
A block placed on a horizontal surface is being pushed by a farce $F$ making an angle $\theta $ with the vertical. The coefficient of friction between block and surface is $\mu $. The force required to slide the block with uniform velocity on the floor is:
A. \[\dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{\left( {sin\theta - \mu cos\theta } \right)}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{\left( {sin\theta - \mu cos\theta } \right)}}{{\mu mg}}\]
C. \[\mu mg\]
D. None of these.
Answer
519.5k+ views
Hint: To make the stationary block just slide on a surface the minimum requirement is that the frictional force should be equal to the force acting in the opposite direction of the frictional force on the block. This is because to slide the block the force must overcome or just to be equal to the frictional force (since frictional force is a resistive force) to slide the block.
Complete answer:
Let the mass of the given block is \[m\],
and it is given that the frictional coefficient in between the block and the surface is $\mu $.
Then we will prepare a free body diagram in which each force acting on the block is shown properly and then we will resolve the forces also. So, the free body diagram related to the question is as follows,
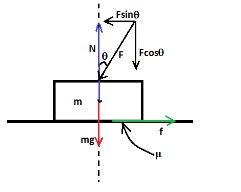
In the diagram the force $F$ which is a push is shown at an angle $\theta $ with the vertical then it is resolved in its vertical and horizontal components.
A force due to the gravity is $mg$
acting downward and $f$ is the frictional force acting on the block.$N$ is a normal reaction force acting on the block.
To slide the block with uniform velocity on the floor is the minimum requirement is that the forces acting opposite are equal.
Now we will equate the frictional force with the horizontal component of the force $F$.
So $F\sin \theta = f$
$ \Rightarrow F\sin \theta = \mu N$
A we know that the value of the normal force will be equal to the sum of all the forces acting in the vertically downward direction. So, $N = (mg + F\cos \theta )$.
Now, $F\sin \theta = \mu (mg + F\cos \theta )$
$ \Rightarrow F\sin \theta = \mu mg + \mu F\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow F\sin \theta - \mu F\cos \theta = \mu mg$
$ \Rightarrow F(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta ) = \mu mg$
$ \Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )}}$
Hence the force required to slide the block with uniform velocity on the floor is $\dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Friction is a resistance to the motion of any object moving relative to the other object or the surface. As forces like gravity and the electromagnetisms are the fundamental forces but the friction force is not a fundamental force. Friction force is the force which acts between the surfaces which are sliding or trying to slide across each other. It’s always made the object slower.
Complete answer:
Let the mass of the given block is \[m\],
and it is given that the frictional coefficient in between the block and the surface is $\mu $.
Then we will prepare a free body diagram in which each force acting on the block is shown properly and then we will resolve the forces also. So, the free body diagram related to the question is as follows,

In the diagram the force $F$ which is a push is shown at an angle $\theta $ with the vertical then it is resolved in its vertical and horizontal components.
A force due to the gravity is $mg$
acting downward and $f$ is the frictional force acting on the block.$N$ is a normal reaction force acting on the block.
To slide the block with uniform velocity on the floor is the minimum requirement is that the forces acting opposite are equal.
Now we will equate the frictional force with the horizontal component of the force $F$.
So $F\sin \theta = f$
$ \Rightarrow F\sin \theta = \mu N$
A we know that the value of the normal force will be equal to the sum of all the forces acting in the vertically downward direction. So, $N = (mg + F\cos \theta )$.
Now, $F\sin \theta = \mu (mg + F\cos \theta )$
$ \Rightarrow F\sin \theta = \mu mg + \mu F\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow F\sin \theta - \mu F\cos \theta = \mu mg$
$ \Rightarrow F(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta ) = \mu mg$
$ \Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )}}$
Hence the force required to slide the block with uniform velocity on the floor is $\dfrac{{\mu mg}}{{(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Friction is a resistance to the motion of any object moving relative to the other object or the surface. As forces like gravity and the electromagnetisms are the fundamental forces but the friction force is not a fundamental force. Friction force is the force which acts between the surfaces which are sliding or trying to slide across each other. It’s always made the object slower.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




