
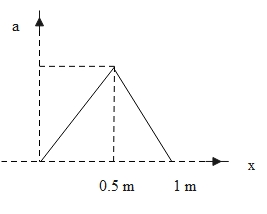
A body initially at rest, starts moving along the x-axis in such a way so that its acceleration vs displacement plot is as shown in figure. The maximum velocity of particle is :-
\[\begin{align}
& A.\,1\,{m}/{s}\; \\
& B.\,6\,{m}/{s}\; \\
& C.\,2\,{m}/{s}\; \\
& D.\,\dfrac{1}{2}\,{m}/{s}\; \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint: Firstly, we will define the relation between the acceleration and the displacement, as the given graph is acceleration versus displacement graph. So, we will integrate the acceleration equation to represent the velocity in terms of displacement and will find the maximum value of the velocity of the particle.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& v=\dfrac{dx}{dt} \\
& a=\dfrac{dv}{dt} \\
\end{align}\]
Complete answer:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
Displacement is the vector difference between the starting and ending position of an object/body. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
The differentiation of the displacement results in velocity. The differentiation of the velocity results in acceleration. Similarly, the integration of the acceleration results in velocity. The integration of the velocity results in displacement.
The gradient or the slope of the acceleration displacement graph gives the value of \[\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}}{2}\], where v is the final velocity and u is the initial velocity.
The graph given represents the acceleration versus displacement graph. So, let us build the relation between the acceleration and the displacement of the object first. So, we have,
As the acceleration is rate of change of velocity, so the mathematical representation of the same is,
\[a=\dfrac{dv}{dt}\]
The rate of change of velocity is the displacement, so the mathematical representation of the same is,
\[a=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{dv}{dx}\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)\]
\[\therefore a=v\left( \dfrac{dv}{dx} \right)\]
Now, cross multiply on both the sides.
\[a\,dx=v\,dv\]
Integrate the above equations.
\[\int{a\,dx}=\int{v}\,dv\]
Continue the further computation.
\[\begin{align}
& \int\limits_{0}^{{{v}_{m}}}{v\,dv}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1\times 1 \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{2} \right]_{0}^{{{v}_{m}}}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{v_{m}^{2}}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \therefore {{v}_{m}}=1\,{m}/{s}\; \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \]The maximum velocity of a particle is\[1\,{m}/{s}\;\], thus, option (A) is correct.
Note:
The slope of a displacement time graph gives the value of velocity. The slope of a velocity time graph gives the value of acceleration. The slope of the acceleration time graph gives the jerk (the change in acceleration).
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& v=\dfrac{dx}{dt} \\
& a=\dfrac{dv}{dt} \\
\end{align}\]
Complete answer:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
Displacement is the vector difference between the starting and ending position of an object/body. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
The differentiation of the displacement results in velocity. The differentiation of the velocity results in acceleration. Similarly, the integration of the acceleration results in velocity. The integration of the velocity results in displacement.
The gradient or the slope of the acceleration displacement graph gives the value of \[\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}}{2}\], where v is the final velocity and u is the initial velocity.
The graph given represents the acceleration versus displacement graph. So, let us build the relation between the acceleration and the displacement of the object first. So, we have,
As the acceleration is rate of change of velocity, so the mathematical representation of the same is,
\[a=\dfrac{dv}{dt}\]
The rate of change of velocity is the displacement, so the mathematical representation of the same is,
\[a=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{dv}{dx}\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)\]
\[\therefore a=v\left( \dfrac{dv}{dx} \right)\]
Now, cross multiply on both the sides.
\[a\,dx=v\,dv\]
Integrate the above equations.
\[\int{a\,dx}=\int{v}\,dv\]
Continue the further computation.
\[\begin{align}
& \int\limits_{0}^{{{v}_{m}}}{v\,dv}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1\times 1 \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{2} \right]_{0}^{{{v}_{m}}}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{v_{m}^{2}}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \therefore {{v}_{m}}=1\,{m}/{s}\; \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \]The maximum velocity of a particle is\[1\,{m}/{s}\;\], thus, option (A) is correct.
Note:
The slope of a displacement time graph gives the value of velocity. The slope of a velocity time graph gives the value of acceleration. The slope of the acceleration time graph gives the jerk (the change in acceleration).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




