
A bob is suspended from a crane by a cable of length $5m$. The crane and load are moving at a constant speed ${v_o}$. The crane is stopped by a bumper and the bob on the cable swings out at an angle of $60^\circ $. Find the initial speed ${v_o}$. $\left( {g = 9.8m/{s^2}} \right)$
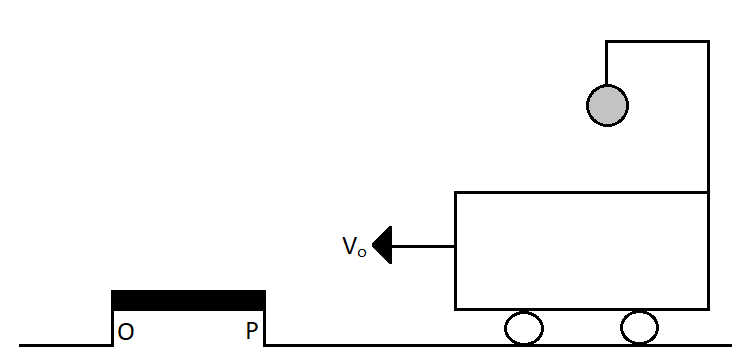
(A) $2m{s^{ - 1}}$
(B) $3m{s^{ - 1}}$
(C) $5m{s^{ - 1}}$
(D) $7m{s^{ - 1}}$

Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint
When the crane is moving, the bob is moving with the same velocity. When the crane comes to rest, the bob swings like a pendulum. So the kinetic energy of the bob gets converted to the potential energy for which it rises. From this equation, we can find the initial velocity.
In this solution, we will be using the following formulas,
$\Rightarrow K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
where $K.E.$ is the kinetic energy, $m$ is the mass and $v$ is the velocity.
and $P.E. = mgh$
where $P.E.$ is the potential energy, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height.
Complete step by step answer
When the crane is moving with the initial velocity of ${v_o}$, the bob which is suspended from the crane is also moving with the same velocity of ${v_o}$. Now, when the crane suddenly comes to rest, the bob starts swinging like a pendulum. So the initial velocity of the bob before it starts swinging is ${v_o}$ .The final velocity of the bob becomes zero when the bob reaches the swing of $60^\circ $ according to the question.
So we can draw the bob after the crane comes to rest as,
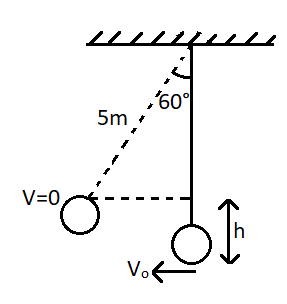
Therefore, from the law of conservation of energy, the kinetic energy of the bob at the initial position gets converted to potential energy when it reaches a height $h$.
Hence we can write,
$\Rightarrow K.E. = P.E.$
Now the kinetic energy of the bob is given by $K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_o}^2$ where $m$ is the mass of the bob.
And the potential energy at the height $h$ is $P.E. = mgh$.
Now the height $h$ can be written from the figure as, $h = 5 - 5\cos 60^\circ $
So on substituting all the values we get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_o}^2 = mg\left( {5 - 5\cos 60^\circ } \right)$
The $m$ gets cancelled on both the sides and multiplying both the sides with 2 we get,
$\Rightarrow {v_o}^2 = 2g5\left( {1 - \cos 60^\circ } \right)$
The value of $\cos 60^\circ $ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{2}$. So substituting these values we get
$\Rightarrow {v_o}^2 = 2g5\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$
On substituting the value of $g = 9.8m/{s^2}$ as from the question and calculating we get,
$\Rightarrow {v_o}^2 = 10 \times 9.8 \times \dfrac{1}{2}$
On taking square root on both the sides we have,
$\Rightarrow {v_o} = \sqrt {49} $
Therefore, we get the initial velocity as,
$\Rightarrow {v_o} = 7m/s$
Hence the correct answer is option (D).
Note
Here we have taken the kinetic energy of the pendulum equal to its potential energy from the law of conservation of energy. It states that the total energy of any isolated system always remains constant and can only change from one form to another.
When the crane is moving, the bob is moving with the same velocity. When the crane comes to rest, the bob swings like a pendulum. So the kinetic energy of the bob gets converted to the potential energy for which it rises. From this equation, we can find the initial velocity.
In this solution, we will be using the following formulas,
$\Rightarrow K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
where $K.E.$ is the kinetic energy, $m$ is the mass and $v$ is the velocity.
and $P.E. = mgh$
where $P.E.$ is the potential energy, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height.
Complete step by step answer
When the crane is moving with the initial velocity of ${v_o}$, the bob which is suspended from the crane is also moving with the same velocity of ${v_o}$. Now, when the crane suddenly comes to rest, the bob starts swinging like a pendulum. So the initial velocity of the bob before it starts swinging is ${v_o}$ .The final velocity of the bob becomes zero when the bob reaches the swing of $60^\circ $ according to the question.
So we can draw the bob after the crane comes to rest as,

Therefore, from the law of conservation of energy, the kinetic energy of the bob at the initial position gets converted to potential energy when it reaches a height $h$.
Hence we can write,
$\Rightarrow K.E. = P.E.$
Now the kinetic energy of the bob is given by $K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_o}^2$ where $m$ is the mass of the bob.
And the potential energy at the height $h$ is $P.E. = mgh$.
Now the height $h$ can be written from the figure as, $h = 5 - 5\cos 60^\circ $
So on substituting all the values we get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v_o}^2 = mg\left( {5 - 5\cos 60^\circ } \right)$
The $m$ gets cancelled on both the sides and multiplying both the sides with 2 we get,
$\Rightarrow {v_o}^2 = 2g5\left( {1 - \cos 60^\circ } \right)$
The value of $\cos 60^\circ $ is equal to $\dfrac{1}{2}$. So substituting these values we get
$\Rightarrow {v_o}^2 = 2g5\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$
On substituting the value of $g = 9.8m/{s^2}$ as from the question and calculating we get,
$\Rightarrow {v_o}^2 = 10 \times 9.8 \times \dfrac{1}{2}$
On taking square root on both the sides we have,
$\Rightarrow {v_o} = \sqrt {49} $
Therefore, we get the initial velocity as,
$\Rightarrow {v_o} = 7m/s$
Hence the correct answer is option (D).
Note
Here we have taken the kinetic energy of the pendulum equal to its potential energy from the law of conservation of energy. It states that the total energy of any isolated system always remains constant and can only change from one form to another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




