
A block of mass $m$ kg is kept on a weighing machine in an elevator. If the elevator retarding upwards by acceleration $a$ $m{s^{ - 2}}$ , the reading of weighing machine is (kgf)
A. $mg$
B. $m(g - a)$
C. $m\left( {1 - \dfrac{a}{g}} \right)$
D. $m(g + a)$
Answer
510.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, the concept of apparent weight of a body in an elevator is used which says that when an elevator accelerates in upward direction, the apparent weight of the body inside the elevator increases and when an elevator accelerates in downward direction, the apparent weight of the body decreases.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider a body of mass $m$kg is put on a weighing machine placed in an elevator. The actual weight of the body acts on the weighing machine and offers a Normal reaction $N$ given by the reading of the weighing machine. This reaction $N$ exerted by the surface of contact on the body is apparent weight of the body.
In our condition, an elevator is moving upwards with acceleration $a$ as shown in fig., .
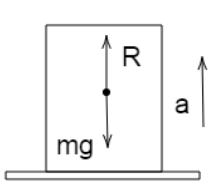
When the elevator lifts upwards, the mass of the body exerts additional weight on the surface of the elevator, due to this fact, the apparent weight seems to be increased. Normal reaction $N$ and weight $mg$ of the body are in opposite directions and the acceleration is in the same direction as $N$. Hence, the net upward force on the body is given by
$N - mg = ma$
$\therefore N = mg + ma$
Apparent weight, $N = m(g + a)$. This apparent weight of the body offers the reading of the weighing machine.Thus, Reading of the weighing machine is $m(g + a)$.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: While calculation the net upward force from the free body diagram, do not subtract the normal reaction $N$ from weight of body $mg$ . This is because the weight normal reaction $N$ is of the elevator and the weight of the elevator is always greater than that of the body in case of upward motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider a body of mass $m$kg is put on a weighing machine placed in an elevator. The actual weight of the body acts on the weighing machine and offers a Normal reaction $N$ given by the reading of the weighing machine. This reaction $N$ exerted by the surface of contact on the body is apparent weight of the body.
In our condition, an elevator is moving upwards with acceleration $a$ as shown in fig., .

When the elevator lifts upwards, the mass of the body exerts additional weight on the surface of the elevator, due to this fact, the apparent weight seems to be increased. Normal reaction $N$ and weight $mg$ of the body are in opposite directions and the acceleration is in the same direction as $N$. Hence, the net upward force on the body is given by
$N - mg = ma$
$\therefore N = mg + ma$
Apparent weight, $N = m(g + a)$. This apparent weight of the body offers the reading of the weighing machine.Thus, Reading of the weighing machine is $m(g + a)$.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: While calculation the net upward force from the free body diagram, do not subtract the normal reaction $N$ from weight of body $mg$ . This is because the weight normal reaction $N$ is of the elevator and the weight of the elevator is always greater than that of the body in case of upward motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




