
A block of mass m is kept on a rough plank which moves with a horizontal acceleration a. If the plank was at rest at t = 0 and the block does not slide relative to the plank. Find the work done by friction on the plane during time t.
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: As the work done is the product of the force applied and the displacement, so, we will use this basic concept to solve this question. Here the force applied is equal to the frictional force between the block and the surface, on which the block is placed and the displacement of the block with respect to the ground. The work done will be considered negative because of the opposite direction.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& {{f}_{s}}=ma \\
& s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step answer:
The formula for calculating the work done is,
\[W=F\times s\]
Where F is the force applied and s is the displacement.
The work done by the friction on the plane during time t is calculated as follows.
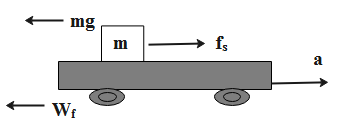
This work done is a product of the frictional force between the block and the surface, on which the block is placed and the displacement of the block with respect to the ground.
Firstly, we will find the value of the frictional force between the block and the surface.
\[{{f}_{s}}=ma\]….. (1)
Where m is the mass of the block and a is the acceleration of the block
Now, we will find the value of the displacement of the block with respect to the ground.
\[s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}\]
Where u is the initial velocity, a is the acceleration and t is the time taken.
As, the block will be at rest initially, so, the initial velocity will be equated to 0. So the equation reduces to,
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}\]…… (2)
The work done by the friction on the plane will be taken to be negative, as the direction of the work done will be in the opposite direction.
Now multiply the equations (1) and (2) to find the value of the work done by friction on the plane during time t.
\[\begin{align}
& {{W}_{f}}=-{{f}_{s}}\times s \\
& \Rightarrow {{W}_{f}}=-ma\times \dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{W}_{f}}=-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{a}^{2}}{{t}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the value of the work done by friction on the plane during time t is equal to \[-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{a}^{2}}{{t}^{2}}\].
Note:
Only arriving at the magnitude of the result is not sufficient, even the representation of direction is important. In the above case, the frictional force and the work done are in the direction opposite to each other. So, the mentioning of the negative direction is important, otherwise, the whole answer will be considered to be wrong.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& {{f}_{s}}=ma \\
& s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step answer:
The formula for calculating the work done is,
\[W=F\times s\]
Where F is the force applied and s is the displacement.
The work done by the friction on the plane during time t is calculated as follows.

This work done is a product of the frictional force between the block and the surface, on which the block is placed and the displacement of the block with respect to the ground.
Firstly, we will find the value of the frictional force between the block and the surface.
\[{{f}_{s}}=ma\]….. (1)
Where m is the mass of the block and a is the acceleration of the block
Now, we will find the value of the displacement of the block with respect to the ground.
\[s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}\]
Where u is the initial velocity, a is the acceleration and t is the time taken.
As, the block will be at rest initially, so, the initial velocity will be equated to 0. So the equation reduces to,
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}\]…… (2)
The work done by the friction on the plane will be taken to be negative, as the direction of the work done will be in the opposite direction.
Now multiply the equations (1) and (2) to find the value of the work done by friction on the plane during time t.
\[\begin{align}
& {{W}_{f}}=-{{f}_{s}}\times s \\
& \Rightarrow {{W}_{f}}=-ma\times \dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{W}_{f}}=-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{a}^{2}}{{t}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the value of the work done by friction on the plane during time t is equal to \[-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{a}^{2}}{{t}^{2}}\].
Note:
Only arriving at the magnitude of the result is not sufficient, even the representation of direction is important. In the above case, the frictional force and the work done are in the direction opposite to each other. So, the mentioning of the negative direction is important, otherwise, the whole answer will be considered to be wrong.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




