
A block of mass \[M\] is pulled along a horizontal frictionless surface by rope of mass \[m\] by applying a force \[P\] at one end of the rope. The force which the rope exerts on the block is
(A) \[\dfrac{{PM}}{{M - m}}\]
(B) \[\dfrac{{MP}}{{M + m}}\]
(C) \[\dfrac{{pm}}{{M + m}}\]
(D) \[P\]
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint:Consider Newton's third law of motion; recall the concept of action-reaction pair.There is a reaction force that is present when we apply a force on the block.The whole system will move with a single acceleration.We can use the free body diagram of the rope.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider the Newton’s second law of motion,
\[force(f) = mass \times acceleration(a)\]
Force (\[P\]) is applied at the end of the rope, the other end is attached with the block.
And mention that there is a frictionless surface, so we can neglect the frictional force contribution.
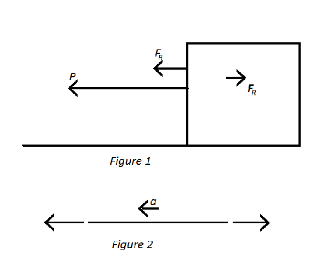
The figure\[1\]has shown the block mass \[M\] is attached with a rope having mass \[m\] pulled by the rope with a force\[P\].
There is a force \[{F_B}\]is acting on the block at the end of rope, there is also a reactive force coming from the block is
\[{F_R} = \dfrac{{(M + m)P}}{{M + m}} - \dfrac{{mP}}{{M + m}} = \dfrac{{MP}}{{M + m}}\]
\[{F_R} = {F_B}\]
The whole system has same acceleration and denoted by \[a\]
Acceleration is equal to the total applied force divided by total mass.
Total mass \[ = m + M\]
Applied force \[ = P\]
Acceleration \[a = \dfrac{P}{{M + m}}\]
Consider figure\[2\], the free body diagram of rope is shown.
From this,
The reaction force is opposite to the applied force, so the difference is,
\[P - {F_R} = mass \times acceleration\]
Substitute the acceleration of rope and mass. Then,
\[P - {F_R} = m \times \dfrac{P}{{M + m}}\]
Rearrange the equation,
\[P - {F_R} = \dfrac{{mP}}{{M + m}}\]
\[{F_R} = P - \dfrac{{mP}}{{M + m}}\]
\[{F_R} = \dfrac{{(M + m)P}}{{M + m}} - \dfrac{{mP}}{{M + m}} = \dfrac{{MP}}{{M + m}}\]
From action-reaction pair, so that these reaction force from the box is equal to the force applied by the end of the rope, in equation,
\[{F_R} = {F_B}\]
\[{F_B} = \dfrac{{MP}}{{M + m}}\]
So the answer is (B) \[\dfrac{{MP}}{{M + m}}\]
Note:Always remember following points in order to solve such type of problems:
1)Action reaction is always paired.
2)Easy to solve this kind of problem with a free body diagram.
3)Any force can equate to product mass of mass and acceleration.

Complete step by step answer:
Consider the Newton’s second law of motion,
\[force(f) = mass \times acceleration(a)\]
Force (\[P\]) is applied at the end of the rope, the other end is attached with the block.
And mention that there is a frictionless surface, so we can neglect the frictional force contribution.
The figure\[1\]has shown the block mass \[M\] is attached with a rope having mass \[m\] pulled by the rope with a force\[P\].
There is a force \[{F_B}\]is acting on the block at the end of rope, there is also a reactive force coming from the block is
\[{F_R} = \dfrac{{(M + m)P}}{{M + m}} - \dfrac{{mP}}{{M + m}} = \dfrac{{MP}}{{M + m}}\]
\[{F_R} = {F_B}\]
The whole system has same acceleration and denoted by \[a\]
Acceleration is equal to the total applied force divided by total mass.
Total mass \[ = m + M\]
Applied force \[ = P\]
Acceleration \[a = \dfrac{P}{{M + m}}\]
Consider figure\[2\], the free body diagram of rope is shown.
From this,
The reaction force is opposite to the applied force, so the difference is,
\[P - {F_R} = mass \times acceleration\]
Substitute the acceleration of rope and mass. Then,
\[P - {F_R} = m \times \dfrac{P}{{M + m}}\]
Rearrange the equation,
\[P - {F_R} = \dfrac{{mP}}{{M + m}}\]
\[{F_R} = P - \dfrac{{mP}}{{M + m}}\]
\[{F_R} = \dfrac{{(M + m)P}}{{M + m}} - \dfrac{{mP}}{{M + m}} = \dfrac{{MP}}{{M + m}}\]
From action-reaction pair, so that these reaction force from the box is equal to the force applied by the end of the rope, in equation,
\[{F_R} = {F_B}\]
\[{F_B} = \dfrac{{MP}}{{M + m}}\]
So the answer is (B) \[\dfrac{{MP}}{{M + m}}\]
Note:Always remember following points in order to solve such type of problems:
1)Action reaction is always paired.
2)Easy to solve this kind of problem with a free body diagram.
3)Any force can equate to product mass of mass and acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




