to B\[ \Rightarrow {u_B} = {u_A} + g{t_{AB}}\]
Where \[{t_{AB}}\] is the time taken to move from A to B
\[{u_B} = 10{t_{AB}}\]
\[\left( {\therefore {u_A} = 0} \right)\]\[ - - - - - - \left( 1 \right)\]
For journey B to C\[ \Rightarrow {u_C} = {u_B} + g{t_{BC}}\]
\[{u_C} = {u_B} + 20\] \
[\left( {\therefore {t_{BC}} = 2} \right)\]
We get \[S = {u_B}{t_{BC}} + \dfrac{1}{2}gt_{BC}^2\]
\[S = 2{u_B} + 20\]\[ - - - - - - \left( 2 \right)\]
For journey C to D\[ \Rightarrow {u_D} = {u_C} + g{t_{CD}}\]
\[{u_D} = {u_C} + 10\]
\[\left( {\therefore {t_{BC}} = 1} \right)\]
We get \[S = {u_C}{t_{CD}} + \dfrac{1}{2}gt_{CD}^2\]
\[S = {u_C} + 5\]\[ - - - - - - \left( 3 \right)\]
Equation (2)-(3), we get
$\Rightarrow$\[S - S = 2{u_B} + 20 - {u_C} - 5\]
$\Rightarrow$\[0 = 2{u_B} - {u_C} + 15\]
\[\left( {\therefore {u_C} = {u_B} + 20} \right)\]
$\Rightarrow$\[0 = 2{u_B} - {u_B} - 20 + 15\]
$\Rightarrow$\[{u_B} = 5\]
From equation 1, we get
$\Rightarrow$\[{u_B} = 10{t_{AB}}\]
$\Rightarrow$\[5 = 10{t_{AB}}\]
$\Rightarrow$\[{t_{AB}} = \dfrac{1}{2} = 0.5s\]
Hence, the time taken to move from A to B is \[0.5\sec \].
Option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: A particle is freely falling under the influence of gravity, so, we’ll make use of the law of motion formulae to resolve this problem.
The equation of the second law of motion is given as follows:
\[S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\] Where, \[s\]is the distance, \[u\]is initial velocity, \[t\] is the time, and \[a\] is the acceleration.
This equation of the second law of motion should be expressed in terms of height reached by the particle and also the acceleration should be replaced with gravitational constant.
Thus, we get,
\[h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}\]
Formula used: \[v = u + gt\]
\[S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}\]
Where, \[u\]-initial velocity, \[v\]-final velocity, \[t\]-time taken and \[S\]-distance traveled
Complete step-by-step solution:
The velocity of the body at point A, \[{u_A} = 0\]
Let the velocity of the body at point B and C will be \[{u_B},{u_C}\]
Let \[BC = CD = S\]
For journey A to B\[ \Rightarrow {u_B} = {u_A} + g{t_{AB}}\]
Where \[{t_{AB}}\] is the time taken to move from A to B
\[{u_B} = 10{t_{AB}}\]
\[\left( {\therefore {u_A} = 0} \right)\]\[ - - - - - - \left( 1 \right)\]
For journey B to C\[ \Rightarrow {u_C} = {u_B} + g{t_{BC}}\]
\[{u_C} = {u_B} + 20\] \
[\left( {\therefore {t_{BC}} = 2} \right)\]
We get \[S = {u_B}{t_{BC}} + \dfrac{1}{2}gt_{BC}^2\]
\[S = 2{u_B} + 20\]\[ - - - - - - \left( 2 \right)\]
For journey C to D\[ \Rightarrow {u_D} = {u_C} + g{t_{CD}}\]
\[{u_D} = {u_C} + 10\]
\[\left( {\therefore {t_{BC}} = 1} \right)\]
We get \[S = {u_C}{t_{CD}} + \dfrac{1}{2}gt_{CD}^2\]
\[S = {u_C} + 5\]\[ - - - - - - \left( 3 \right)\]
Equation (2)-(3), we get
$\Rightarrow$\[S - S = 2{u_B} + 20 - {u_C} - 5\]
$\Rightarrow$\[0 = 2{u_B} - {u_C} + 15\]
\[\left( {\therefore {u_C} = {u_B} + 20} \right)\]
$\Rightarrow$\[0 = 2{u_B} - {u_B} - 20 + 15\]
$\Rightarrow$\[{u_B} = 5\]
From equation 1, we get
$\Rightarrow$\[{u_B} = 10{t_{AB}}\]
$\Rightarrow$\[5 = 10{t_{AB}}\]
$\Rightarrow$\[{t_{AB}} = \dfrac{1}{2} = 0.5s\]
Hence, the time taken to move from A to B is \[0.5\sec \].
Option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: A particle is freely falling under the influence of gravity, so, we’ll make use of the law of motion formulae to resolve this problem.
The equation of the second law of motion is given as follows:
\[S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\] Where, \[s\]is the distance, \[u\]is initial velocity, \[t\] is the time, and \[a\] is the acceleration.
This equation of the second law of motion should be expressed in terms of height reached by the particle and also the acceleration should be replaced with gravitational constant.
Thus, we get,
\[h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




