
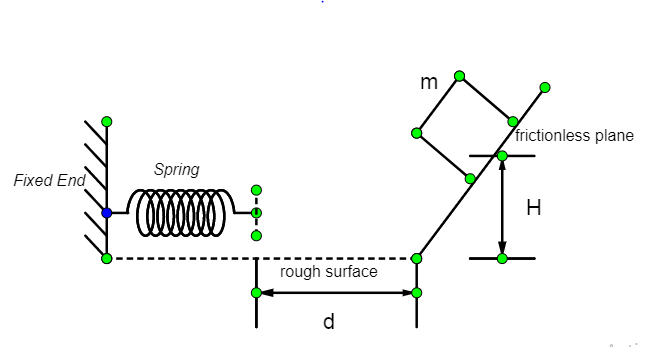
A block of mass m slides from rest at a height H on a frictionless inclined plane as shown in the figure. It travels a distance d across a rough horizontal surface with coefficient of kinetic friction μ, and compresses a spring of spring constant k by a distance x before coming to rest momentarily. Then the spring extends and the lock travels back attaining a final height of h. Then:
A. $h=H-2\mu (d+x)$
B. $h=H+2\mu (d-x)$
C. $h=H-2\mu d+\dfrac{k{{x}^{2}}}{mg}$
D. \[h=H-2\mu (d+x)\]

Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: We can divide the entire motion into 3 parts. First part is the descent on the frictionless surface; second part is the motion on the rough surface and third part is the ascent on the frictionless surface. In all the parts, we apply the conservation of energy equation to obtain height h.
Formula section:
\[{{K}_{i}}+{{P}_{i}}+{{W}_{nc}}+O{{E}_{i}}={{K}_{f}}+{{P}_{f}}+O{{E}_{f}}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
The conservation of energy is a classic concept of physics. It states the within a system the total amount of energy remains constant. Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. The conservation of energy formula is:
\[{{K}_{i}}+{{P}_{i}}+{{W}_{nc}}+O{{E}_{i}}={{K}_{f}}+{{P}_{f}}+O{{E}_{f}}\]………. (1)
where \[{{K}_{i}}\]is initial kinetic energy, \[{{P}_{i}}\] is initial potential energy, \[{{W}_{nc}}\]is work done by non-conservative forces, \[O{{E}_{i}}\] is other initial energies, \[{{K}_{f}}\]is final kinetic energy, \[{{P}_{f}}\]is final potential energy, \[O{{E}_{f}}\] is other final energies.
Let the mass of the block be m.. We can solve the problem by dividing it into three parts.
Part1: The descent of the block on the frictionless incline plane
As the inclined plane is frictionless, work done by non-conservative forces is 0.
\[{{W}_{nc}}\]= 0, \[{{K}_{i}}\]= 0, \[{{P}_{i}}\]= mgH, \[{{K}_{f}}\]= K, \[{{P}_{f}}\]= 0.
Let’s substitute the above values in equation (1):
\[0+mgH+0=K+0\]
\[\Rightarrow K=mgH\]
Part 2: Motion on the rough surface
External Non conservative force = Friction = -\[\mu mg\]
Distance travelled by the block on the rough surface = \[2\times (d+x)\]
Work done \[{{W}_{nc}}\]= F dx = -\[2\times (d+x)\]\[\mu mg\]
\[{{K}_{i}}\]= mgH, \[{{P}_{i}}\]= 0, \[{{K}_{f}}\]= K, \[{{P}_{f}}\]= 0.
Let’s substitute the above values in equation (1):
\[mgH+0-2\times (d+x)\times \mu mg=K+0+0\]
\[\Rightarrow K=mgH-2\times (d+x)\times \mu mg\]
Part 3: The ascent of the block on the frictionless incline plane
Non conservative forces = 0
\[{{K}_{i}}=mgH-2\times (d+x)\times \mu mg\], \[{{P}_{i}}\]= 0, \[{{K}_{f}}\]= 0, \[{{P}_{f}}\]= mgh
Let’s substitute the above values in equation (1):
\[mgH-2\times (d+x)\times \mu mg+0=0+mgh\]
On dividing the above equation by mg, we get
\[h=H-2\mu (d+x)\]
Hence the correct option is (A).
Note: The possibility of the mistake is that you may choose option (B) because you may forget that the friction force is an opposing force so the magnitude is –ve. It is important to remember this otherwise you will get option (B).
Formula section:
\[{{K}_{i}}+{{P}_{i}}+{{W}_{nc}}+O{{E}_{i}}={{K}_{f}}+{{P}_{f}}+O{{E}_{f}}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
The conservation of energy is a classic concept of physics. It states the within a system the total amount of energy remains constant. Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. The conservation of energy formula is:
\[{{K}_{i}}+{{P}_{i}}+{{W}_{nc}}+O{{E}_{i}}={{K}_{f}}+{{P}_{f}}+O{{E}_{f}}\]………. (1)
where \[{{K}_{i}}\]is initial kinetic energy, \[{{P}_{i}}\] is initial potential energy, \[{{W}_{nc}}\]is work done by non-conservative forces, \[O{{E}_{i}}\] is other initial energies, \[{{K}_{f}}\]is final kinetic energy, \[{{P}_{f}}\]is final potential energy, \[O{{E}_{f}}\] is other final energies.
Let the mass of the block be m.. We can solve the problem by dividing it into three parts.
Part1: The descent of the block on the frictionless incline plane
As the inclined plane is frictionless, work done by non-conservative forces is 0.
\[{{W}_{nc}}\]= 0, \[{{K}_{i}}\]= 0, \[{{P}_{i}}\]= mgH, \[{{K}_{f}}\]= K, \[{{P}_{f}}\]= 0.
Let’s substitute the above values in equation (1):
\[0+mgH+0=K+0\]
\[\Rightarrow K=mgH\]
Part 2: Motion on the rough surface
External Non conservative force = Friction = -\[\mu mg\]
Distance travelled by the block on the rough surface = \[2\times (d+x)\]
Work done \[{{W}_{nc}}\]= F dx = -\[2\times (d+x)\]\[\mu mg\]
\[{{K}_{i}}\]= mgH, \[{{P}_{i}}\]= 0, \[{{K}_{f}}\]= K, \[{{P}_{f}}\]= 0.
Let’s substitute the above values in equation (1):
\[mgH+0-2\times (d+x)\times \mu mg=K+0+0\]
\[\Rightarrow K=mgH-2\times (d+x)\times \mu mg\]
Part 3: The ascent of the block on the frictionless incline plane
Non conservative forces = 0
\[{{K}_{i}}=mgH-2\times (d+x)\times \mu mg\], \[{{P}_{i}}\]= 0, \[{{K}_{f}}\]= 0, \[{{P}_{f}}\]= mgh
Let’s substitute the above values in equation (1):
\[mgH-2\times (d+x)\times \mu mg+0=0+mgh\]
On dividing the above equation by mg, we get
\[h=H-2\mu (d+x)\]
Hence the correct option is (A).
Note: The possibility of the mistake is that you may choose option (B) because you may forget that the friction force is an opposing force so the magnitude is –ve. It is important to remember this otherwise you will get option (B).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




