
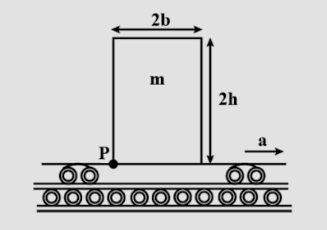
A block of mass mm height 2h and width 2b rests on a flat car which moves horizontally with constant acceleration as shown in figure. Determine
a. the value of the acceleration at which slipping of the block on the car starts, if the coefficient of friction is μ.
b. the value of the acceleration at which block topples about P, assuming sufficient friction to prevent slipping
c. the shortest distance in which it can be stopped from a speed of 20ms-1 with constant deceleration so that the block is not disturbed. The following data are given b=0.6m, h=0.9, μ=0.5, b=0.6m, h=0.9, μ=0.5 and g = $10 ms^{-2}$

Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: If two bodies are in contact with each other and if it is moving then frictional force acts. For example, when you walk on the road there is a contact between foot and road, a frictional force acts which is responsible for balancing your walk while walking. In the first case, use frictional force and maximum acceleration formula. In the second case, use the torque concept. In the third case, use the kinematic equation.
Complete step by step solution:
The block on a car will not sleep until the acceleration provided by the frictional force between car and block is equal to the acceleration of the car. The direction of maximum frictional force acting between car and block (point of contact) is on the right side.
a.) Because of friction, the maximum acceleration produced is,
$a=\dfrac{\mu mg}{m}=\mu g=5m/{{s}^{2}}$
Where $f=\mu mg$
It means that when a block exceeds $a=5m/{{s}^{2}}$, the block will sleep.
b.) In the second part, when it is in topple condition, normal reaction N acts upward from point of contact. This time the frictional force will be in static nature.
Frictional force f is given by,
$f=ma$
And normal force is given by,
$N=mg$
Now lets balance force at the centre of the block, then
$\begin{align}
& N\times b=f\times h \\
& mgb=mah \\
& a=\dfrac{gb}{h}=\dfrac{10\times 0.6}{0.9}=\dfrac{60}{9}m/{{s}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
It means that when a block exceeds the above value, the block will start to topple.
c.) Car is covering the shortest distance, it means cars do maximum deceleration but the block should not be disturb.
Means maximum acceleration is $5m/{{s}^{2}}$after that block will sleep means deceleration value must be below $5m/{{s}^{2}}$ or $5m/{{s}^{2}}$.
Using the kinematic equation, we get
${{v}^{2}}={{u}^{2}}-2as$
Initially, the car was at rest there u=0. Then
$\begin{align}
& s=\dfrac{{{u}^{2}}}{2a}=\dfrac{{{(20)}^{2}}}{10}=40m \\
& s=40m \\
\end{align}$
The shortest distance in which it can be stopped from a speed of 20ms-1 with constant deceleration so that the block is not disturbed is 40m.
Note: Formula of force is mass and acceleration. If there is a condition of slipping then always use frictional force concept with the use of the coefficient of friction. If the case is related to condition then use the balance equation as we used in the second case. If the question is about to calculate the final value of velocity or acceleration, then always use a kinematic equation.
Complete step by step solution:
The block on a car will not sleep until the acceleration provided by the frictional force between car and block is equal to the acceleration of the car. The direction of maximum frictional force acting between car and block (point of contact) is on the right side.
a.) Because of friction, the maximum acceleration produced is,
$a=\dfrac{\mu mg}{m}=\mu g=5m/{{s}^{2}}$
Where $f=\mu mg$
It means that when a block exceeds $a=5m/{{s}^{2}}$, the block will sleep.
b.) In the second part, when it is in topple condition, normal reaction N acts upward from point of contact. This time the frictional force will be in static nature.
Frictional force f is given by,
$f=ma$
And normal force is given by,
$N=mg$
Now lets balance force at the centre of the block, then
$\begin{align}
& N\times b=f\times h \\
& mgb=mah \\
& a=\dfrac{gb}{h}=\dfrac{10\times 0.6}{0.9}=\dfrac{60}{9}m/{{s}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
It means that when a block exceeds the above value, the block will start to topple.
c.) Car is covering the shortest distance, it means cars do maximum deceleration but the block should not be disturb.
Means maximum acceleration is $5m/{{s}^{2}}$after that block will sleep means deceleration value must be below $5m/{{s}^{2}}$ or $5m/{{s}^{2}}$.
Using the kinematic equation, we get
${{v}^{2}}={{u}^{2}}-2as$
Initially, the car was at rest there u=0. Then
$\begin{align}
& s=\dfrac{{{u}^{2}}}{2a}=\dfrac{{{(20)}^{2}}}{10}=40m \\
& s=40m \\
\end{align}$
The shortest distance in which it can be stopped from a speed of 20ms-1 with constant deceleration so that the block is not disturbed is 40m.
Note: Formula of force is mass and acceleration. If there is a condition of slipping then always use frictional force concept with the use of the coefficient of friction. If the case is related to condition then use the balance equation as we used in the second case. If the question is about to calculate the final value of velocity or acceleration, then always use a kinematic equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




