
A bob hangs from a rigid support by an inextensible string of length \[l\] (from the lowest position) keeping the string straight, and then released. The speed of the bob at the lowest position is
A.\[\sqrt {gl} \]
B.\[\sqrt {3gl} \]
C.\[\sqrt {2gl} \]
D.\[\sqrt {5gl} \]

Answer
543.3k+ views
Hint: We need to use the principle of conservation of energy between the highest point and the lowest point. For calculation of potential energy, find the vertical distance of the bob at the highest position from the lowest position.
Formula used:
In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[PE = mgh\] where \[PE\] is the potential energy of a body from a reference point, \[m\] is the mass of that body, \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity and \[h\] is the vertical height of the body from the reference point.
\[KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] where \[KE\] is the kinetic energy of the body, and \[v\] is the velocity of the body.
Complete answer:
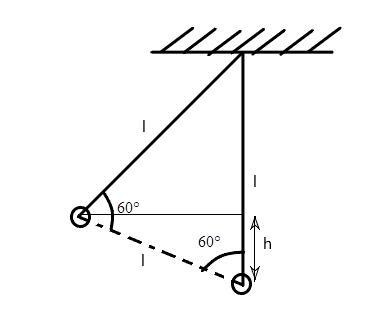
First, we see from diagram, that the height of the bob above the lowest point can be given by
\[h = l\cos 60 = \dfrac{l}{2}\]
Now, using the lowest point as the reference point, the potential energy of the bob can be found using the formula
\[PE = mgh\] where \[m\] is the mass of that body, \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity and \[h\] is the vertical height of the body from the reference point.
Hence,
\[PE = mg\dfrac{l}{2}\]
Now, according to the principle of conservation of energy, all the potential at the highest point will be converted to kinetic energy at the lowest point. The kinetic energy is
\[KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] where \[v\] is the velocity of the body.
Hence,
\[mg\dfrac{l}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\]
Hence, by making \[v\] subject of the formula, we have
\[v = \sqrt {gl} \]
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
For clarity, note that the point of reference is not essential to the calculation of the velocity, any point can be used as a reference point. The potential energy is always based on some point of reference.
Formula used:
In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[PE = mgh\] where \[PE\] is the potential energy of a body from a reference point, \[m\] is the mass of that body, \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity and \[h\] is the vertical height of the body from the reference point.
\[KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] where \[KE\] is the kinetic energy of the body, and \[v\] is the velocity of the body.
Complete answer:

First, we see from diagram, that the height of the bob above the lowest point can be given by
\[h = l\cos 60 = \dfrac{l}{2}\]
Now, using the lowest point as the reference point, the potential energy of the bob can be found using the formula
\[PE = mgh\] where \[m\] is the mass of that body, \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity and \[h\] is the vertical height of the body from the reference point.
Hence,
\[PE = mg\dfrac{l}{2}\]
Now, according to the principle of conservation of energy, all the potential at the highest point will be converted to kinetic energy at the lowest point. The kinetic energy is
\[KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] where \[v\] is the velocity of the body.
Hence,
\[mg\dfrac{l}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\]
Hence, by making \[v\] subject of the formula, we have
\[v = \sqrt {gl} \]
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
For clarity, note that the point of reference is not essential to the calculation of the velocity, any point can be used as a reference point. The potential energy is always based on some point of reference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




