
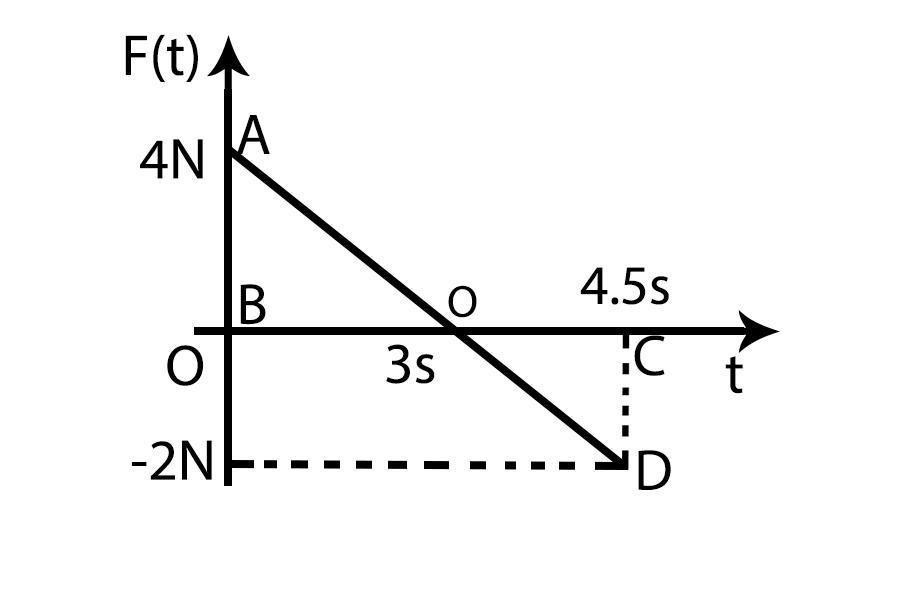
A block of mass 2 kg is free to move along the x-axis. It is at rest and from t=0 onwards it is subjected to a time-dependent force F (t) in the x direction. The force F (t) varies with t as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the block after 4.5 seconds is:
A.4.50 J
B.7.50 J
C.5.06 J
D.14.06 J

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, carefully observe the given diagram the area under the F−t graph gives the change in momentum of the block. Then we can calculate the value of kinetic energy by using the relation between the kinetic energy and momentum.
Complete step by step answer:
Area under the F−t graph gives the change in momentum of the block.
Area A = Area of triangle ABO - Area of triangle DCO
Area= $\dfrac{1}{2}(base) (height)$
\begin{align*}
\therefore A &=\dfrac{1}{2}(4)\times (3) −\dfrac{1}{2}(2)\times (1.5)\\
&=4.5 Ns
\end{align*}
The Initial momentum of the block Pi=0
Using
\begin{align*}
A &= {p_{f - }}{p_i}\\
&=4.5-0\\
\Rightarrow &{p_f}=4.5 Ns\\
\end{align*}
Thus final kinetic energy of the block KE=$\dfrac{{{p_f}^2}}{{2m}}$
\begin{align*}
KE &= \dfrac{(4.5)^2}{2(2)}\\
&=5.06J
\end{align*}
Hence the correct option is C
Note:
Alternatively we can use the impulse relation
Given:
At t = 4.5 sec, $\mathop F\limits^ \to = - 2N$
Total Impulse is given by
$\begin{array}{l}
= \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4} \right] - \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2 \times 1.5} \right]\\
\Rightarrow I = 6 - 1.5 = 4.5\,\,{\rm{SI}}\,{\rm{Unit}}
\end{array}$
Impulse = change in momentum
\begin{align*}
45 &= 2[v - 0]\\
v &= \dfrac{{45}}{2} = 2.25\,m{s^{ - 1}}\\
K.E &= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2 \times {\left( {2.25} \right)^2}\\
&= 5.06\,J
\end{align*}
Complete step by step answer:
Area under the F−t graph gives the change in momentum of the block.
Area A = Area of triangle ABO - Area of triangle DCO
Area= $\dfrac{1}{2}(base) (height)$
\begin{align*}
\therefore A &=\dfrac{1}{2}(4)\times (3) −\dfrac{1}{2}(2)\times (1.5)\\
&=4.5 Ns
\end{align*}
The Initial momentum of the block Pi=0
Using
\begin{align*}
A &= {p_{f - }}{p_i}\\
&=4.5-0\\
\Rightarrow &{p_f}=4.5 Ns\\
\end{align*}
Thus final kinetic energy of the block KE=$\dfrac{{{p_f}^2}}{{2m}}$
\begin{align*}
KE &= \dfrac{(4.5)^2}{2(2)}\\
&=5.06J
\end{align*}
Hence the correct option is C
Note:
Alternatively we can use the impulse relation
Given:
At t = 4.5 sec, $\mathop F\limits^ \to = - 2N$
Total Impulse is given by
$\begin{array}{l}
= \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4} \right] - \left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2 \times 1.5} \right]\\
\Rightarrow I = 6 - 1.5 = 4.5\,\,{\rm{SI}}\,{\rm{Unit}}
\end{array}$
Impulse = change in momentum
\begin{align*}
45 &= 2[v - 0]\\
v &= \dfrac{{45}}{2} = 2.25\,m{s^{ - 1}}\\
K.E &= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2 \times {\left( {2.25} \right)^2}\\
&= 5.06\,J
\end{align*}
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




